Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2015 Nov;19(6):507-514. 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.6.507.
Nitric Oxide-Induced Autophagy in MC3T3-E1 Cells is Associated with Cytoprotection via AMPK Activation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Physiology, Dental Science Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 61186, Korea. jjy@jnu.ac.kr, wjkim@jnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral Anatomy, Dental Science Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 61186, Korea.
- 3Department of Oral Medicine, Dental Science Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 61186, Korea.
- KMID: 2070790
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.6.507
Abstract
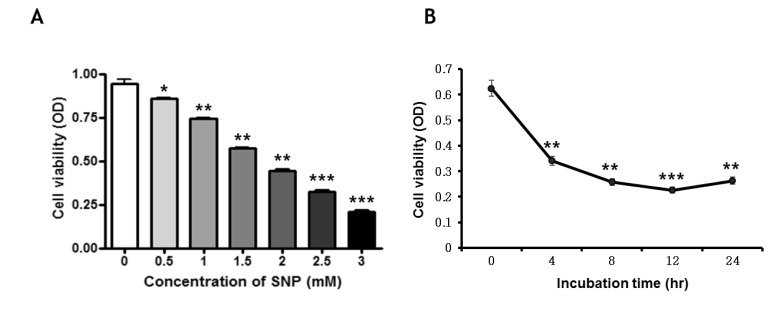
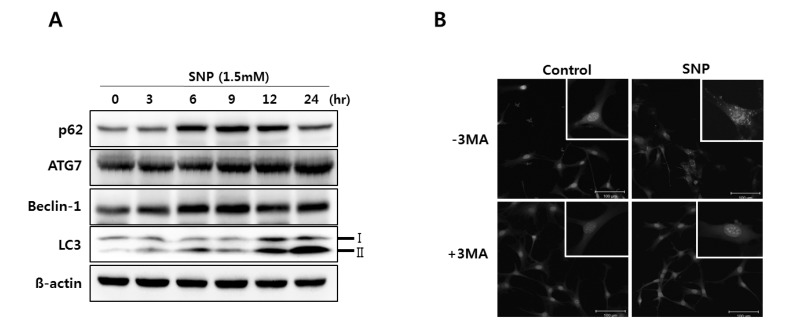
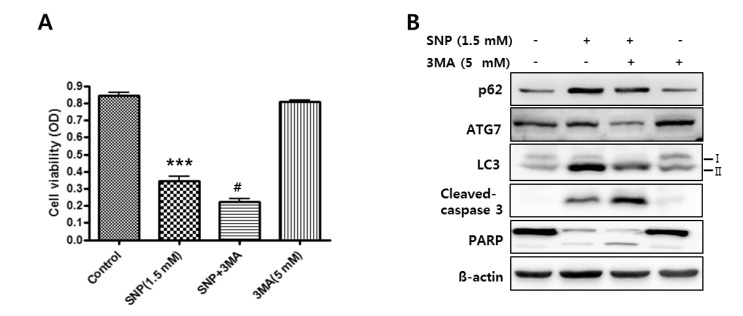
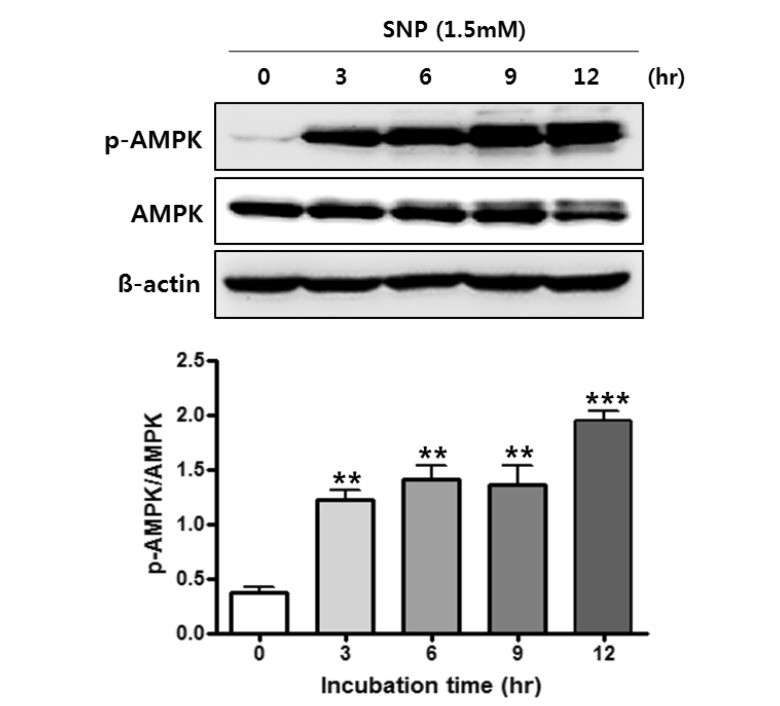
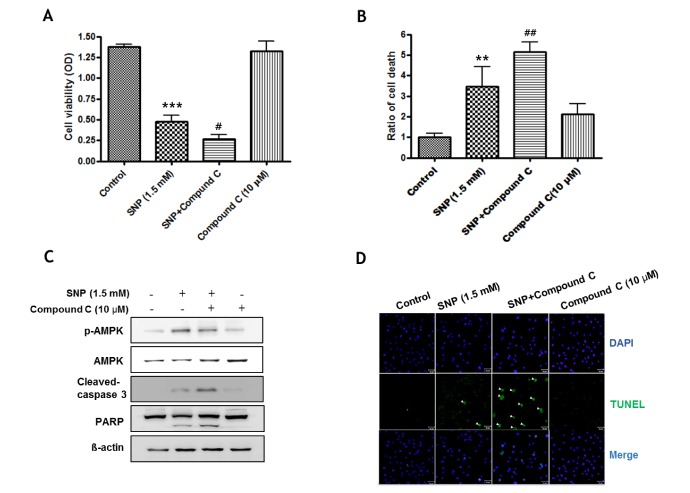
- Nitric oxide (NO) is important in the regulation of bone remodeling, whereas high concentration of NO promotes cell death of osteoblast. However, it is not clear yet whether NO-induced autophagy is implicated in cell death or survival of osteoblast. The present study is aimed to examine the role of NO-induced autophagy in the MC3T3-E1 cells and their underlying molecular mechanism. The effect of sodium nitroprusside (SNP), an NO donor, on the cytotoxicity of the MC3T3-E1 cells was determined by MTT assay and expression of apoptosis or autophagy associated molecules was evaluated by western blot analysis. The morphological observation of autophagy and apoptosis by acridine orange stain and TUNEL assay were performed, respectively. Treatment of SNP decreased the cell viability of the MC3T3-E1 cells in dose- and time-dependent manner. SNP increased expression levels of p62, ATG7, Beclin-1 and LC3-II, as typical autophagic markers and augmented acidic autophagolysosomal vacuoles, detected by acridine orange staining. However, pretreatment with 3-methyladenine (3MA), the specific inhibitor for autophagy, decreased cell viability, whereas increased the cleavage of PARP and caspase-3 in the SNP-treated MC3T3-E1 cells. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a major autophagy regulatory kinase, was activated in SNP-treated MC3T3-E1 cells. In addition, pretreatment with compound C, an inhibitor of AMPK, decreased cell viability, whereas increased the number of apoptotic cells, cleaved PARP and caspase-3 levels compared to those of SNP-treated MC3T3-E1 cells. Taken together, it is speculated that NO-induced autophagy functions as a survival mechanism via AMPK activation against apoptosis in the MC3T3-E1 cells.
MeSH Terms
-
Acridine Orange
AMP-Activated Protein Kinases*
Apoptosis
Autophagy*
Blotting, Western
Bone Remodeling
Caspase 3
Cell Death
Cell Survival
Cytoprotection*
Humans
In Situ Nick-End Labeling
Nitric Oxide
Nitroprusside
Osteoblasts
Phosphotransferases
Tissue Donors
Vacuoles
AMP-Activated Protein Kinases
Acridine Orange
Caspase 3
Nitric Oxide
Nitroprusside
Phosphotransferases
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Novel functional roles of caspase-related genes in the regulation of apoptosis and autophagy
Ju-Hyun Shin, Sang-Hyun Min
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;20(6):573-580. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.6.573.Novel functional roles of caspase-related genes in the regulation of apoptosis and autophagy
Ju-Hyun Shin, Sang-Hyun Min
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;20(6):573-580. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.6.573.
Reference
-
1. Armour KE, Van'T Hof RJ, Grabowski PS, Reid DM, Ralston SH. Evidence for a pathogenic role of nitric oxide in inflamm ation-induced osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 1999; 14:2137–2142. PMID: 10620073.2. Andrew PJ, Mayer B. Enzymatic function of nitric oxide synthases. