J Breast Cancer.
2008 Jun;11(2):56-63. 10.4048/jbc.2008.11.2.56.
Changes of Coregulators, MAP Kinase Activity and p27/kip1 with Estrogen or Antiestrogen Treatment in Breast Cancer Cell Line
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bwpark@yuhs.ac
- 2Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2241932
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2008.11.2.56
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: Estrogen, various polypeptide hormones and growth factors are associated with the development and progression of breast cancer. Coregulatory proteins are also associated with estrogen receptor (ER) transcriptional activity and tamoxifen resistance. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the change of coregulator mRNAs and various cell proliferation proteins and cell cycle-related proteins after treatment with estrogen or antiestrogen.
METHODS
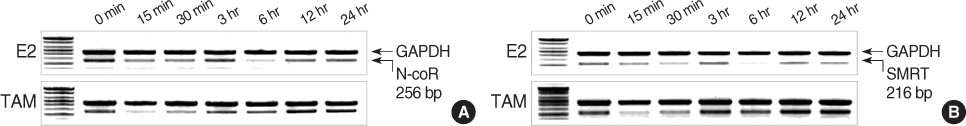
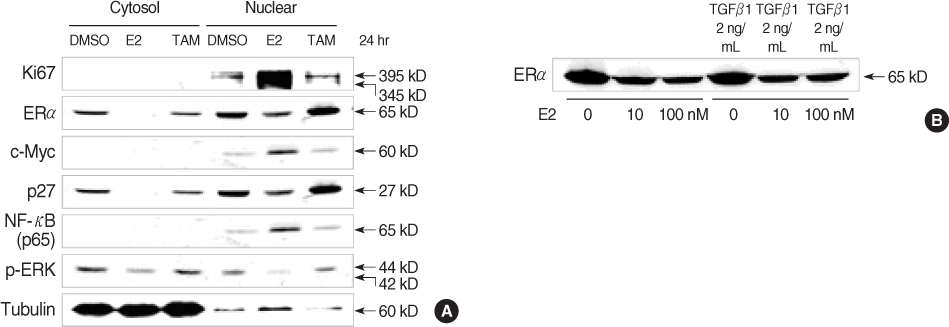
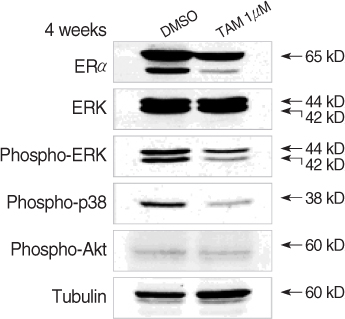
MCF-7 cells were maintained in dextran-coated charcoal stripped 10% Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM). To measure the change of the coactivators' (src-1, P/CAF, CBP, AIB1) mRNAs and corepressors' (SMRT, N-coR) mRNAs, multiple PCR was carried out using specific primers. In addition, intracellular proteins related to cell proliferation and cell cycle regulation were measured by performing Western blotting after treatment with estrogen or tamoxifen. The change of mitogen activated protein kinases was also measured by performing Western after tamoxifen treatment for 4 weeks.
RESULTS
Coactivator mRNAs expression rapidly decreased in 15 min after estrogen treatment but this recovered to the initial level in 3 hr. The pattern was similar for the case of tamoxifen treatment. Corepressor mRNAs expression rapidly decreased in 15 min after estrogen treatment and it remained at a lower level until 24 hr after estrogen treatment. With tamoxifen treatment, the initial response was similar to the cases of estrogen treatment, but the xpression gradually increased 3 hr after tamoxifen treatment. Treatment of estrogen induced intracellular concentrations of c-myc and Ki-67 and it increased nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB and phosphor-ERK and it decreased the intracellular cell cycle suppressor p27/kip1. Tamoxifen treatment increased nuclear p27/kip1 but it decreased c-myc, NF-kappaB and phosphor-ERK. Long-term (4 weeks) treatment of tamoxifen was associated with decrease of activated ERK and p38 but there was no change in phospho-Akt level.
CONCLUSION
Estrogen induced cell proliferation and the survival pathway-related factors, but it decreased the cell cycle suppressor p27/kip1. Long-term treatment with antiestrogen tamoxifen might decrease the MAPK activities in ERalpha-expressing tumor cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Blotting, Western
Breast
Breast Neoplasms
Cell Cycle
Cell Line
Cell Proliferation
Charcoal
Eagles
Estrogen Receptor Modulators
Estrogens
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
MCF-7 Cells
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
NF-kappa B
Peptide Hormones
Phosphotransferases
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Proteins
RNA, Messenger
Tamoxifen
Charcoal
Estrogen Receptor Modulators
Estrogens
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
NF-kappa B
Peptide Hormones
Phosphotransferases
Proteins
RNA, Messenger
Tamoxifen
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dubik D, Dembinski TC, Shiu RP. Stimulation of c-myc oncogene expression associated with estrogen-induced proliferation of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1987. 47:6517–6521.2. Ignar-Trowbridge DM, Pimentel M, Parker MG, McLachlan JA, Korach KS. Peptide growth factor cross-talk with the estrogen receptor requires the A/B domain and occurs independently of protein kinase C or estradiol. Endocrinology. 1996. 137:1735–1744.
Article3. Bunone G, Briand PA, Miksicek RJ, Picard D. Activation of the unliganded estrogen receptor by EGF involves the MAP kinase pathway and direct phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1996. 15:2174–2183.
Article4. Wiesen JF, Young P, Werb Z, Cunha GR. Signaling through the stromal epidermal growth factor receptor is necessary for mammary ductal development. Development. 1999. 126:335–344.
Article5. Normanno N, Di Maio M, De Maio E, De Luca A, de Matteis A, Giordano A, et al. Mechanisms of endocrine resistance and novel therapeutic strategies in breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005. 12:721–747.
Article6. Girault I, Lerebours F, Amarir S, Tozlu S, Tubiana-Hulin M, Lidereau R, et al. Expression analysis of estrogen receptor alpha coregulators in breast carcinoma: evidence that NCOR1 expression is predictive of the response to tamoxifen. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. 9:1259–1266.7. Graham JD, Bain DL, Richer JK, Jackson TA, Tung L, Horwitz KB. Nuclear receptor conformation, coregulators, and tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer. Steroids. 2000. 65:579–584.
Article8. Danielian PS, White R, Lees JA, Parker MG. Identification of a conserved region required for hormone dependent transcriptional activation by steroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992. 11:1025–1033.
Article9. Parker MG. Structure and function of estrogen receptors. Vitam Horm. 1995. 51:267–287.
Article10. Shiau AK, Barstad D, Loria PM, Cheng L, Kushner PJ, Agard DA, et al. The structural basis of estrogen receptor/coactivator recognition and the antagonism of this interaction by tamoxifen. Cell. 1998. 95:927–937.
Article11. Torres-Arzayus MI, Font de Mora J, Yuan J, Vazquez F, Bronson R, Rue M, et al. High tumor incidence and activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in transgenic mice define AIB1 as an oncogene. Cancer Cell. 2004. 6:263–274.
Article12. Osborne CK, Bardou V, Hopp TA, Chamness GC, Hilsenbeck SG, Fuqua SA, et al. Role of the estrogen receptor coactivator AIBI (SRC-3) and HER-2/neu in tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003. 95:353–361.
Article13. Lavinsky RM, Jepsen K, Heinzel T, Torchia J, Mullen TM, Schiff R, et al. Diverse signaling pathways modulate nuclear receptor recruitment of N-CoR and SMRT complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998. 95:2920–2925.
Article14. Newby JC, Johnston SR, Smith IE, Dowsett M. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and c-erbB2 during the development of tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1997. 3:1643–1651.15. Nicholson RI, Hutcheson IR, Harper ME, Knowlden JM, Barrow D, McClelland RA, et al. Modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor in endocrine-resistant, oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2001. 8:175–182.
