Yonsei Med J.
2017 Jan;58(1):206-216. 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.1.206.
Angiopoietin-1 Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hematology, The Qilu Childrens’ Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong Province, P.R. China. lyssyl88@sina.com 2598260466@qq.com
- 2Department of Pediatrics, The Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong Province, P.R. China. lyssyl88@sina.com 2598260466@qq.com
- KMID: 2374208
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2017.58.1.206
Abstract
- PURPOSE
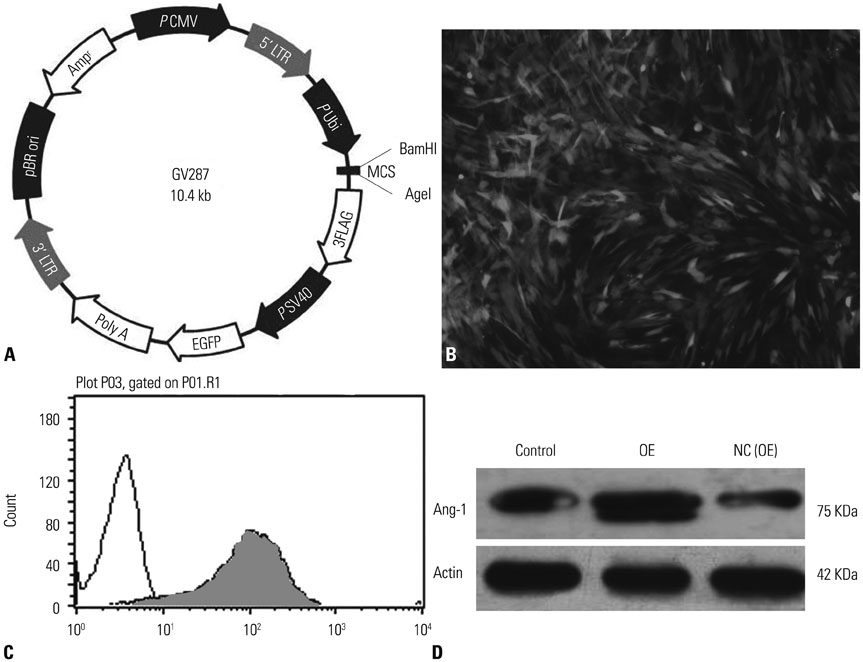
Angiopoietin-1 (Ang1) is a critical factor for vascular stabilization and endothelial survival via inhibition of endothelial permeability and leukocyte- endothelium interactions. Hence, we hypothesized that treatment with umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UCMSCs) carrying the Ang1 gene (UCMSCs-Ang1) might be a potential approach for acute lung injury (ALI) induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
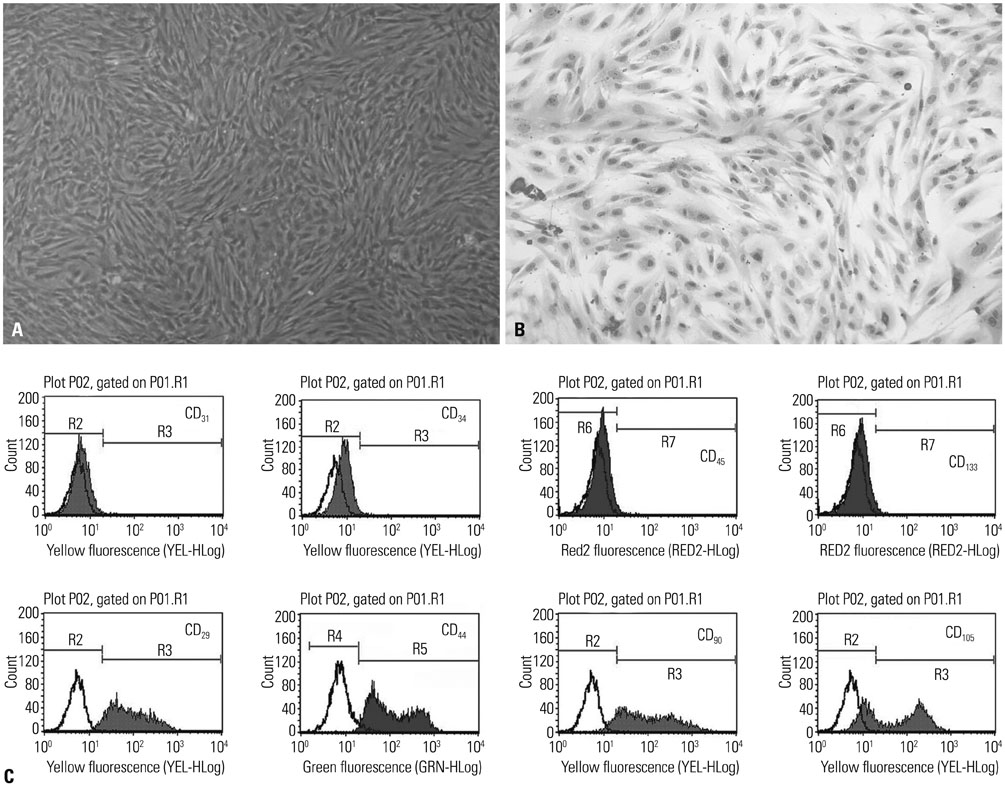
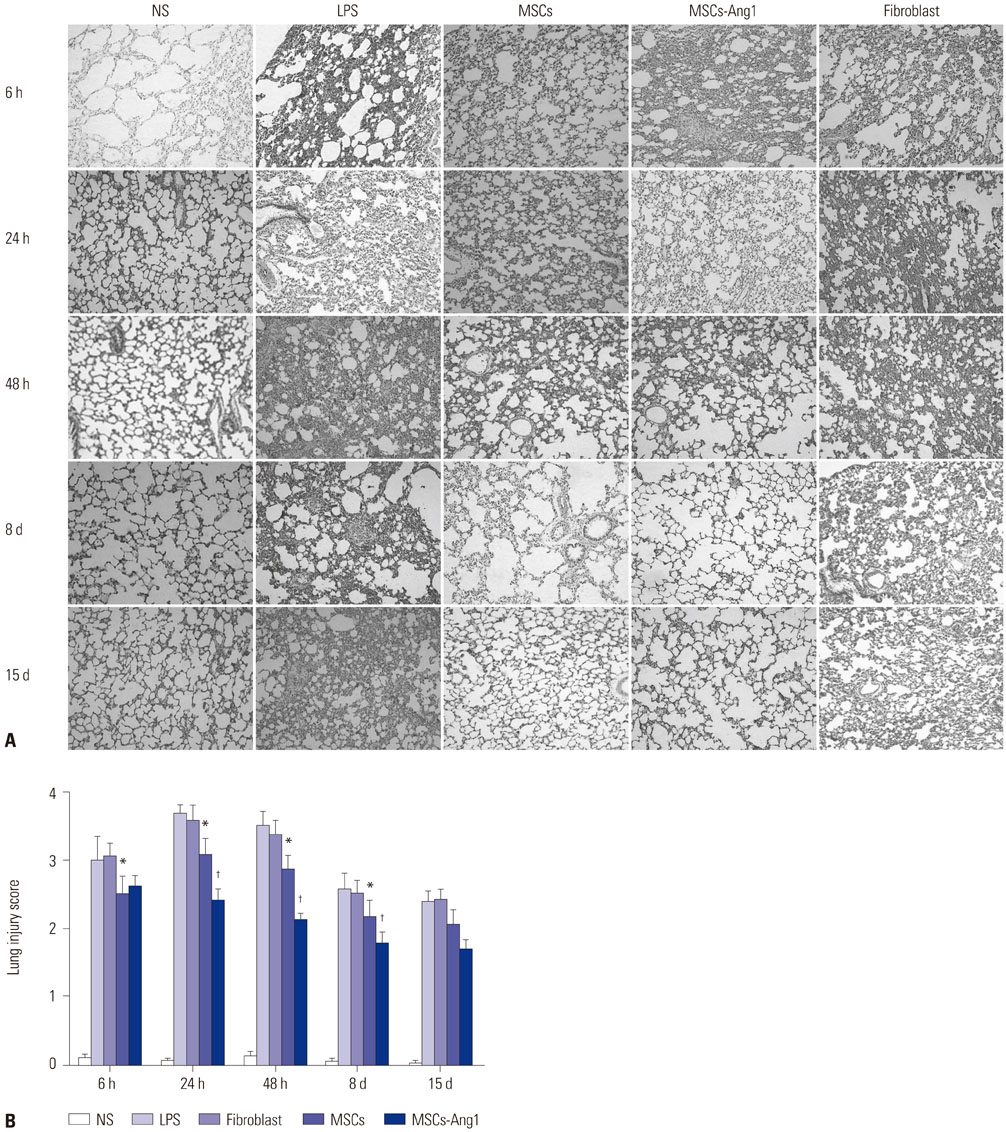
UCMSCs with or without transfection with the human Ang1 gene were delivered intravenously into rats one hour after intra-abdominal instillation of LPS to induce ALI. After the rats were sacrificed at 6 hours, 24 hours, 48 hours, 8 days, and 15 days post-injection of LPS, the serum, the lung tissues, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were harvested for analysis, respectively.
RESULTS
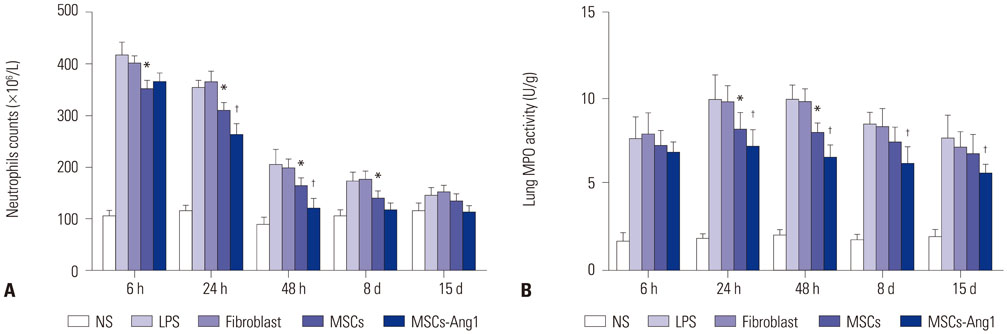
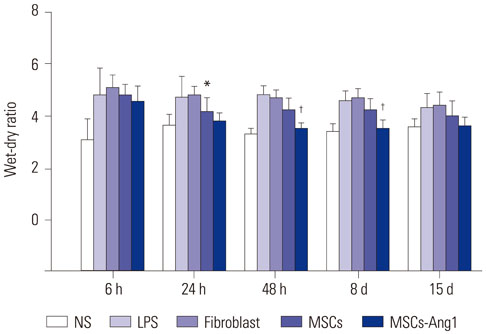
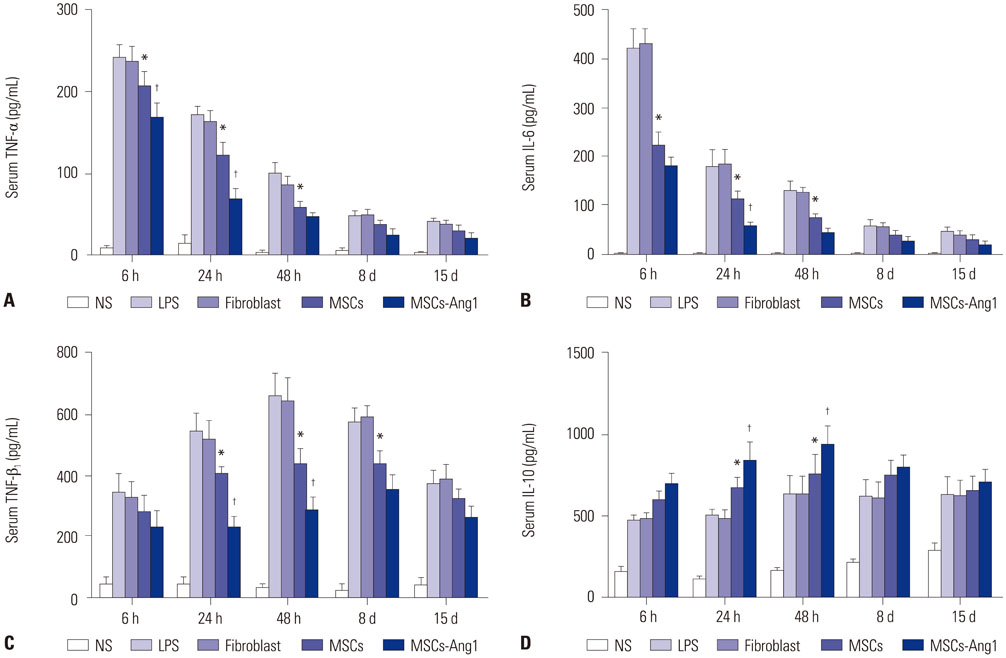
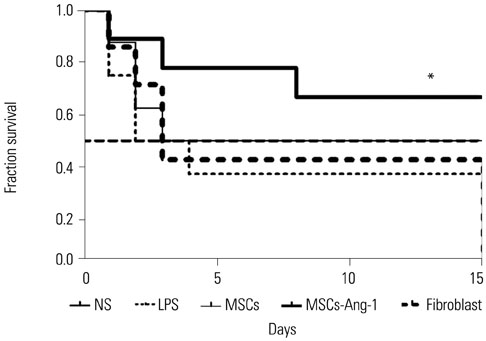
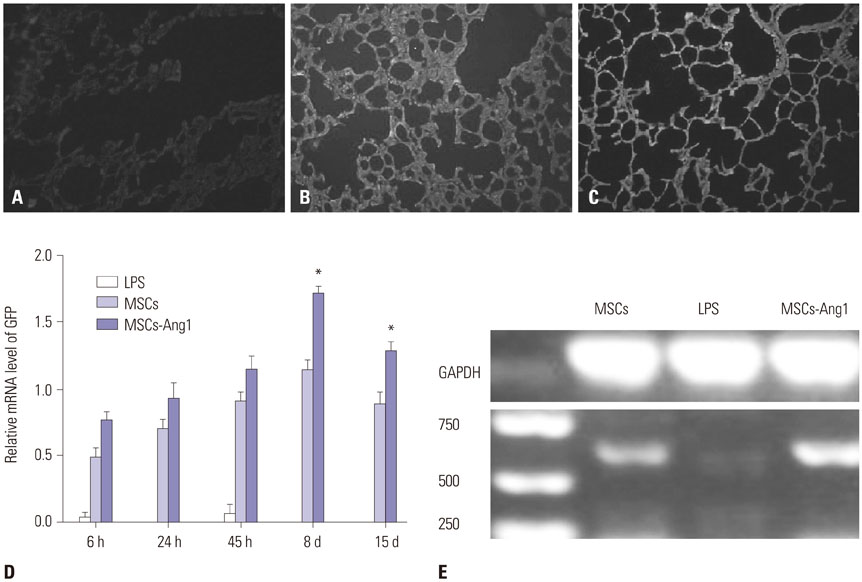
Administration of fluorescence microscope confirmed the increased presence of UCMSCs in the injured lungs. The evaluation of UCMSCs and UCMSCs-Ang1 actions revealed that Ang1 overexpression further decreased the levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, TGF-β1, and IL-6 and increased the expression of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in the injured lungs. This synergy caused a substantial decrease in lung airspace inflammation and vascular leakage, characterized by significant reductions in wet/dry ratio, differential neutrophil counts, myeloperoxidase activity, and BALF. The rats treated by UCMSCs-Ang1 showed improved survival and lower ALI scores.
CONCLUSION
UCMSCs-Ang1 could improve both systemic inflammation and alveolar permeability in ALI. UC-derived MSCs-based Ang1 gene therapy may be developed as a potential novel strategy for the treatment of ALI.
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Lung Injury/chemically induced/*therapy
Angiopoietin-1/*genetics
Animals
Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid
Cytokines/metabolism
Endotoxins
Genetic Therapy
Interleukin-10/metabolism
Interleukin-6/metabolism
Leukocyte Count
Lipopolysaccharides
Lung/metabolism
Male
*Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells/metabolism
Neutrophils/metabolism
Rats
Transforming Growth Factor beta1/metabolism
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/metabolism
Umbilical Cord/*cytology
Angiopoietin-1
Cytokines
Endotoxins
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-6
Lipopolysaccharides
Transforming Growth Factor beta1
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mei SH, McCarter SD, Deng Y, Parker CH, Liles WC, Stewart DJ. Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing angiopoietin 1. PLoS Med. 2007; 4:e269.
