Korean J Urol.
2011 Dec;52(12):852-857.
Comparison of Human Muscle-Derived Stem Cells and Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in Neurogenic Trans-Differentiation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Ltd. Seoul, Korea. uroljy@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Stem Cell Research Center, RNL Bio Co., Ltd. Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Erectile dysfunction (ED) remains a major complication from cavernous nerve injury during radical prostatectomy. Recently, stem cell treatment for ED has been widely reported. This study was conducted to investigate the availability, differentiation into functional cells, and potential of human muscle-derived stem cells (hMDSCs) and human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) for ED treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We compared the neural differentiation of hMDSCs and hADSCs. Human muscle and adipose tissues were digested with collagenase, followed by filtering and centrifugation. For neural induction, isolated hMDSCs and hADSCs were incubated in neurobasal media containing forskolin, laminin, basic-fibroblast growth factor, and epidermal growth factor for 5 days. Following neural induction, hMDSCs and hADSCs were differentiated into neural cells, including neurons and glia, in vitro.
RESULTS
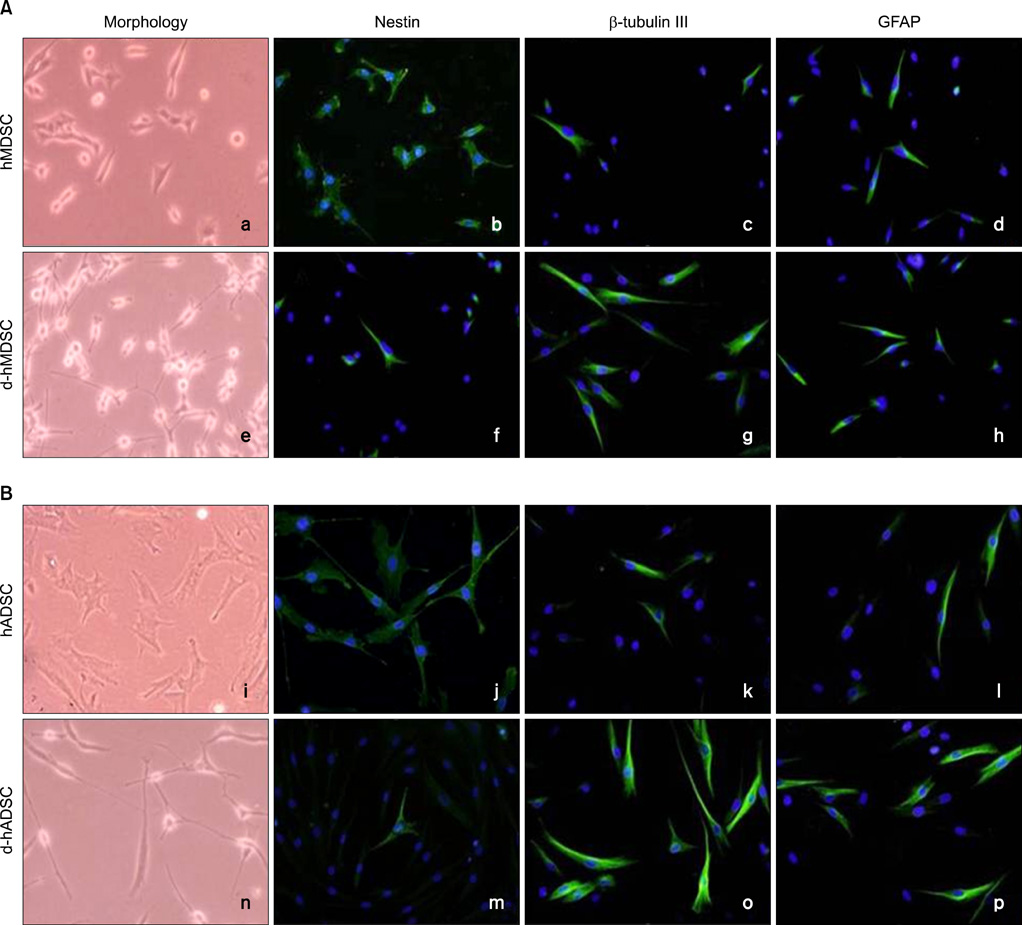
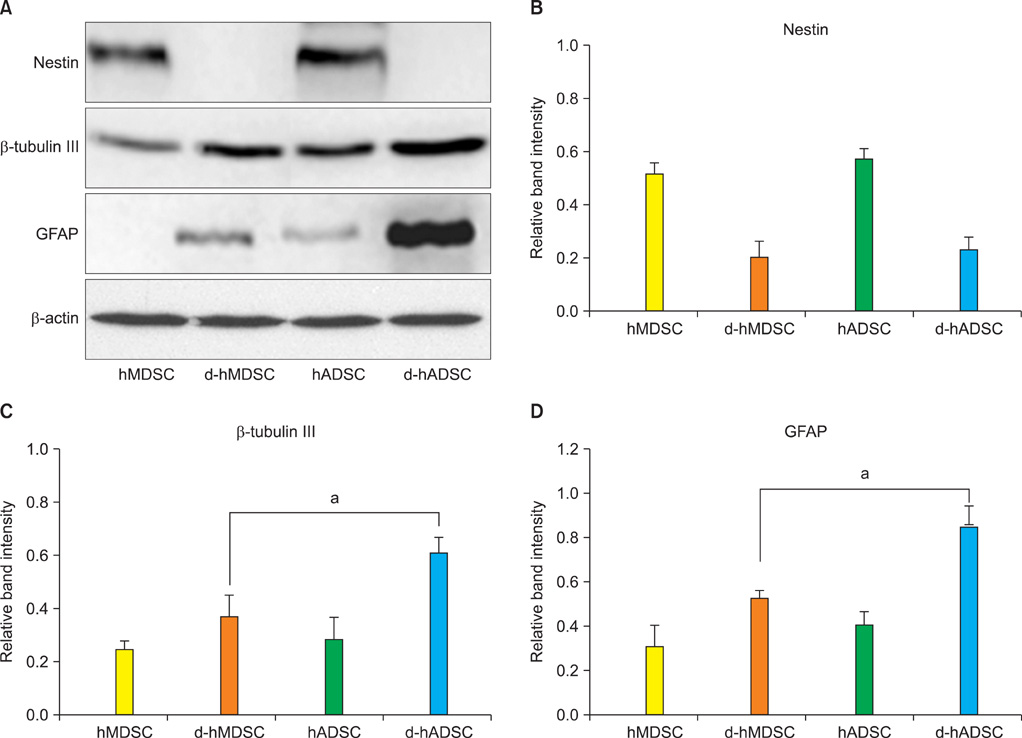
In neural differentiated hMDSCs (d-hMDSCs) and differentiated hADSCs (d-hADSCs), neural stem cell marker (nestin) showed a significant decrease by immunocytochemistry, and neuronal marker (beta-tubulin III) and glial marker (GFAP) showed a significant increase, compared with primary hMDSCs and hADSCs. Real-time chain reaction analysis and Western blotting demonstrated significantly elevated levels of mRNA and protein of beta-tubulin III and GFAP in d-hADSCs compared with d-hMDSCs.
