Korean J Hematol.
2008 Sep;43(3):194-197. 10.5045/kjh.2008.43.3.194.
A Case of Central Nervous System Myelomatosis Developing after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. deogyeon@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2252189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2008.43.3.194
Abstract
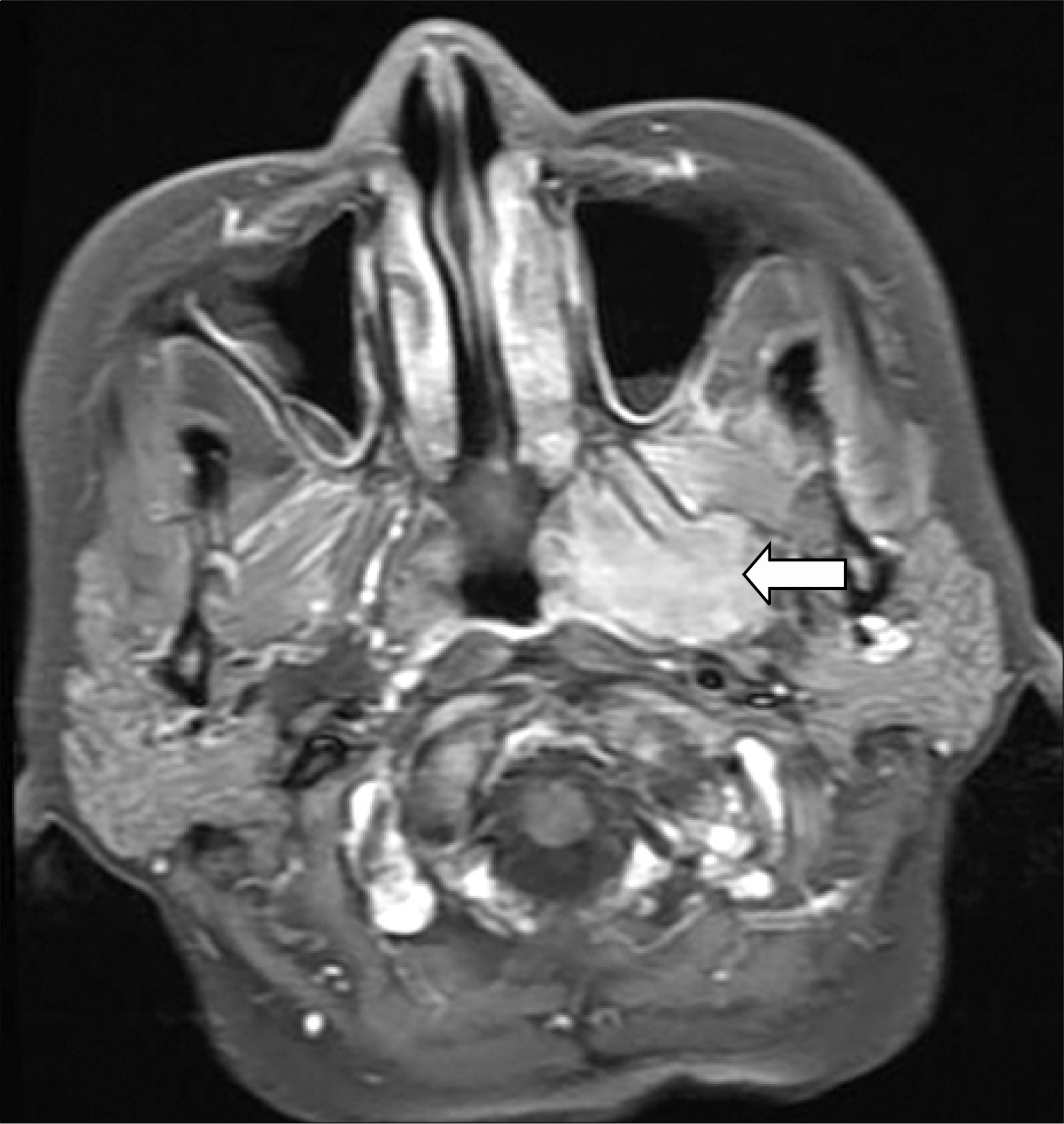
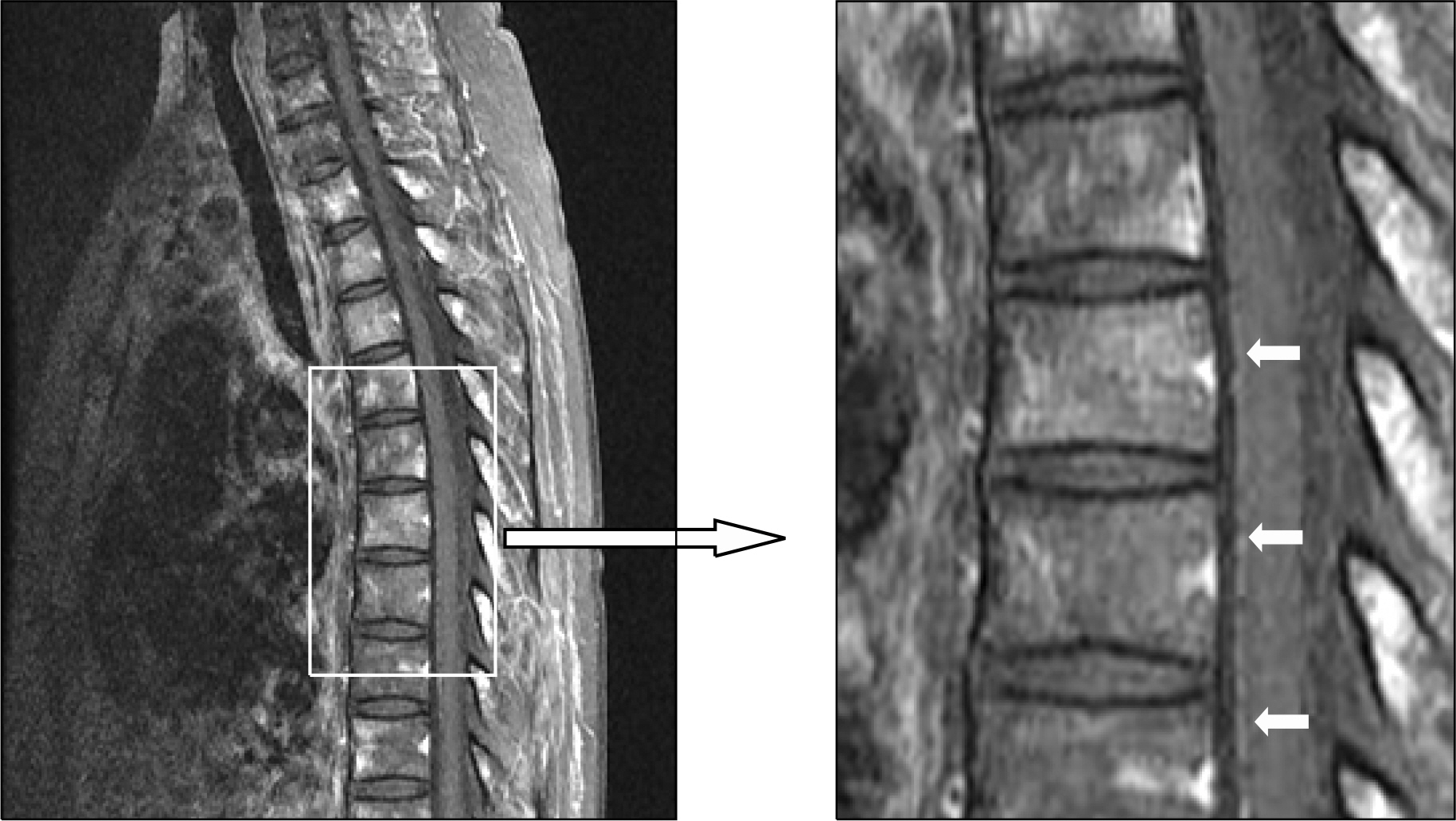
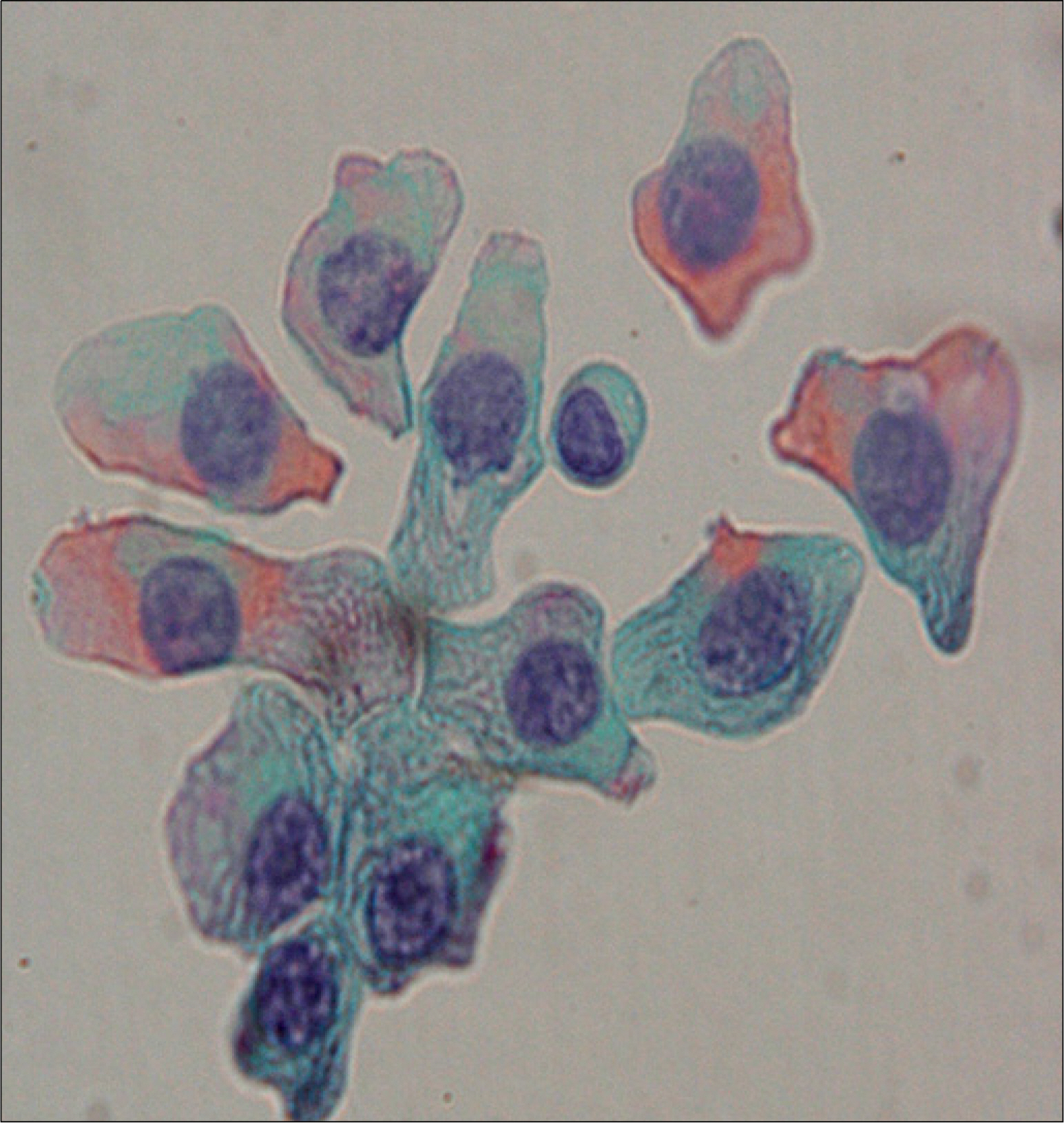
- Central nervous system (CNS) myelomatosis, which is the presence of monoclonal plasma cells in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), is extremely rare. We report a case of CNS myelomatosis developed in a 45-year-old woman with multiple myeloma in complete response, which was achieved by allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation using a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen consisting of melphalan, fludarabine, and antithymocyte globulin. Two months after the transplant, she developed a moderate motor and sensory weakness in both lower extremities. Atypical plasma cells were found in the CSF, and immunofixation revealed monoclonal light chain in the CSF. She was given three courses of weekly intra-thecal chemotherapy consisting of methotrexate, cytarabine, and dexamethasone, which cleared the CSF. This case indicates that the allogeneic transplantation could not control CNS myelomatosis, despite successfully treating the bone marrow myeloma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Antilymphocyte Serum
Bone Marrow
Central Nervous System
Cytarabine
Dexamethasone
Female
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Humans
Light
Lower Extremity
Melphalan
Methotrexate
Middle Aged
Multiple Myeloma
Nervous System
Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
Plasma Cells
Transplantation, Homologous
Transplants
Vidarabine
Antilymphocyte Serum
Cytarabine
Dexamethasone
Melphalan
Methotrexate
Vidarabine
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Central Nervous System Myelomatosis with Complex Chromosome Aberrations
Hae In Bang, Jin Young Yoo, Kyoung Ha Kim, Rojin Park, Jeong Won Shin, Tae Youn Choi, Sang-Cheol Lee, Hee-Sook Park, Jong-Ho Won
Korean J Lab Med. 2010;30(4):334-338. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.4.334.
Reference
-
1). Brenner B., Carter A., Tatarsky I., Gruszkiewicz J., Peyser E. Incidence, prognostic significance and therapeutic modalities of central nervous system involvement in multiple myeloma. Acta Haematol. 1982. 68:77–83.
Article2). Fassas ABT., Muwalla F., Berryman T, et al. Myeloma of the central nervous system: association with high-risk chromosomal abnormalities, plasmablastic morphology and extramedullary manifestations. Br J Haematol. 2002. 117:103–8.
Article3). Kim YM., Jeon MY., Chi JG. Cytologic features and distribution of primary sites of malignant cells in cerebrospinal fluid. Korean J Cytopathol. 2000. 11:65–73.4). Nieuwenhuizen L., Biesma DH. Central nervous system myelomatosis: review of the literature. Eur J Haematol. 2008. 80:1–9.
Article5). Sasser RL., Yam LT., Li C. Myeloma with involvement of the serous cavities. Cytologic and immu-nochemical diagnosis and literature review. Acta Cytol. 1990. 34:479–85.6). Péter A. The plasma cells of the cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol Sci. 1967. 4:227–39.
Article7). Moulopoulos LA., Granfield CA., Dimopoulos MA., Kim EE., Alexanian R., Libshitz HI. Extraosseous multiple myeloma: imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994. 161:1083–7.
Article8). Umapathi T., Chaudhry V. Toxic neuropathy. Curr Opin Neurol. 2005. 18:574–80.
Article9). de la Fuente J., Prieto I., Albo C., Sopeña B., Somoli-nos N., Martinez C. Plasma cell myeloma presented as myelomatous meningitis. Eur J Haematol. 1994. 53:244–5.10). Cavanna L., Invernizzi R., Berte R., Vallisa D., Buscarini L. Meningeal involvement in multiple myeloma: report of a case with cytologic and immunocytochemical diagnosis. Acta Cytol. 1996. 40:571–75.11). Spiers AS., Halpern R., Ross SC., Neiman RS., Harawi S., Zipoli TE. Meningeal myelomatosis. Arch Intern Med. 1980. 140:256–9.
Article12). Patriarca F., Zaja F., Silvestri F, et al. Meningeal and cerebral involvement in multiple myeloma patients. Ann Hematol. 2001. 80:758–62.
Article13). Patriarca F., Prosdocimo S., Tomadini V., Vasciaveo A., Bruno B., Fanin R. Efficacy of bortezomib therapy for extramedullary relapse of myeloma after autologous and non-myeloablative allogeneic transplantation. Haematologica. 2005. 90:278–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Disseminated Invasive Aspergillosis with Multiple Brain Abscess after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Treated Successfully with Voriconazole and Neurosurgical Intervention
- Long-Term Complete Remission in an Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient with Isolated Central Nervous System Relapse after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- A case of pneumomediastinum combined with chronic graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Cerebral salt-wasting syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adolescents: 3 case reports
- Comparison of Quality of Life of Autologous and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients