Anesth Pain Med.
2020 Jan;15(1):41-48. 10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.41.
Protective role of curcumin against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis in human neutrophil
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Kwangju Christian Hospital, Gwangju, Korea
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School and Hospital, Gwangju, Korea
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Brain Korea 21 Project, Center for Creative Biomedical Scientists at Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea
- KMID: 2500453
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.41
Abstract
- Background
Sepsis, an uncontrolled host response to infection, may be life-threatening organ injury. Neutrophils play a critical role in regulation of host immune response to infection. Curcumin, known as a spice and food coloring agent, possesses anti-inflammatory properties. In this study, we investigated the effects of curcumin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neutrophil activation with its signaling pathways.
Methods
Isolated human neutrophils were incubated without or with LPS and curcumin, and the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-8 were assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. The expression of mitogen-activated protein kinases such as p38, extracellularsignal- regulated kinase (ERK)1/2, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) were evaluated by Western blot analysis. Neutrophil apoptosis was also measured by fluorescenceactivated cell sorting (annexin V/propidium iodide) in LPS-stimulated neutrophils under treatment with curcumin.
Results
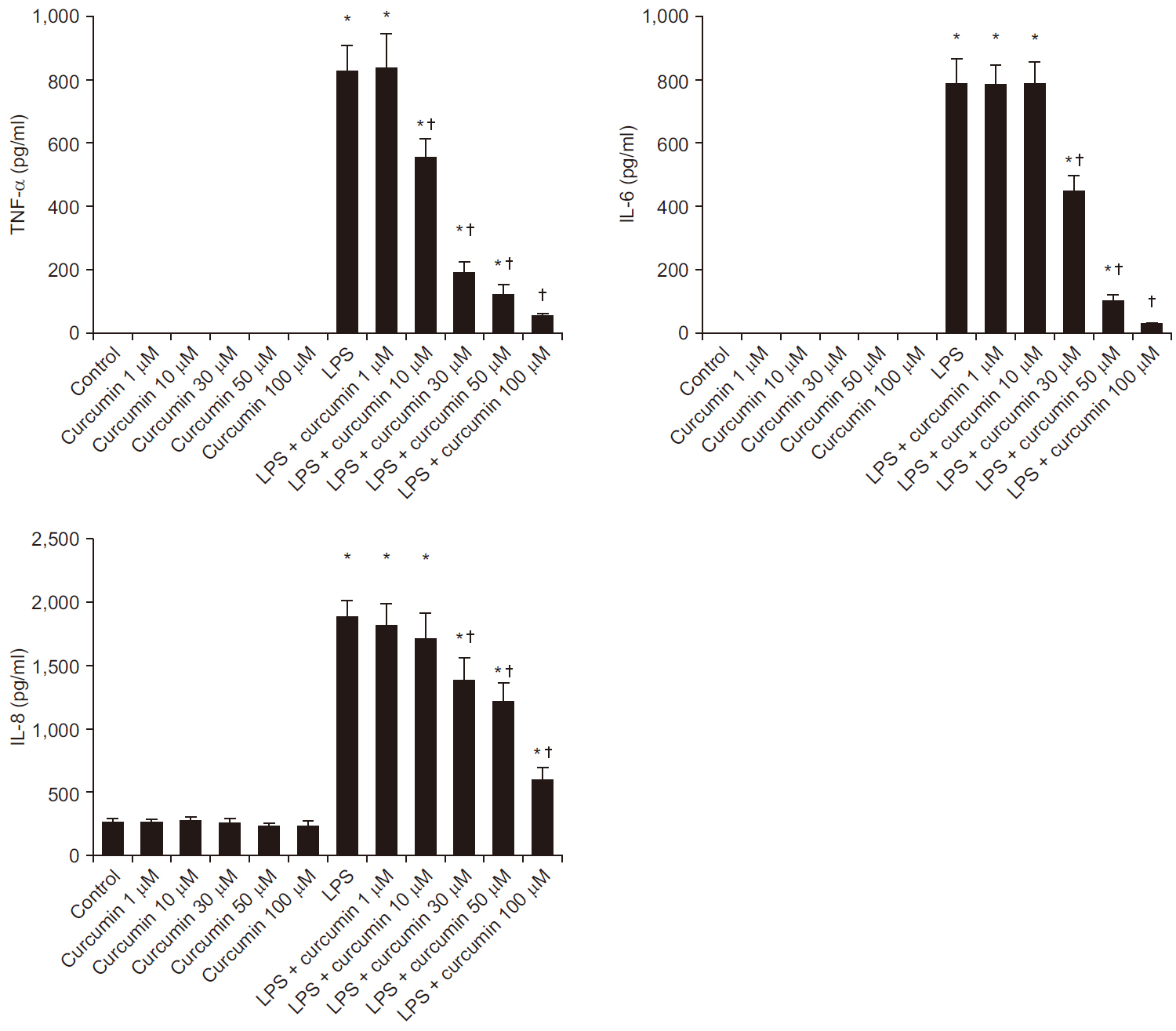
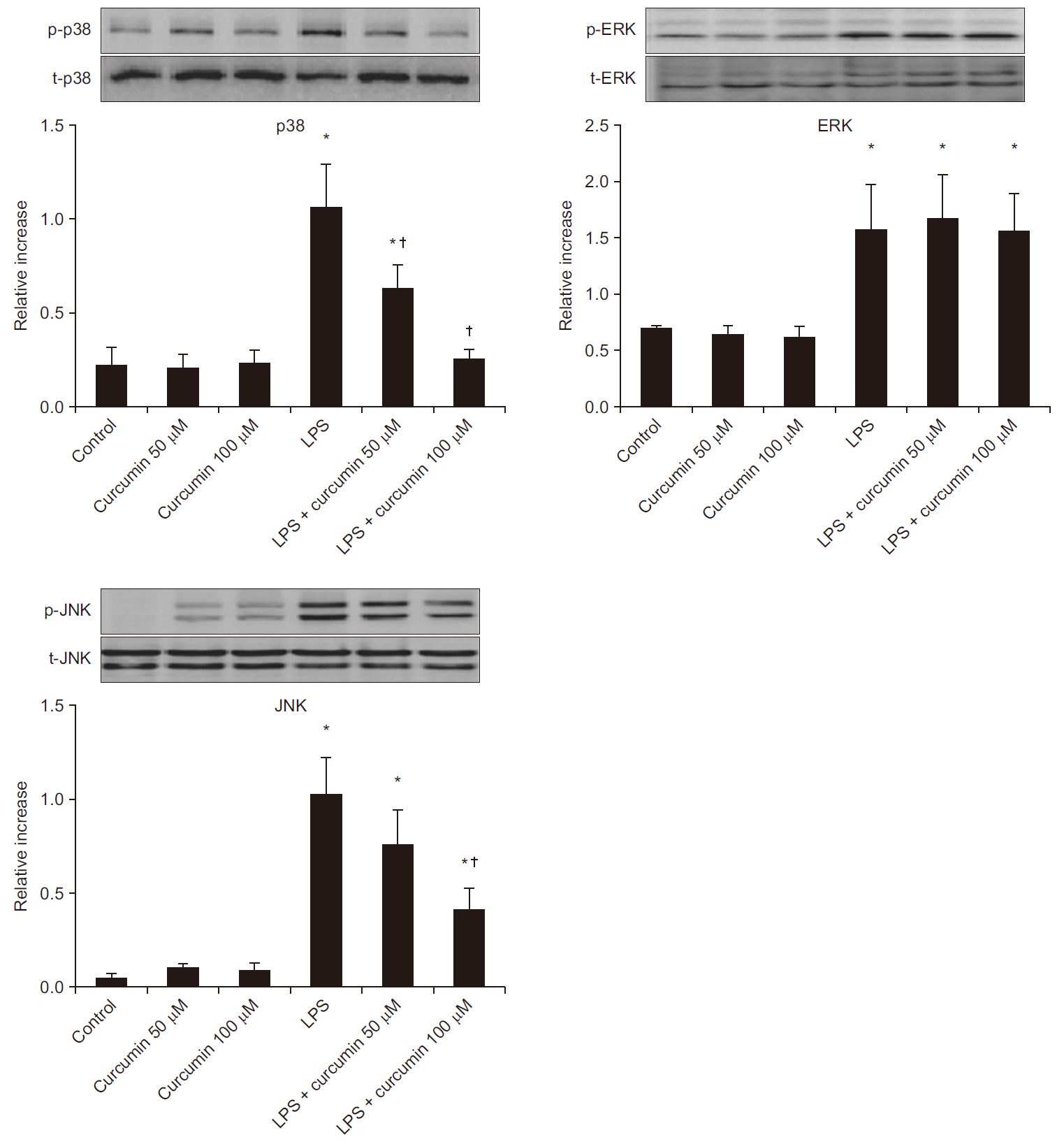
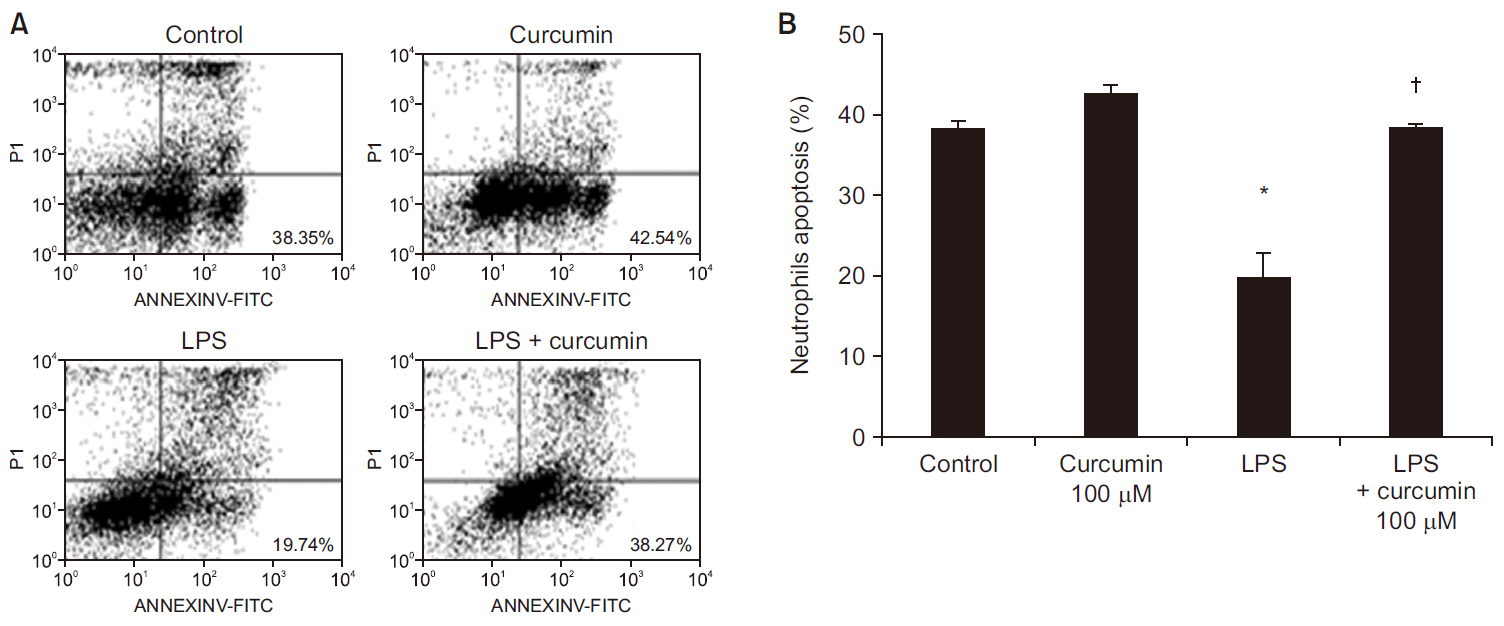
Curcumin attenuated expression of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 and the phosphorylation levels of p38 and JNK, but not ERK1/2, in LPS-stimulated neutrophils. Additionally, curcumin restored the delayed neutrophil apoptosis by LPS-stimulated neutrophils(19.7 ± 3.2 to 38.2 ± 0.5%, P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Our results reveal the underlying mechanism of how curcumin attenuate neutrophil activation and suggest potential clinic applications of curcumin supplementation for patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Additional clinical studies are required to confirm these in vitro findings.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
Singer M., Deutschman CS., Seymour CW., Shankar-Hari M., Annane D., Bauer M, et al. 2016. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 315:801–10. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. PMID: 26903338. PMCID: PMC4968574.Ferrer R., Martin-Loeches I., Phillips G., Osborn TM., Townsend S., Dellinger RP, et al. 2014. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit Care Med. 42:1749–55. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000330. PMID: 24717459.Rhee C., Dantes R., Epstein L., Murphy DJ., Seymour CW., Iwashyna TJ, et al. 2017. Incidence and trends of sepsis in US hospitals using clinical vs claims data, 2009-2014. JAMA. 318:1241–9. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2017.13836. PMID: 28903154. PMCID: PMC5710396.van Zanten AR AR., Brinkman S., Arbous MS., Abu-Hanna A., Levy MM., de Keizer NF NF. 2014. Guideline bundles adherence and mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 42:1890–8. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000297. PMID: 24670937.El Kebir D D., Filep JG. 2013. Targeting neutrophil apoptosis for enhancing the resolution of inflammation. Cells. 2:330–48. DOI: 10.3390/cells2020330. PMID: 24709704. PMCID: PMC3972676.Aomatsu K., Kato T., Fujita H., Hato F., Oshitani N., Kamata N, et al. 2008. Toll-like receptor agonists stimulate human neutrophil migration via activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases. Immunology. 123:171–80. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02684.x. PMID: 17662043. PMCID: 2433295.Chen L., Deng H., Cui H., Fang J., Zuo Z., Deng J, et al. 2017. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget. 9:7204–18. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.23208. PMID: 29467962. PMCID: 5805548.Chousterman BG., Swirski FK., Weber GF. 2017. Cytokine storm and sepsis disease pathogenesis. Semin Immunopathol. 39:517–28. DOI: 10.1007/s00281-017-0639-8. PMID: 28555385.Wang Y., Shan X., Dai Y., Jiang L., Chen G., Zhang Y, et al. 2015. Curcumin analog L48H37 prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced TLR4 signaling pathway activation and sepsis via targeting MD2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 353:539–50. DOI: 10.1124/jpet.115.222570. PMID: 25862641.Wu Y., Liu Z., Wu W., Lin S., Zhang N., Wang H, et al. 2018. Effects of FM0807, a novel curcumin derivative, on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory factor release via the ROS/JNK/p53 pathway in RAW264.7 cells. Biosci Rep. 38:BSR20180849. DOI: 10.1042/BSR20180849. PMID: 30249753. PMCID: PMC6200701.Camacho-Barquero L., Villegas I., Sánchez-Calvo JM., Talero E., Sánchez-Fidalgo S., Motilva V, et al. 2007. Curcumin, a curcuma longa constituent, acts on MAPK p38 pathway modulating COX-2 and iNOS expression in chronic experimental colitis. Int Immunopharmacol. 7:333–42. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2006.11.006. PMID: 17276891.Chen L., Lu Y., Zhao L., Hu L., Qiu Q., Zhang Z, et al. 2018. Curcumin attenuates sepsis-induced acute organ dysfunction by preventing inflammation and enhancing the suppressive function of Tregs. Int Immunopharmacol. 61:1–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.04.041. PMID: 29778842.Alves-Filho JC., Spiller F., Cunha FQ. 2010. Neutrophil paralysis in sepsis. Shock. 34(Suppl 1):15–21. DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181e7e61b. PMID: 20714263.Mitra S., Abraham E. 2006. Participation of superoxide in neutrophil activation and cytokine production. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1762:732–41. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2006.06.011. PMID: 16919916.Gaddipati JP., Sundar SV., Calemine J., Seth P., Sidhu GS., Maheshwari RK. 2003. Differential regulation of cytokines and transcription factors in liver by curcumin following hemorrhage/resuscitation. Shock. 19:150–6. DOI: 10.1097/00024382-200302000-00011. PMID: 12578124.Siddiqui AM., Cui X., Wu R., Dong W., Zhou M., Hu M, et al. 2006. The anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin in an experimental model of sepsis is mediated by up-regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Crit Care Med. 34:1874–82. DOI: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000221921.71300.BF. PMID: 16715036.Ventura JJ., Cogswell P., Flavell RA., Baldwin AS Jr., Davis RJ. 2004. JNK potentiates TNF-stimulated necrosis by increasing the production of cytotoxic reactive oxygen species. Genes Dev. 18:2905–15. DOI: 10.1101/gad.1223004. PMID: 15545623. PMCID: PMC534651.Matsuzawa A., Ichijo H. 2005. Stress-responsive protein kinases in redox-regulated apoptosis signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 7:472–81. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2005.7.472. PMID: 15706095.Jung WK., Ahn YW., Lee SH., Choi YH., Kim SK., Yea SS, et al. 2009. Ecklonia cava ethanolic extracts inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in BV2 microglia via the MAP kinase and NF-kappaB pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:410–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.11.041. PMID: 19111593.Hou RC., Chen YS., Chen CH., Chen YH., Jeng KC. 2006. Protective effect of 1,2,4-benzenetriol on LPS-induced NO production by BV2 microglial cells. J Biomed Sci. 13:89–99. DOI: 10.1007/s11373-005-9039-5. PMID: 16308662.Karunakaran S., Ravindranath V. 2009. Activation of p38 MAPK in the substantia nigra leads to nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB in MPTP-treated mice: implication in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 109:1791–9. DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06112.x. PMID: 19457134.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Selective Effects of Curcumin on CdSe/ZnS Quantum-dot-induced Phototoxicity Using UVA Irradiation in Normal Human Lymphocytes and Leukemia Cells
- Effects of Curcumin on Apoptosis in SW480 Human Colon Cancer Cell Line
- Role of heat shock protein 70 in regulation of anti-inflammatory response to curcumin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- Delayed Human Neutrophil Apoptosis by Trichomonas vaginalis Lysate
- Curcumin Enhances Docetaxel-Induced Apoptosis of 8505C Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma Cells