Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2017 Nov;21(6):625-632. 10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.6.625.
MPTP-induced vulnerability of dopamine neurons in A53T α-synuclein overexpressed mice with the potential involvement of DJ-1 downregulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Dongguk University, Seoul 04620, Korea.
- 2Research Institute, Dongkwang Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd., Seoul 04535, Korea.
- 3Department of Biomedical Sciences, Center for Creative Biomedical Scientists at Chonnam National University, Gwangju 61469, Korea. jsong0304@chonnam.ac.kr
- 4School of Biomedical Sciences, Charles Sturt University, Bathurst, NSW 2795, Australia.
- 5Department of Korean Medical Science, Graduate School of Korean Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 02447, Korea.
- 6Studies of Translational Acupuncture Research (STAR), Acupuncture & Meridian Science Research Center (AMSRC), Kyung Hee University, Seoul 02447, Korea.
- 7Department of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Dongguk University of Korea Medicine, Dongguk University Bundang Korean Medical Hospital, Seongnam 13601, Korea.
- KMID: 2395257
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.6.625
Abstract
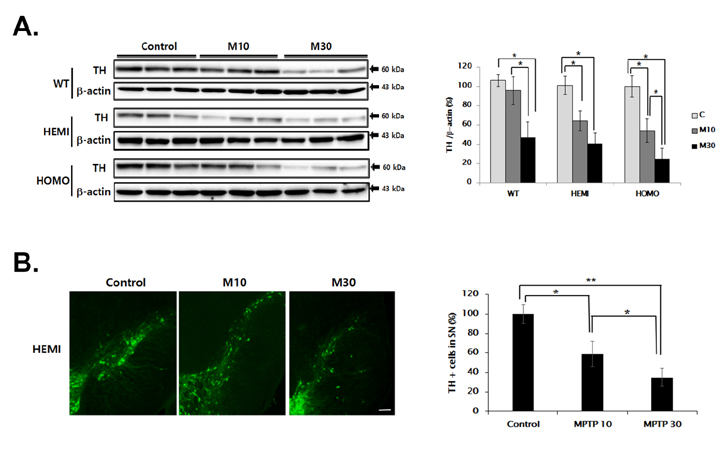
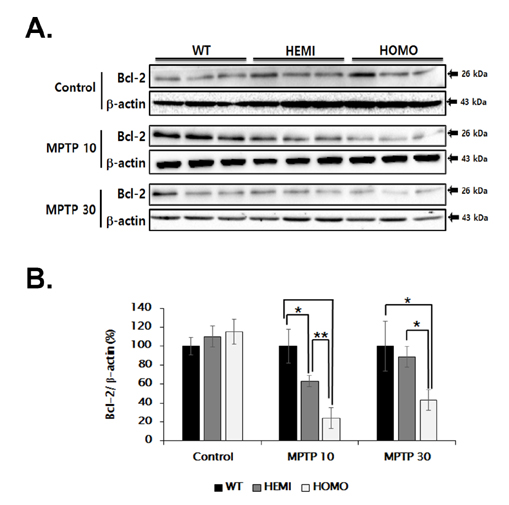
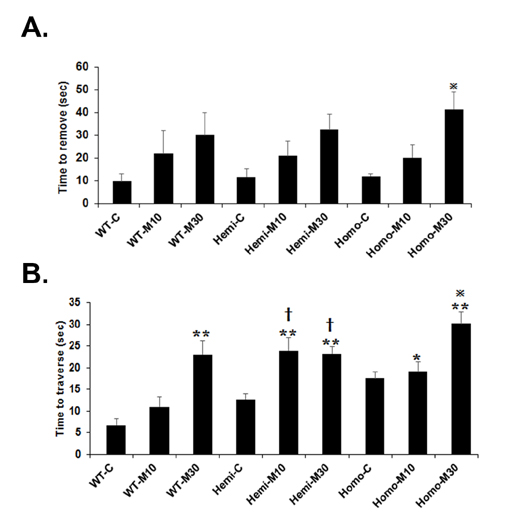
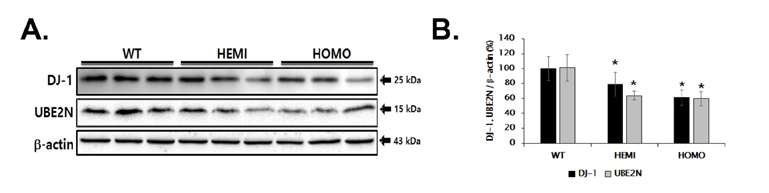
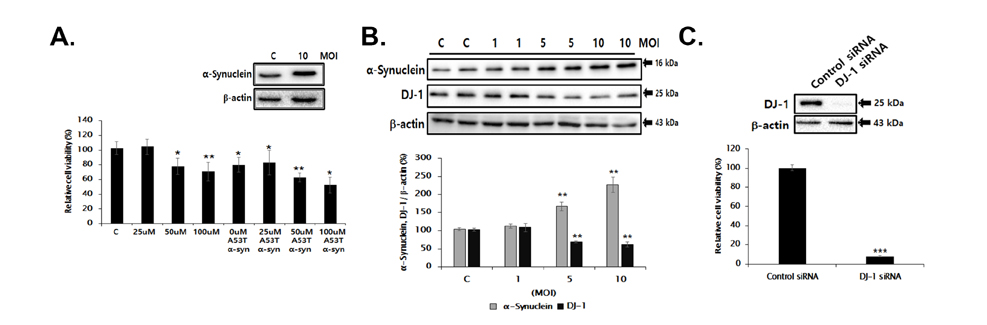
- Familial Parkinson's disease (PD) has been linked to point mutations and duplication of the α-synuclein (α-syn) gene. Mutant α-syn expression increases the vulnerability of neurons to exogenous insults. In this study, we developed a new PD model in the transgenic mice expressing mutant hemizygous (hemi) or homozygous (homo) A53T α-synuclein (α-syn Tg) and their wildtype (WT) littermates by treatment with sub-toxic (10 mg/kg, i.p., daily for 5 days) or toxic (30 mg/kg, i.p., daily for 5 days) dose of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). Tyrosine hydroxylase and Bcl-2 levels were reduced in the α-syn Tg but not WT mice by sub-toxic MPTP injection. In the adhesive removal test, time to remove paper was significantly increased only in the homo α-syn Tg mice. In the challenging beam test, the hemi and homo α-syn Tg mice spent significantly longer time to traverse as compared to that of WT group. In order to find out responsible proteins related with vulnerability of mutant α-syn expressed neurons, DJ-1 and ubiquitin enzyme expressions were examined. In the SN, DJ-1 and ubiquitin conjugating enzyme, UBE2N, levels were significantly decreased in the α-syn Tg mice. Moreover, A53T α-syn overexpression decreased DJ-1 expression in SH-SY5Y cells. These findings suggest that the vulnerability to oxidative injury such as MPTP of A53T α-syn mice can be explained by downregulation of DJ-1.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
Adhesives
Animals
Apoptosis
Dopamine*
Dopaminergic Neurons*
Down-Regulation*
Hominidae
Humans
Mice*
Mice, Transgenic
Neurons
Parkinson Disease
Point Mutation
Synucleins
Tyrosine 3-Monooxygenase
Ubiquitin
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
Adhesives
Dopamine
Synucleins
Tyrosine 3-Monooxygenase
Ubiquitin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Habibi E, Masoudi-Nejad A, Abdolmaleky HM, Haggarty SJ. Emerging roles of epigenetic mechanisms in Parkinson's disease. Funct Integr Genomics. 2011; 11:523–537.2. Jenner P, Olanow CW. Understanding cell death in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 1998; 44:3 Suppl 1. S72–S84.3. de Silva HR, Khan NL, Wood NW. The genetics of Parkinson's disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2000; 10:292–298.4. Iwai A, Masliah E, Yoshimoto M, Ge N, Flanagan L, de Silva HA, Kittel A, Saitoh T. The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer's disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron. 1995; 14:467–475.5. Krüger R, Kuhn W, Müller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kösel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schöls L, Riess O. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nat Genet. 1998; 18:106–108.6. Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science. 1997; 276:2045–2047.7. van der Putten H, Wiederhold KH, Probst A, Barbieri S, Mistl C, Danner S, Kauffmann S, Hofele K, Spooren WP, Ruegg MA, Lin S, Caroni P, Sommer B, Tolnay M, Bilbe G. Neuropathology in mice expressing human alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci. 2000; 20:6021–6029.8. Matsuoka Y, Vila M, Lincoln S, McCormack A, Picciano M, LaFrancois J, Yu X, Dickson D, Langston WJ, McGowan E, Farrer M, Hardy J, Duff K, Przedborski S, Di Monte DA. Lack of nigral pathology in transgenic mice expressing human alpha-synuclein driven by the tyrosine hydroxylase promoter. Neurobiol Dis. 2001; 8:535–539.9. Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Vol. 1. 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Harbor Laboratory Press;1989. p. 11.10. Feany MB, Bender WW. A Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Nature. 2000; 404:394–398.11. Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Takeda A, Sagara Y, Sisk A, Mucke L. Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science. 2000; 287:1265–1269.12. Richfield EK, Thiruchelvam MJ, Cory-Slechta DA, Wuertzer C, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG, Di Monte DA, Federoff HJ. Behavioral and neurochemical effects of wild-type and mutated human alphasynuclein in transgenic mice. Exp Neurol. 2002; 175:35–48.13. Bonini NM, Giasson BI. Snaring the function of alpha-synuclein. Cell. 2005; 123:359–361.14. Scott DA, Tabarean I, Tang Y, Cartier A, Masliah E, Roy S. A pathologic cascade leading to synaptic dysfunction in alpha-synucleininduced neurodegeneration. J Neurosci. 2010; 30:8083–8095.15. Gómez-Santos C, Ferrer I, Reiriz J, Viñals F, Barrachina M, Ambrosio S. MPP+ increases alpha-synuclein expression and ERK/MAP-kinase phosphorylation in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Brain Res. 2002; 935:32–39.16. Ko L, Mehta ND, Farrer M, Easson C, Hussey J, Yen S, Hardy J, Yen SH. Sensitization of neuronal cells to oxidative stress with mutated human alpha-synuclein. J Neurochem. 2000; 75:2546–2554.17. Canet-Avilés RM, Wilson MA, Miller DW, Ahmad R, McLendon C, Bandyopadhyay S, Baptista MJ, Ringe D, Petsko GA, Cookson MR. The Parkinson's disease protein DJ-1 is neuroprotective due to cysteine-sulfinic acid-driven mitochondrial localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:9103–9108.18. Shendelman S, Jonason A, Martinat C, Leete T, Abeliovich A. DJ-1 is a redox-dependent molecular chaperone that inhibits alphasynuclein aggregate formation. PLoS Biol. 2004; 2:e362.19. Zhou W, Bercury K, Cummiskey J, Luong N, Lebin J, Freed CR. Phenylbutyrate up-regulates the DJ-1 protein and protects neurons in cell culture and in animal models of Parkinson disease. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286:14941–14951.20. Sun SY, An CN, Pu XP. DJ-1 protein protects dopaminergic neurons against 6-OHDA/MG-132-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Brain Res Bull. 2012; 88:609–616.21. Rockenstein E, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Song D, Shults CW, Lang I, Masliah E. Differential neuropathological alterations in transgenic mice expressing alpha-synuclein from the platelet-derived growth factor and Thy-1 promoters. J Neurosci Res. 2002; 68:568–578.22. Lu J, Sun F, Ma H, Qing H, Deng Y. Comparison between α-synuclein wild-type and A53T mutation in a progressive Parkinson's disease model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015; 464:988–993.23. Burke RE, O'Malley K. Axon degeneration in Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol. 2013; 246:72–83.24. Chau YP, Lin SY, Chen JH, Tai MH. Endostatin induces autophagic cell death in EAhy926 human endothelial cells. Histol Histopathol. 2003; 18:715–726.25. Kanda S, Bishop JF, Eglitis MA, Yang Y, Mouradian MM. Enhanced vulnerability to oxidative stress by alpha-synuclein mutations and C-terminal truncation. Neuroscience. 2000; 97:279–284.26. Lee FJ, Liu F, Pristupa ZB, Niznik HB. Direct binding and functional coupling of alpha-synuclein to the dopamine transporters accelerate dopamine-induced apoptosis. FASEB J. 2001; 15:916–926.27. Nieto M, Gil-Bea FJ, Dalfó E, Cuadrado M, Cabodevilla F, Sánchez B, Catena S, Sesma T, Ribé E, Ferrer I, Ramírez MJ, Gómez-Isla T. Increased sensitivity to MPTP in human alpha-synuclein A30P transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2006; 27:848–856.28. Przedborski S, Chen Q, Vila M, Giasson BI, Djaldatti R, Vukosavic S, Souza JM, Jackson-Lewis V, Lee VM, Ischiropoulos H. Oxidative post-translational modifications of alpha-synuclein in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) mouse model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 2001; 76:637–640.29. Song DD, Shults CW, Sisk A, Rockenstein E, Masliah E. Enhanced substantia nigra mitochondrial pathology in human alpha-synuclein transgenic mice after treatment with MPTP. Exp Neurol. 2004; 186:158–172.30. Rathke-Hartlieb S, Kahle PJ, Neumann M, Ozmen L, Haid S, Okochi M, Haass C, Schulz JB. Sensitivity to MPTP is not increased in Parkinson's disease-associated mutant alpha-synuclein transgenic mice. J Neurochem. 2001; 77:1181–1184.31. Yu WH, Matsuoka Y, Sziráki I, Hashim A, Lafrancois J, Sershen H, Duff KE. Increased dopaminergic neuron sensitivity to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in transgenic mice expressing mutant A53T alpha-synuclein. Neurochem Res. 2008; 33:902–911.32. Liu FT, Yang YJ, Wu JJ, Li S, Tang YL, Zhao J, Liu ZY, Xiao BG, Zuo J, Liu W, Wang J. Fasudil, a Rho kinase inhibitor, promotes the autophagic degradation of A53T α-synuclein by activating the JNK 1/Bcl-2/beclin 1 pathway. Brain Res. 2016; 1632:9–18.33. Zondler L, Miller-Fleming L, Repici M, Gonçalves S, Tenreiro S, Rosado-Ramos R, Betzer C, Straatman KR, Jensen PH, Giorgini F, Outeiro TF. DJ-1 interactions with α-synuclein attenuate aggregation and cellular toxicity in models of Parkinson's disease. Cell Death Dis. 2014; 5:e1350.34. Nijholt DA, De Kimpe L, Elfrink HL, Hoozemans JJ, Scheper W. Removing protein aggregates: the role of proteolysis in neurodegeneration. Curr Med Chem. 2011; 18:2459–2476.35. Ciechanover A. Proteolysis: from the lysosome to ubiquitin and the proteasome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005; 6:79–87.36. Rubinsztein DC. The roles of intracellular protein-degradation pathways in neurodegeneration. Nature. 2006; 443:780–786.37. Cook C, Stetler C, Petrucelli L. Disruption of protein quality control in Parkinson's disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012; 2:a009423.38. Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992; 61:761–807.39. Marques C, Pereira P, Taylor A, Liang JN, Reddy VN, Szweda LI, Shang F. Ubiquitin-dependent lysosomal degradation of the HNEmodified proteins in lens epithelial cells. FASEB J. 2004; 18:1424–1426.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Subdiaphragmatic Vagotomy in the MPTP-induced Neurotoxicity in the Striatum and Colon of Mice
- Transmission of Synucleinopathies in the Enteric Nervous System of A53T Alpha-Synuclein Transgenic Mice
- Bee venom phospholipase A2 ameliorates motor dysfunction and modulates microglia activation in Parkinson's disease alpha-synuclein transgenic mice
- Effects of a Silkworm Extract on Dopamine and Monoamine Oxidase-B Activity in an MPTP-induced Parkinsons Disease Model
- L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia in a Genetic Drosophila Model of Parkinson’s Disease