Acute Crit Care.
2018 Feb;33(1):34-41. 10.4266/acc.2017.00577.
The Effects of Flecainide Acetate on Inflammatory-Immune Response in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Neutrophils and on Mortality in Septic Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital and Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. shkwak@jnu.ac.kr
- 2Brain Korea 21 Project, Center for Creative Biomedical Scientists at Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Gwangju Christian Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2436305
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2017.00577
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Flecainide acetate is a drug used primarily for cardiac arrhythmia. Some studies also imply that flecainide acetate has the potential to regulate inflammatory-immune responses; however, its mechanism of action is contended. We determined the effects of flecainide acetate on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human neutrophils in vitro and on mortality in a septic rat model.
METHODS
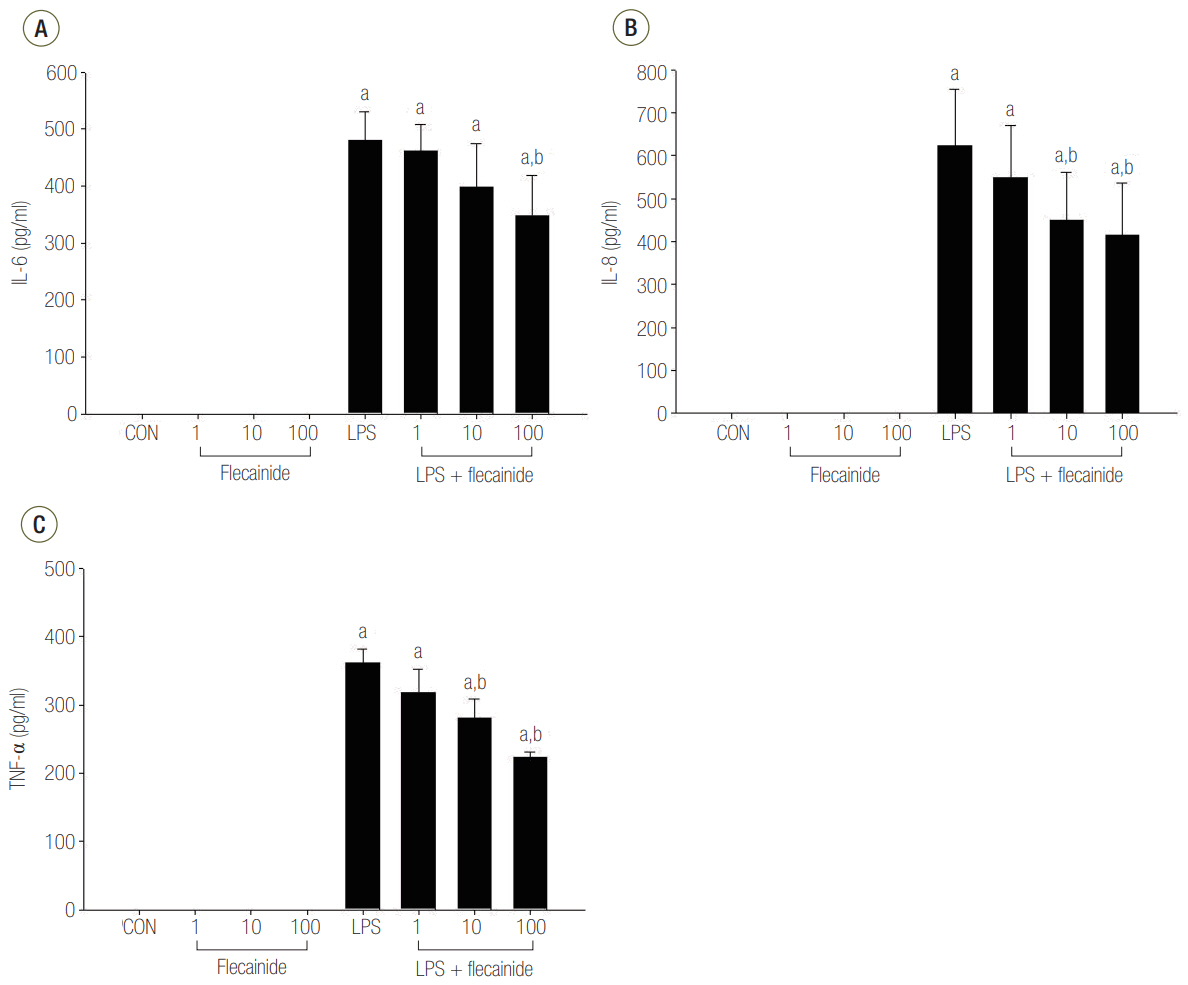
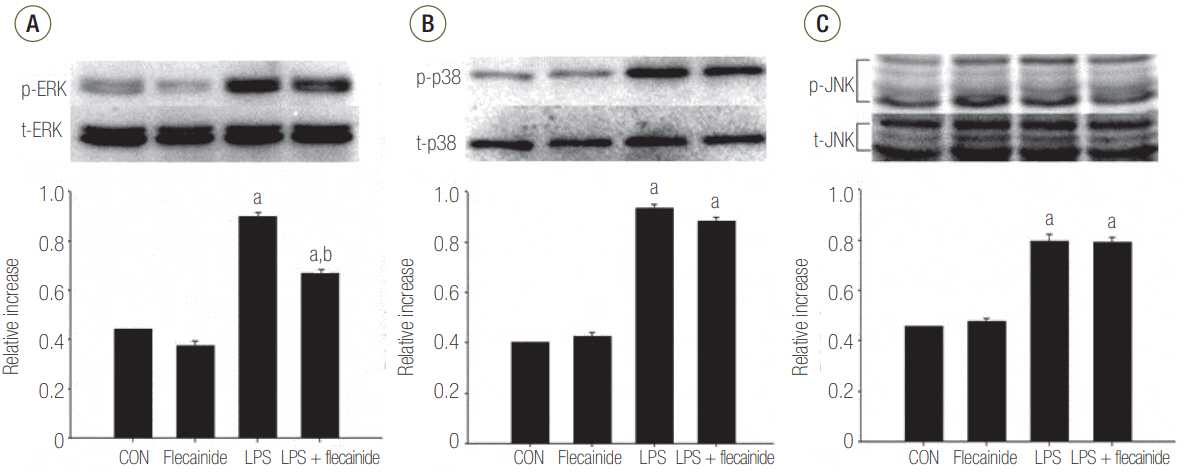
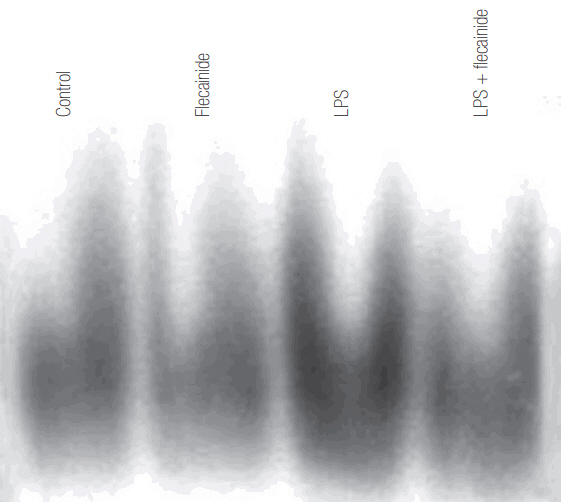
Neutrophils from human blood were cultured with varying concentrations of flecainide acetate (1 μM, 10 μM, or 100 μM) with or without LPS (100 ng/ml). To assess neutrophil activation, the protein levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 were measured after a 4-hour culture period. To assess the intracellular signaling pathways, the levels of phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) were measured after a 30-minute culture period, and the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB was measured after a 1-hour culture period. Additionally, the survival rate was investigated in a rat sepsis model.