Article16. Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002. 296:1655–1657.
Article17. Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976. 72:248–254.
Article18. Benz CC, Scott GK, Sarup JC, Johnson RM, Tripathy D, Coronado E, et al. Estrogen-dependent, tamoxifen-resistant tumorigenic growth of MCF-7 cells transfected with HER2/neu. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1993. 24:85–95.
Article19. Dowsett M. Overexpression of HER-2 as a resistance mechanism to hormonal therapy for breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2001. 8:191–195.
Article20. Piccart M, Lohrisch C, Di Leo A, Larsimont D. The predictive value of HER2 in breast cancer. Oncology. 2001. 61:73–82.
Article21. Mass R. The role of HER-2 expression in predicting response to therapy in breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2000. 27:46–52.22. Kurokawa H, Lenferink AE, Simpson JF, Pisacane PI, Sliwkowski MX, Forbes JT. Inhibition of HER2/neu (erbB-2) and mitogenactivated protein kinases enhances tamoxifen action against HER2-overexpressing, tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:5887–5894.23. Nicholson RI, Hutcheson IR, Harper ME, Knowlden JM, Barrow D, McClelland RA, et al. Modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor in endocrine-resistant, estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. 963:104–115.
Article24. Witters LM, Kumar R, Chinchilli VM, Lipton A. Enhanced antiproliferative activity of the combination of tamoxifen plus HER-2-neu antibody. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1997. 42:1–5.
Article25. Witters L, Engle L, Lipton A. Restoration of estrogen responsiveness by blocking the HER-2/neu pathway. Oncol Rep. 2002. 9:1163–1166.
Article26. Fond de Mora J, Brown M. AIBI is a conduit for kinase-mediated growth factor signaling to the estrogen receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. 20:5041–5047.
Article27. Lewandowski S, Kalita K, Kaczmarek L. Estrogen receptorβ: potential functional significance of a variety of mRNA isoforms. FEBS Lett. 2002. 524:1–5.28. Nawaz Z, Lonard DM, Dennis AP, Smith CL, O'Malley BW. Proteasome-dependent degradation of the human estrogen receptor. PNAS. 1999. 96:1858–1862.
Article29. Tschugguel W, Dietrich W, Zhegu Z, Stonek F, Kolbus A, Huber JC. Differential regulation of proteasome-dependent estrogen receptor alpha and beta turnover in cultured human uterine artery endothelial cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 88:2281–2287.
Article30. Knabbe C, Lippman ME, Wakefield LM, Flanders KC, Kasid A, Derynck R, et al. Evidence that transforming growth factor beta is a hormonally regulated negative growth factor in human breast cancer cells. Cell. 1987. 48:417–428.
Article31. Petrel TA, Brueggemeier RW. Increased proteasome-dependent degradation of estrogen receptor-alpha by TGF-beta1 in breast cancer cell lines. J Cell Biochem. 2003. 88:181–190.
Article32. Ekholm SV, Reed SI. Regulation of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases in the mammalian cell cycle. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000. 12:676–684.
Article33. Slingerland J, Pagano M. Regulation of the cdk inhibitor p27 and its deregulation in cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2000. 183:10–17.
Article34. Barnes A, Pinder S, Bell J, Paish E, Wencyk P, Robertson J, et al. Expression of p27kip1 in breast cancer and its prognostic significance. J Pathol. 2003. 201:451–459.
Article35. Zhang CC, Shapiro DJ. Activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by estrogen or by 4-hydroxytamoxifen is coupled to estrogen receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:479–486.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Significance of the Expression of p27(Kip1) Protein in Human Breast Cancer
- Different Expression of p27(kip1) and p57(kip2) by Genistein Treatment in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells
- Expression of p27kip1, Cyclin D1 and p53 Protein in Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast
- The Relevance of Women's Diseases, Jun Activation-domain Binding Protein 1 (JAB1) and p27(kip1)
- Expression of p34(cdc2), p27(Kip1), p21(WAF1/Cip1) and p53 in Human Breast Cancers