Korean J Hematol.
2010 Sep;45(3):164-170. 10.5045/kjh.2010.45.3.164.
Early central nervous system complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, Department of Pediatrics, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hojim@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2252057
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2010.45.3.164
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Central nervous system (CNS) complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) have not been well characterized in the pediatric population.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed data of 202 consecutive children who underwent allogeneic HSCT (60 from matched related donors, 9 from mismatched related donors, and 133 from unrelated donors) at Asan Medical Center between 1998 and 2009.
RESULTS
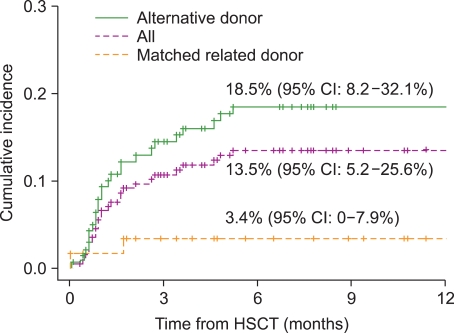
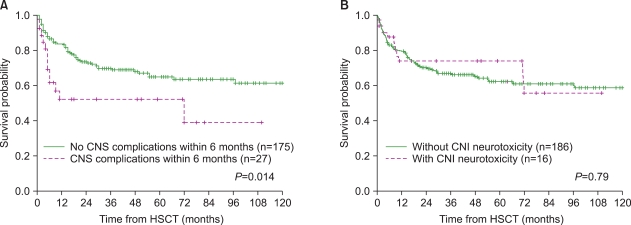
Twenty-seven children (13.5%) developed CNS complications within 6 months after HSCT. Calcineurin inhibitor (CNI)-associated neurotoxicity was the most common CNS complication (n=16), followed by CNS infection (n=2), cerebrovascular events (n=2), thrombotic microangiopathy-associated events (n=2), metabolic encephalopathy (n=2), irradiation/chemotherapy injury (n=1), and encephalopathy/myelopathy of unknown causes (n=2). Univariate analysis showed that a transplant from an alternative donor and the occurrence of acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (>grade 2) were associated with a significantly increased risk of CNS complications. In the multivariate analysis, acute GVHD >grade 2 was identified as an independent risk factor for early CNS complications. The 5-year overall survival rate was significantly lower in patients with CNS complications (52.1% vs. 64.9%, P=0.014), whereas CNI-associated neurotoxicity did not affect the survival outcome.
CONCLUSION
CNS complications are frequent among children undergoing HSCT, contributing to early death after transplant. More attention should be paid to the development of CNS complications for recipients of alternative donor transplants and patients with severe acute GVHD who are at increased risk for CNS complications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Recent advances in haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using
ex vivo T cell-depleted graft in children and adolescents
Ho Joon Im, Kyung-Nam Koh, Jong Jin Seo
Blood Res. 2016;51(1):8-16. doi: 10.5045/br.2016.51.1.8.
Reference
-
1. Iguchi A, Kobayashi R, Yoshida M, et al. Neurological complications after stem cell transplantation in childhood. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999; 24:647–652. PMID: 10490731.
Article2. Antonini G, Ceschin V, Morino S, et al. Early neurologic complications following allogeneic bone marrow transplant for leukemia: a prospective study. Neurology. 1998; 50:1441–1445. PMID: 9596002.
Article3. Faraci M, Lanino E, Dini G, et al. Severe neurologic complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. Neurology. 2002; 59:1895–1904. PMID: 12499480.
Article4. Uckan D, Cetin M, Yigitkanli I, et al. Life-threatening neurological complications after bone marrow transplantation in children. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005; 35:71–76. PMID: 15531898.
Article5. Siegal D, Keller A, Xu W, et al. Central nervous system complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: incidence, manifestations, and clinical significance. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007; 13:1369–1379. PMID: 17950923.
Article6. Kishi Y, Miyakoshi S, Kami M, et al. Early central nervous system complications after reduced-intensity stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2004; 10:561–568. PMID: 15282534.
