J Lipid Atheroscler.
2020 Jan;9(1):184-194. 10.12997/jla.2020.9.1.184.
Curcumin Attenuates Acrolein-induced COX-2 Expression and Prostaglandin Production in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. yongseek@khu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biomedical Science, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2470810
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12997/jla.2020.9.1.184
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Inflammation is crucial to limiting vascular disease. Previously we reported that acrolein, a known toxin in tobacco smoke, might play an important role in the progression of atherosclerosis via an inflammatory response involving cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and prostaglandin production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Curcumin has been known to improve vascular function and have anti-inflammatory properties. In this study, we investigated whether curcumin prevents the induction of inflammatory response caused by acrolein.
METHODS
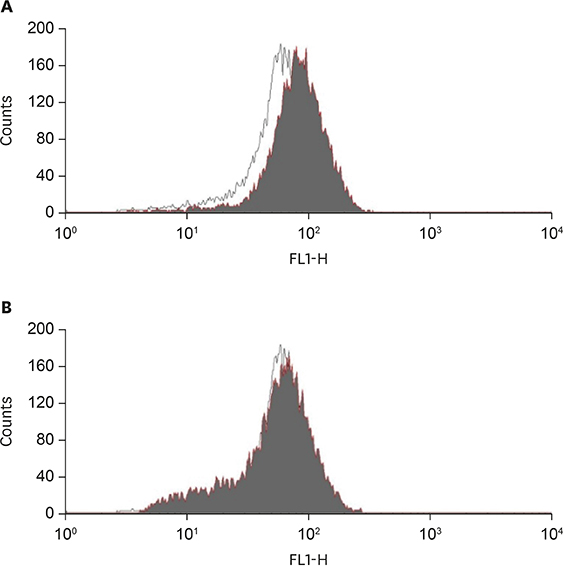
Anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin were examined in acrolein-stimulated HUVECs. Induction of proteins, mRNA, prostaglandin and reactive oxygen species (ROS) were measured using immunoblot analysis, real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and flow cytometry, respectively.
RESULTS
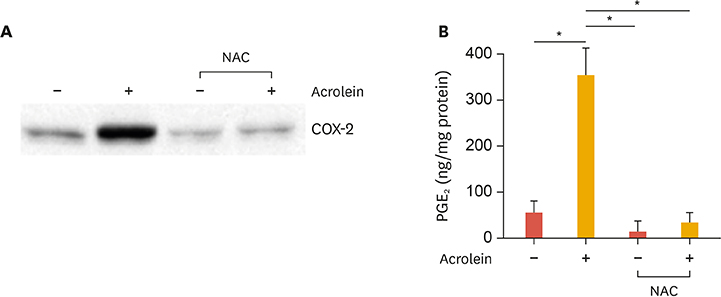
Curcumin attenuates inflammatory response via inhibition of COX-2 expression and prostaglandin production in acrolein-induced human endothelial cells. This inhibition by curcumin results in the abolition of phosphorylation of protein kinase C, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, and cAMP response element-binding protein. Furthermore, curcumin suppresses the production of ROS and endoplasmic reticulum stress via phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor-2α caused by acrolein.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that curcumin might be a useful agent against endothelial dysfunction caused by acrolein-induced inflammatory response.
MeSH Terms
-
Acrolein
Atherosclerosis
Curcumin*
Cyclic AMP Response Element-Binding Protein
Cyclooxygenase 2
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
Endothelial Cells
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Flow Cytometry
Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells*
Humans*
Inflammation
Phosphorylation
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Protein Kinase C
Protein Kinases
Reactive Oxygen Species
RNA, Messenger
Smoke
Tobacco
Vascular Diseases
Acrolein
Curcumin
Cyclic AMP Response Element-Binding Protein
Cyclooxygenase 2
Protein Kinase C
Protein Kinases
RNA, Messenger
Reactive Oxygen Species
Smoke
Figure
Reference
-
1. Geovanini GR, Libby P. Atherosclerosis and inflammation: overview and updates. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018; 132:1243–1252.
Article2. Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012; 32:2045–2051.
Article3. Ambrose JA, Barua RS. The pathophysiology of cigarette smoking and cardiovascular disease: an update. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004; 43:1731–1737.4. Stevens JF, Maier CS. Acrolein: sources, metabolism, and biomolecular interactions relevant to human health and disease. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008; 52:7–25.
Article5. Thweatt WD, Harward CN Sr, Parrish ME. Measurement of acrolein and 1,3-butadiene in a single puff of cigarette smoke using lead-salt tunable diode laser infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2007; 67:16–24.
Article6. Zirak MR, Mehri S, Karimani A, Zeinali M, Hayes AW, Karimi G. Mechanisms behind the atherothrombotic effects of acrolein, a review. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019; 129:38–53.
Article7. Park YS, Kim J, Misonou Y, Takamiya R, Takahashi M, Freeman MR, et al. Acrolein induces cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: roles of p38 MAP kinase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007; 27:1319–1325.
Article8. Park YS, Taniguchi N. Acrolein induces inflammatory response underlying endothelial dysfunction: a risk factor for atherosclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008; 1126:185–189.
Article9. Rumzhum NN, Ammit AJ. Cyclooxygenase 2: its regulation, role and impact in airway inflammation. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016; 46:397–410.
Article10. Gupta SC, Patchva S, Aggarwal BB. Therapeutic roles of curcumin: lessons learned from clinical trials. AAPS J. 2013; 15:195–218.
Article11. Kunnumakkara AB, Bordoloi D, Padmavathi G, Monisha J, Roy NK, Prasad S, et al. Curcumin, the golden nutraceutical: multitargeting for multiple chronic diseases. Br J Pharmacol. 2017; 174:1325–1348.