RESULTS
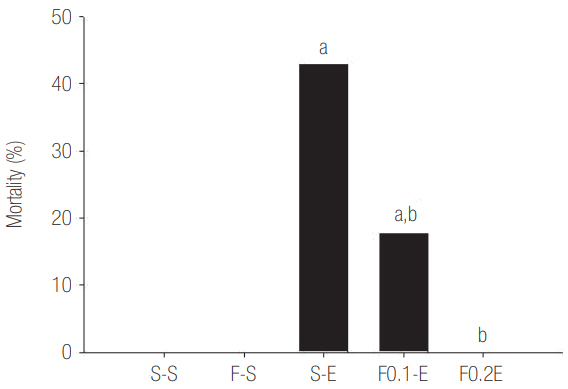
Flecainide acetate down-regulated the activation of proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6 and IL-8, and intracellular signaling pathways including ERK 1/2 and NF-κB. Flecainide acetate also improved the survival rate in the rat sepsis model.
CONCLUSIONS
Collectively, these findings indicate that flecainide acetate can improve survival in a rat sepsis model by attenuating LPS-induced neutrophil responses. We therefore suggest that flecainide acetate plays an important role in modulating inflammatory-immune responses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Arrhythmias, Cardiac
Cytokines
Flecainide*
Humans
In Vitro Techniques
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Lipopolysaccharides
Models, Animal
Mortality*
Neutrophil Activation
Neutrophils*
Phosphorylation
Phosphotransferases
Protein Kinases
Rats*
Sepsis
Sodium Channel Blockers
Survival Rate
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Cytokines
Flecainide
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Lipopolysaccharides
Phosphotransferases
Protein Kinases
Sodium Channel Blockers
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ferrer R, Martin-Loeches I, Phillips G, Osborn TM, Townsend S, Dellinger RP, et al. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit Care Med. 2014; 42:1749–55.2. Rhee C, Dantes R, Epstein L, Murphy DJ, Seymour CW, Iwashyna TJ, et al. Incidence and trends of sepsis in US hospitals using clinical vs claims data, 2009-2014. JAMA. 2017; 318:1241–9.
Article3. van Zanten AR, Brinkman S, Arbous MS, Abu-Hanna A, Levy MM, de Keizer NF, et al. Guideline bundles adherence and mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2014; 42:1890–8.
Article4. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016; 315:801–10.
Article5. Doerschuk CM, Tasaka S, Wang Q. CD11/CD18-dependent and -independent neutrophil emigration in the lungs: how do neutrophils know which route to take? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2000; 23:133–6.6. Windsor AC, Mullen PG, Fowler AA, Sugerman HJ. Role of the neutrophil in adult respiratory distress syndrome. Br J Surg. 1993; 80:10–7.
Article7. Samlowski WE, Frame RN, Logue GL. Flecanide-induced immune neutropenia: documentation of a hapten-mediated mechanism of cell destruction. Arch Intern Med. 1987; 147:383–4.
Article8. Nojima S, Kobuchi H, Saibara T, Yasuda T, Utsumi K. Selective inhibition of human TNF-alpha action by flecainide acetate, an antiarrhythmic drug. Physiol Chem Phys Med NMR. 1995; 27:77–89.9. Kwak SH, Mitra S, Bdeir K, Strassheim D, Park JS, Kim JY, et al. The kringle domain of urokinase-type plasminogen activator potentiates LPS-induced neutrophil activation through interaction with αVβ3 integrins. J Leukoc Biol. 2005; 78:937–45.10. Yum HK, Arcaroli J, Kupfner J, Shenkar R, Penninger JM, Sasaki T, et al. Involvement of phosphoinositide 3-kinases in neutrophil activation and the development of acute lung injury. J Immunol. 2001; 167:6601–8.
Article11. Arcaroli J, Yang KY, Yum HK, Kupfner J, Pitts TM, Park JS, et al. Effects of catecholamines on kinase activation in lung neutrophils after hemorrhage or endotoxemia. J Leukoc Biol. 2002; 72:571–9.12. Harris VK, Danda D, Murali NS, Das PK, Abraham M, Cherian AM, et al. Unusual association of Kikuchi’s disease and dengue virus infection evolving into systemic lupus erythematosus. J Indian Med Assoc. 2000; 98:391–3.13. Nick JA, Avdi NJ, Young SK, Lehman LA, McDonald PP, Frasch SC, et al. Selective activation and functional significance of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1999; 103:851–8.
Article14. Baigrie RJ, Lamont PM, Kwiatkowski D, Dallman MJ, Morris PJ. Systemic cytokine response after major surgery. Br J Surg. 1992; 79:757–60.
Article15. Selvatici R, Falzarano S, Mollica A, Spisani S. Signal transduction pathways triggered by selective formylpeptide analogues in human neutrophils. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006; 534:1–11.
Article16. Avdi NJ, Nick JA, Whitlock BB, Billstrom MA, Henson PM, Johnson GL, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway in human neutrophils: integrin involvement in a pathway leading from cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:2189–99.17. Rane MJ, Carrithers SL, Arthur JM, Klein JB, McLeish KR. Formyl peptide receptors are coupled to multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades by distinct signal transduction pathways: role in activation of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidase. J Immunol. 1997; 159:5070–8.18. Goebel LJ, Crespo RD, Abraham RT, Masho SW, Glover ED. Correlates of youth smokeless tobacco use. Nicotine Tob Res. 2000; 2:319–25.
Article19. Esmon CT, Fukudome K, Mather T, Bode W, Regan LM, Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, et al. Inflammation, sepsis, and coagulation. Haematologica. 1999; 84:254–9.20. Hardaway RM. A review of septic shock. Am Surg. 2000; 66:22–9.21. Karima R, Matsumoto S, Higashi H, Matsushima K. The molecular pathogenesis of endotoxic shock and organ failure. Mol Med Today. 1999; 5:123–32.
Article22. Lien E, Ingalls RR. Toll-like receptors. Crit Care Med. 2002; 30(1 Supp):S1–11.
Article23. Pace JL, Russell SW. Activation of mouse macrophages for tumor cell killing. I. Quantitative analysis of interactions between lymphokine and lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1981; 126:1863–7.24. West MA, Koons A, Crandall M, Skinner R, Worley M, Shapiro MB. Whole blood leukocyte mitogen activated protein kinases activation differentiates intensive care unit patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis. J Trauma. 2007; 62:805–11.
Article25. Khan I, Oriowo MA, Anim JT. Amelioration of experimental colitis by Na-H exchanger-1 inhibitor amiloride is associated with reversal of IL-1ss and ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005; 40:578–85.26. Sikes PJ, Zhao P, Maass DL, White J, Horton JW. Sodium/hydrogen exchange activity in sepsis and in sepsis complicated by previous injury: 31P and 23Na NMR study. Crit Care Med. 2005; 33:605–15.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acute Ventricular Capture Threshold Rise Associated with Flecainide Acetate
- Flecainide Improve Sepsis Induced Acute Lung Injury by Controlling Inflammatory Response
- Protective role of curcumin against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis in human neutrophil
- A Case of Life-Threatening Supraventricular Tachycardia Related to Flecainide Toxicity
- Flecainide-Induced Torsade de Pointes Successfully Treated with Intensive Pharmacological Therapy