Endocrinol Metab.
2015 Dec;30(4):576-583. 10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.576.
Melanocortin 4 Receptor and Dopamine D2 Receptor Expression in Brain Areas Involved in Food Intake
- Affiliations
-
- 1Molecular Neurobiology Laboratory, Department of Life Sciences, Korea University College of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Seoul, Korea. jahyunb@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2169668
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.576
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) is involved in the regulation of homeostatic energy balance by the hypothalamus. Recent reports showed that MC4R can also control the motivation for food in association with a brain reward system, such as dopamine. We investigated the expression levels of MC4R and the dopamine D2 receptor (D2R), which is known to be related to food rewards, in both the hypothalamus and brain regions involved in food rewards.
METHODS
We examined the expression levels of D2R and MC4R by dual immunofluorescence histochemistry in hypothalamic regions and in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), the central amygdala, and the ventral tegmental area of transgenic mice expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein under the control of the D2R gene.
RESULTS
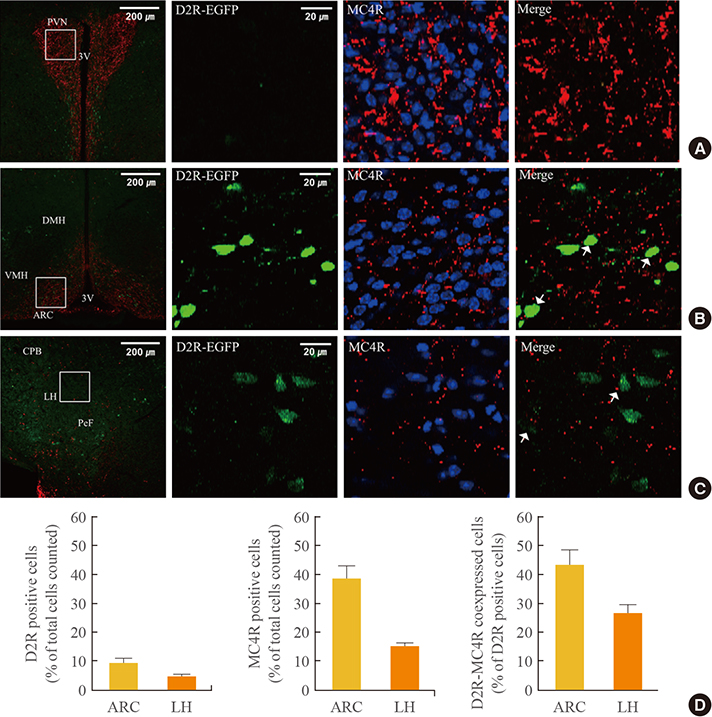
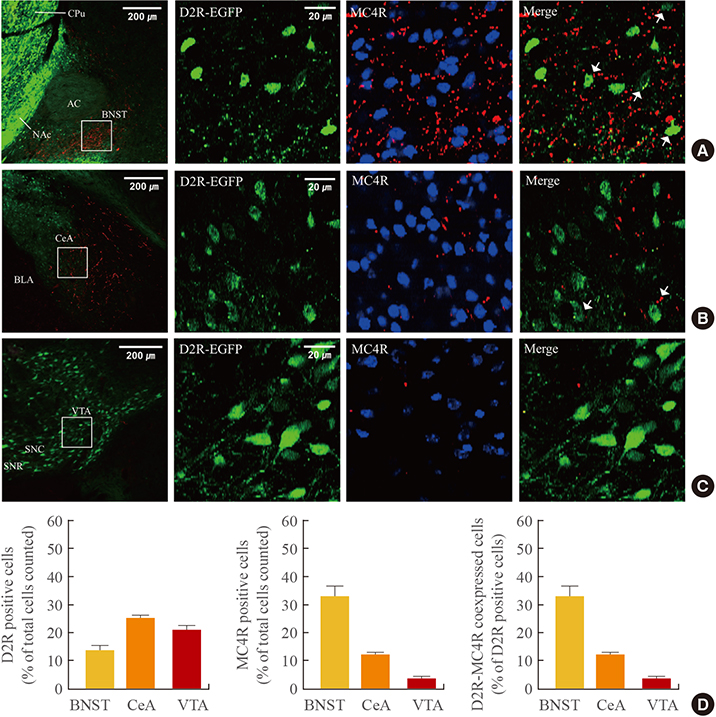
In the hypothalamic area, significant coexpression of MC4R and D2R was observed in the arcuate nucleus. We observed a significant coexpression of D2R and MC4R in the BNST, which has been suggested to be an important site for food reward.
CONCLUSION
We suggest that MC4R and D2R function in the hypothalamus for control of energy homeostasis and that within the brain regions related with rewards, such as the BNST, the melanocortin system works synergistically with dopamine for the integration of food motivation in the control of feeding behaviors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Amygdala
Animals
Arcuate Nucleus
Brain*
Dopamine*
Eating*
Feeding Behavior
Fluorescent Antibody Technique
Homeostasis
Hypothalamus
Mice
Mice, Transgenic
Motivation
Obesity
Receptor, Melanocortin, Type 4*
Receptors, Dopamine D2*
Reward
Ventral Tegmental Area
Dopamine
Receptor, Melanocortin, Type 4
Receptors, Dopamine D2
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D Jr, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature. 2000; 404:661–671.2. Morton GJ, Cummings DE, Baskin DG, Barsh GS, Schwartz MW. Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature. 2006; 443:289–295.3. Saper CB, Chou TC, Elmquist JK. The need to feed: homeostatic and hedonic control of eating. Neuron. 2002; 36:199–211.4. Palmiter RD. Is dopamine a physiologically relevant mediator of feeding behavior? Trends Neurosci. 2007; 30:375–381.5. Baik JH. Dopamine signaling in food addiction: role of dopamine D2 receptors. BMB Rep. 2013; 46:519–526.6. Elmquist JK, Elias CF, Saper CB. From lesions to leptin: hypothalamic control of food intake and body weight. Neuron. 1999; 22:221–232.7. Bjorbaek C, Hollenberg AN. Leptin and melanocortin signaling in the hypothalamus. Vitam Horm. 2002; 65:281–311.8. Cone RD. Studies on the physiological functions of the melanocortin system. Endocr Rev. 2006; 27:736–749.9. Bagnol D, Lu XY, Kaelin CB, Day HE, Ollmann M, Gantz I, et al. Anatomy of an endogenous antagonist: relationship between Agouti-related protein and proopiomelanocortin in brain. J Neurosci. 1999; 19:RC26.10. Cui H, Sohn JW, Gautron L, Funahashi H, Williams KW, Elmquist JK, et al. Neuroanatomy of melanocortin-4 receptor pathway in the lateral hypothalamic area. J Comp Neurol. 2012; 520:4168–4183.11. Huszar D, Lynch CA, Fairchild-Huntress V, Dunmore JH, Fang Q, Berkemeier LR, et al. Targeted disruption of the melanocortin-4 receptor results in obesity in mice. Cell. 1997; 88:131–141.12. Santini F, Maffei M, Pelosini C, Salvetti G, Scartabelli G, Pinchera A. Melanocortin-4 receptor mutations in obesity. Adv Clin Chem. 2009; 48:95–109.13. Kishi T, Aschkenasi CJ, Lee CE, Mountjoy KG, Saper CB, Elmquist JK. Expression of melanocortin 4 receptor mRNA in the central nervous system of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 2003; 457:213–235.14. Alvaro JD, Taylor JR, Duman RS. Molecular and behavioral interactions between central melanocortins and cocaine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003; 304:391–399.15. Lim BK, Huang KW, Grueter BA, Rothwell PE, Malenka RC. Anhedonia requires MC4R-mediated synaptic adaptations in nucleus accumbens. Nature. 2012; 487:183–189.16. Hsu R, Taylor JR, Newton SS, Alvaro JD, Haile C, Han G, et al. Blockade of melanocortin transmission inhibits cocaine reward. Eur J Neurosci. 2005; 21:2233–2242.17. Davis JF, Choi DL, Shurdak JD, Krause EG, Fitzgerald MF, Lipton JW, et al. Central melanocortins modulate mesocorticolimbic activity and food seeking behavior in the rat. Physiol Behav. 2011; 102:491–495.18. Tracy AL, Clegg DJ, Johnson JD, Davidson TL, Benoit SC. The melanocortin antagonist AgRP (83-132) increases appetitive responding for a fat, but not a carbohydrate, reinforcer. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008; 89:263–271.19. Baik JH. Dopamine signaling in reward-related behaviors. Front Neural Circuits. 2013; 7:152.20. Di Chiara G, Imperato A. Drugs abused by humans preferentially increase synaptic dopamine concentrations in the mesolimbic system of freely moving rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988; 85:5274–5278.21. Bassareo V, Di Chiara G. Differential influence of associative and nonassociative learning mechanisms on the responsiveness of prefrontal and accumbal dopamine transmission to food stimuli in rats fed ad libitum. J Neurosci. 1997; 17:851–861.22. Roitman MF, Stuber GD, Phillips PE, Wightman RM, Carelli RM. Dopamine operates as a subsecond modulator of food seeking. J Neurosci. 2004; 24:1265–1271.23. Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Logan J, Pappas NR, Wong CT, Zhu W, et al. Brain dopamine and obesity. Lancet. 2001; 357:354–357.24. Stice E, Spoor S, Bohon C, Small DM. Relation between obesity and blunted striatal response to food is moderated by TaqIA A1 allele. Science. 2008; 322:449–452.25. Johnson PM, Kenny PJ. Dopamine D2 receptors in addiction-like reward dysfunction and compulsive eating in obese rats. Nat Neurosci. 2010; 13:635–641.26. Kim KS, Yoon YR, Lee HJ, Yoon S, Kim SY, Shin SW, et al. Enhanced hypothalamic leptin signaling in mice lacking dopamine D2 receptors. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:8905–8917.27. Sim HR, Choi TY, Lee HJ, Kang EY, Yoon S, Han PL, et al. Role of dopamine D2 receptors in plasticity of stress-induced addictive behaviours. Nat Commun. 2013; 4:1579.28. Song SS, Kang BJ, Wen L, Lee HJ, Sim HR, Kim TH, et al. Optogenetics reveals a role for accumbal medium spiny neurons expressing dopamine D2 receptors in cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014; 8:336.29. Mounien L, Bizet P, Boutelet I, Vaudry H, Jegou S. Expression of melanocortin MC3 and MC4 receptor mRNAs by neuropeptide Y neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus. Neuroendocrinology. 2005; 82:164–170.30. Siljee JE, Unmehopa UA, Kalsbeek A, Swaab DF, Fliers E, Alkemade A. Melanocortin 4 receptor distribution in the human hypothalamus. Eur J Endocrinol. 2013; 168:361–369.31. Pandit R, de Jong JW, Vanderschuren LJ, Adan RA. Neurobiology of overeating and obesity: the role of melanocortins and beyond. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011; 660:28–42.32. Lindblom J, Opmane B, Mutulis F, Mutule I, Petrovska R, Klusa V, et al. The MC4 receptor mediates alpha-MSH induced release of nucleus accumbens dopamine. Neuroreport. 2001; 12:2155–2158.33. Gelez H, Poirier S, Facchinetti P, Allers KA, Wayman C, Bernabe J, et al. Neuroanatomical distribution of the melanocortin-4 receptors in male and female rodent brain. J Chem Neuroanat. 2010; 40:310–324.34. Lippert RN, Ellacott KL, Cone RD. Gender-specific roles for the melanocortin-3 receptor in the regulation of the mesolimbic dopamine system in mice. Endocrinology. 2014; 155:1718–1727.35. Dumont EC. What is the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis? Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009; 33:1289–1290.36. Jalabert M, Aston-Jones G, Herzog E, Manzoni O, Georges F. Role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the control of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009; 33:1336–1346.37. Dumont EC, Mark GP, Mader S, Williams JT. Self-administration enhances excitatory synaptic transmission in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Nat Neurosci. 2005; 8:413–414.38. Figlewicz DP, Bennett-Jay JL, Kittleson S, Sipols AJ, Zavosh A. Sucrose self-administration and CNS activation in the rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011; 300:R876–R884.39. Georges F, Aston-Jones G. Activation of ventral tegmental area cells by the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: a novel excitatory amino acid input to midbrain dopamine neurons. J Neurosci. 2002; 22:5173–5187.40. Areias MF, Prada PO. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in the amygdala: influences on food intake. Behav Brain Res. 2015; 282:209–217.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Dopamine D1 and D2 Receptor mRNAs in the Fetal Rat Retina
- Modulation of Dopamine D2 Receptors as a Basis of Antipsychotic Action
- Expression of Dopamine D2 Receptor in Response to Apomorphine Treatment in the Striatum of the Rat with Experimentally Induced Parkinsonism
- Allelic Association of the Dopamine D2Receptor in Korean Alcoholics
- Expression and Localization of Peripheral Dopamine D1 and D2 Receptors in Rat and Human Seminal Vesicle