Article12. Binion DG, Otterson MF, Rafiee P. Curcumin inhibits VEGF-mediated angiogenesis in human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells through COX-2 and MAPK inhibition. Gut. 2008; 57:1509–1517.
Article13. Devassy JG, Nwachukwu ID, Jones PJ. Curcumin and cancer: barriers to obtaining a health claim. Nutr Rev. 2015; 73:155–165.
Article14. Gardener SL, Rainey-Smith SR, Martins RN. Diet and inflammation in Alzheimer's disease and related chronic diseases: a review. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016; 50:301–334.
Article15. Karimian MS, Pirro M, Johnston TP, Majeed M, Sahebkar A. Curcumin and endothelial function: evidence and mechanisms of protective effects. Curr Pharm Des. 2017; 23:2462–2473.
Article16. Midura-Kiela MT, Radhakrishnan VM, Larmonier CB, Laubitz D, Ghishan FK, Kiela PR. Curcumin inhibits interferon-γ signaling in colonic epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012; 302:G85–G96.
Article17. Cho JW, Park K, Kweon GR, Jang BC, Baek WK, Suh MH, et al. Curcumin inhibits the expression of COX-2 in UVB-irradiated human keratinocytes (HaCaT) by inhibiting activation of AP-1: p38 MAP kinase and JNK as potential upstream targets. Exp Mol Med. 2005; 37:186–192.
Article18. He Y, Yue Y, Zheng X, Zhang K, Chen S, Du Z. Curcumin, inflammation, and chronic diseases: how are they linked? Molecules. 2015; 20:9183–9213.
Article19. Lee SE, Park HR, Park CS, Ahn HJ, Cho JJ, Lee J, et al. Autophagy in crotonaldehyde-induced endothelial toxicity. Molecules. 2019; 24:E1137.
Article20. Lee SE, Park HR, Kim H, Choi Y, Jin YH, Park CS, et al. Effect of crotonaldehyde on the induction of COX-2 expression in human endothelial cells. Mol Cell Toxicol. 2017; 13:345–350.
Article21. Lee SE, Park YS. Korean Red Ginseng water extract inhibits COX-2 expression by suppressing p38 in acrolein-treated human endothelial cells. J Ginseng Res. 2014; 38:34–39.
Article22. Haberzettl P, Vladykovskaya E, Srivastava S, Bhatnagar A. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in acrolein-induced endothelial activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009; 234:14–24.
Article23. Gómez-Hernández A, Martín-Ventura JL, Sánchez-Galán E, Vidal C, Ortego M, Blanco-Colio LM, et al. Overexpression of COX-2, Prostaglandin E synthase-1 and prostaglandin E receptors in blood mononuclear cells and plaque of patients with carotid atherosclerosis: regulation by nuclear factor-κB. Atherosclerosis. 2006; 187:139–149.
Article24. Hatcher H, Planalp R, Cho J, Torti FM, Torti SV. Curcumin: from ancient medicine to current clinical trials. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008; 65:1631–1652.
Article25. Burge K, Gunasekaran A, Eckert J, Chaaban H. Curcumin and intestinal inflammatory diseases: molecular mechanisms of protection. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20:E1912.
Article26. Sharma C, Kaur J, Shishodia S, Aggarwal BB, Ralhan R. Curcumin down regulates smokeless tobacco-induced NF-κB activation and COX-2 expression in human oral premalignant and cancer cells. Toxicology. 2006; 228:1–15.
Article27. Lelli D, Sahebkar A, Johnston TP, Pedone C. Curcumin use in pulmonary diseases: state of the art and future perspectives. Pharmacol Res. 2017; 115:133–148.
Article28. Ghosh S, Banerjee S, Sil PC. The beneficial role of curcumin on inflammation, diabetes and neurodegenerative disease: a recent update. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015; 83:111–124.
Article29. Shehzad A, Ha T, Subhan F, Lee YS. New mechanisms and the anti-inflammatory role of curcumin in obesity and obesity-related metabolic diseases. Eur J Nutr. 2011; 50:151–161.
Article30. Sikora E, Scapagnini G, Barbagallo M. Curcumin, inflammation, ageing and age-related diseases. Immun Ageing. 2010; 7:1.
Article31. Camacho-Barquero L, Villegas I, Sánchez-Calvo JM, Talero E, Sánchez-Fidalgo S, Motilva V, et al. Curcumin, a Curcuma longa constituent, acts on MAPK p38 pathway modulating COX-2 and iNOS expression in chronic experimental colitis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007; 7:333–342.
Article32. Ramírez-Tortosa MC, Mesa MD, Aguilera MC, Quiles JL, Baró L, Ramirez-Tortosa CL, et al. Oral administration of a turmeric extract inhibits LDL oxidation and has hypocholesterolemic effects in rabbits with experimental atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1999; 147:371–378.
Article33. Haybar H, Shahrabi S, Rezaeeyan H, Shirzad R, Saki N. Endothelial cells: from dysfunction mechanism to pharmacological effect in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2019; 19:13–22.
Article34. Incalza MA, D'Oria R, Natalicchio A, Perrini S, Laviola L, Giorgino F. Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vascul Pharmacol. 2018; 100:1–19.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Regulates Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
- The Effect of Erythropoietin on the Production of Endothelin in Human Glomerular and Umbilical Endothelial Cells
- DHA and EPA Down-regulate COX-2 Expression through Suppression of NF-kappa B Activity in LPS-treated Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
- Propofol attenuates hydrogenperoxide-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via multiple signaling pathways
- Curcumin Attenuates Nuclear Factor-kappaB, c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase and p38 in Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha-Stimulated Endothelial Cells