Article2. Gotts JE, Matthay MA. Mesenchymal stem cells and acute lung injury. Crit Care Clin. 2011; 27:719–733.
Article3. Gharib SA, Liles WC, Matute-Bello G, Glenny RW, Martin TR, Altemeier WA. Computational identification of key biological modules and transcription factors in acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006; 173:653–658.
Article4. Slutsky AS, Hudson LD. PEEP or no PEEP--lung recruitment may be the solution. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:1839–1841.
Article5. Harting MT, Jimenez F, Xue H, Fischer UM, Baumgartner J, Dash PK, et al. Intravenous mesenchymal stem cell therapy for traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2009; 110:1189–1197.
Article6. Li J, Li D, Liu X, Tang S, Wei F. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce systemic inflammation and attenuate LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats. J Inflamm (Lond). 2012; 9:33.
Article7. Paul A, Nayan M, Khan AA, Shum-Tim D, Prakash S. Angiopoietin-1-expressing adipose stem cells genetically modified with baculovirus nanocomplex: investigation in rat heart with acute infarction. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012; 7:663–682.8. Xu J, Qu J, Cao L, Sai Y, Chen C, He L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based angiopoietin-1 gene therapy for acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. J Pathol. 2008; 214:472–481.
Article9. Gupta N, Su X, Popov B, Lee JW, Serikov V, Matthay MA. Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves survival and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Immunol. 2007; 179:1855–1863.
Article10. Davies MJ. Myeloperoxidase-derived oxidation: mechanisms of biological damage and its prevention. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2011; 48:8–19.
Article11. Bustos ML, Huleihel L, Kapetanaki MG, Lino-Cardenas CL, Mroz L, Ellis BM, et al. Aging mesenchymal stem cells fail to protect because of impaired migration and antiinflammatory response. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014; 189:787–798.
Article12. Fang X, Neyrinck AP, Matthay MA, Lee JW. Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cells restore epithelial protein permeability in cultured human alveolar type II cells by secretion of angiopoietin-1. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:26211–26222.
Article13. Kanki-Horimoto S, Horimoto H, Mieno S, Kishida K, Watanabe F, Furuya E, et al. Implantation of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing endothelial nitric oxide synthase improves right ventricular impairments caused by pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2006; 114:1 Suppl. I181–I185.
Article14. Yamada M, Kubo H, Kobayashi S, Ishizawa K, Numasaki M, Ueda S, et al. Bone marrow-derived progenitor cells are important for lung repair after lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury. J Immunol. 2004; 172:1266–1272.
Article15. Thurston G, Rudge JS, Ioffe E, Papadopoulos N, Daly C, Vuthoori S, et al. The anti-inflammatory actions of angiopoietin-1. EXS. 2005; (94):233–245.
Article16. Gamble JR, Drew J, Trezise L, Underwood A, Parsons M, Kasminkas L, et al. Angiopoietin-1 is an antipermeability and anti-inflammatory agent in vitro and targets cell junctions. Circ Res. 2000; 87:603–607.
Article17. Piao W, Wang H, Inoue M, Hasegawa M, Hamada H, Huang J. Transplantation of Sendai viral angiopoietin-1-modified mesenchymal stem cells for ischemic limb disease. Angiogenesis. 2010; 13:203–210.
Article18. McCarter SD, Mei SH, Lai PF, Zhang QW, Parker CH, Suen RS, et al. Cell-based angiopoietin-1 gene therapy for acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 175:1014–1026.
Article19. Bhandari V, Choo-Wing R, Lee CG, Zhu Z, Nedrelow JH, Chupp GL, et al. Hyperoxia causes angiopoietin 2-mediated acute lung injury and necrotic cell death. Nat Med. 2006; 12:1286–1293.
Article20. Johnson ER, Matthay MA. Acute lung injury: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010; 23:243–252.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum to “Angiopoietin-1 Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats” by Huang ZW, et al. (Yonsei Med J 2017 Jan;58(1):206-216.)
- Histological Experimental Study on the Effect of Stem Cell Therapy on Adriamycin Induced Chemobrain
- Differentiation of Osteoblast Progenitor Cells from Human Umbilical Cord Blood
- Percutaneous transplantation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a dog suspected to have fibrocartilaginous embolic myelopathy
- Endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells from human cord blood