CONCLUSIONS
We demonstrated that hMDSCs and hADSCs can be induced to undergo phenotypic and molecular changes consistent with neurons. The neural differentiation capacity of hADSCs was better than that of hMDSCs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adipose Tissue
Blotting, Western
Caves
Cell Differentiation
Centrifugation
Collagenases
Epidermal Growth Factor
Erectile Dysfunction
Forskolin
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Laminin
Male
Muscles
Neural Stem Cells
Neuroglia
Neurons
Prostatectomy
RNA, Messenger
Stem Cells
Tubulin
Collagenases
Epidermal Growth Factor
Forskolin
Laminin
RNA, Messenger
Tubulin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lin G, Banie L, Ning H, Bella AJ, Lin CS, Lue TF. Potential of adipose-derived stem cells for treatment of erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2009. 6:Suppl 3. 320–327.2. Zurita M, Vaquero J, Oya S, Bonilla C, Aguayo C. Neurotrophic schwann-cell factors induce neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Neuroreport. 2007. 18:1713–1717.3. Zurita M, Bonilla C, Otero L, Aguayo C, Vaquero J. Neural transdifferentiation of bone marrow stromal cells obtained by chemical agents is a short-time reversible phenomenon. Neurosci Res. 2008. 60:275–280.4. Nolazco G, Kovanecz I, Vernet D, Gelfand RA, Tsao J, Ferrini MG, et al. Effect of muscle-derived stem cells on the restoration of corpora cavernosa smooth muscle and erectile function in the aged rat. BJU Int. 2008. 101:1156–1164.5. Strem BM, Hicok KC, Zhu M, Wulur I, Alfonso Z, Schreiber RE, et al. Multipotential differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Keio J Med. 2005. 54:132–141.6. Krampera M, Marconi S, Pasini A, Galiè M, Rigotti G, Mosna F, et al. Induction of neural-like differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, fat, spleen and thymus. Bone. 2007. 40:382–390.7. Alessandri G, Pagano S, Bez A, Benetti A, Pozzi S, Iannolo G, et al. Isolation and culture of human muscle-derived stem cells able to differentiate into myogenic and neurogenic cell lineages. Lancet. 2004. 364:1872–1883.8. Jiang Y, Vaessen B, Lenvik T, Blackstad M, Reyes M, Verfaillie CM. Multipotent progenitor cells can be isolated from postnatal murine bone marrow, muscle, and brain. Exp Hematol. 2002. 30:896–904.9. Casteilla L, Dani C. Adipose tissue derived cells: from physiology to regenerative medicine. Diabetes Metab. 2006. 32:393–401.10. Safford KM, Hicok KC, Safford SD, Halvorsen YD, Wilkison WO, Gimble JM, et al. Neurogenic differentiation of murine and human adipose-derived stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. 294:371–379.11. Schultz SS, Lucas PA. Human stem cells isolated from adult skeletal muscle differentiate into neural phenotypes. J Neurosci Methods. 2006. 152:144–155.12. Jiang L, Zhu JK, Liu XL, Xiang P, Hu J, Yu WH. Differentiation of rat adipose tissue derived stem cells into Schwann-like cells in vitro. Neuroreport. 2008. 19:1015–1019.13. Zavan B, Michelotto L, Lancerotto L, Della Puppa A, D'Avella D, Abatangelo G, et al. Neural potential of a stem cell population in the adipose and cutaneous tissues. Neurol Res. 2010. 32:47–54.14. Vourc'h P, Romero-Ramos M, Chivatakarn O, Young HE, Lucas PA, El-Kalay M, et al. Isolation and characterization of cells with neurogenic potential from adult skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. 317:893–901.15. Kingham PJ, Kalbermatten DF, Mahay D, Armstrong SJ, Wiberg M, Terenghi G. Adipose-derived stem cells differentiate into a schwann cell phenotype and promote neurite outgrowth in vitro. Exp Neurol. 2007. 207:267–274.16. Safford KM, Safford SD, Gimble JM, Shetty AK, Rice HE. Characterization of neuronal/glial differentiation of murine adipose-derived adult stromal cells. Exp Neurol. 2004. 187:319–328.17. Xu Y, Liu L, Li Y, Zhou C, Xiong F, Liu Z, et al. Myelin-forming ability of schwann cell-like cells induced from rat adipose-derived stem cells in vitro. Brain Res. 2008. 1239:49–55.18. Romero-Ramos M, Vourc'h P, Young HE, Lucas PA, Wu Y, Chivatakarn O, et al. Neuronal differentiation of stem cells isolated from adult muscle. J Neurosci Res. 2002. 69:894–907.19. Xu Y, Liu Z, Liu L, Zhao C, Xiong F, Zhou C, et al. Neurospheres from rat adipose-derived stem cells could be induced into functional Schwann cell-like cells in vitro. BMC Neurosci. 2008. 9:21.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells into Schwann-like cells: fetal bovine serum or human serum?
- Adipose-derived stem cells: characterization and clinical application
- The Rapid Establishment of Human Clonal Adipose Derived Stem Cell (hADSC) Lines with Aspirated Adipose Tissue
- Concise Review: Differentiation of Human Adult Stem Cells Into Hepatocyte-like Cells In vitro
- Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-derived Stem Cells within PLGA(Poly(D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid)) Scaffold in the Nude Mouse