Article7. Narimatsu H, Miyamura K, Iida H, Hamaguchi M, Uchida T, Morishita Y. Early central nervous complications after umbilical cord blood transplantation for adults. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009; 15:92–100. PMID: 19135947.
Article8. Bleggi-Torres LF, de Medeiros BC, Werner B, et al. Neuropathological findings after bone marrow transplantation: an autopsy study of 180 cases. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000; 25:301–307. PMID: 10673702.
Article9. Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995; 15:825–828. PMID: 7581076.10. Sostak P, Padovan CS, Yousry TA, Ledderose G, Kolb HJ, Straube A. Prospective evaluation of neurological complications after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Neurology. 2003; 60:842–848. PMID: 12629244.
Article11. Rubin J, Wide K, Remberger M, Gustafsson B. Acute neurological complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. Pediatr Transplant. 2005; 9:62–67. PMID: 15667614.
Article12. Denier C, Bourhis JH, Lacroix C, et al. Spectrum and prognosis of neurologic complications after hematopoietic transplantation. Neurology. 2006; 67:1990–1997. PMID: 17159106.
Article13. Gleeson JG, duPlessis AJ, Barnes PD, Riviello JJ Jr. Cyclosporin A acute encephalopathy and seizure syndrome in childhood: clinical features and risk of seizure recurrence. J Child Neurol. 1998; 13:336–344. PMID: 9701483.
Article14. Hagensee ME, Bauwens JE, Kjos B, Bowden RA. Brain abscess following marrow transplantation: experience at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, 1984-1992. Clin Infect Dis. 1994; 19:402–408. PMID: 7811856.
Article15. Trullemans F, Grignard F, Van Camp B, Schots R. Clinical findings and magnetic resonance imaging in severe cyclosporine-related neurotoxicity after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Eur J Haematol. 2001; 67:94–99. PMID: 11722596.
Article16. Bartynski WS, Zeigler ZR, Shadduck RK, Lister J. Pretransplantation conditioning influence on the occurrence of cyclosporine or FK-506 neurotoxicity in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:261–269. PMID: 14970028.17. Chohan R, Vij R, Adkins D, et al. Long-term outcomes of allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients after calcineurin inhibitor- induced neurotoxicity. Br J Haematol. 2003; 123:110–113. PMID: 14510951.18. Walter SH, Bertz H, Gerling J. Bilateral optic neuropathy after bone marrow transplantation and cyclosporin A therapy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000; 238:472–476. PMID: 10943669.
Article19. Akagi T, Manabe S, Ishigooka H. A case of cyclosporine-induced optic neuropathy with a normal therapeutic level of cyclosporine. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2010; 54:102–104. PMID: 20151288.
Article20. Pavlakis SG, Frank Y, Chusid R. Hypertensive encephalopathy, reversible occipitoparietal encephalopathy, or reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy: three names for an old syndrome. J Child Neurol. 1999; 14:277–281. PMID: 10342593.21. Lucey MR, Kolars JC, Merion RM, Campbell DA, Aldrich M, Watkins PB. Cyclosporin toxicity at therapeutic blood levels and cytochrome P-450 IIIA. Lancet. 1990; 335:11–15. PMID: 1967328.
Article22. Erer B, Polchi P, Lucarelli G, et al. CsA-associated neurotoxicity and ineffective prophylaxis with clonazepam in patients transplanted for thalassemia major: analysis of risk factors. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1996; 18:157–162. PMID: 8832009.23. Koh JH, Lee HG, Chung YJ, et al. A case of cyclosporine induced reversible cortical blindness. Korean J Hematol. 1997; 32:487–494.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of pneumomediastinum combined with chronic graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- A Case of Central Nervous System Myelomatosis Developing after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- Disseminated Invasive Aspergillosis with Multiple Brain Abscess after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Treated Successfully with Voriconazole and Neurosurgical Intervention
- Long-Term Complete Remission in an Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient with Isolated Central Nervous System Relapse after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- A Case of Nonclassifiable Interstitial Pneumonia after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation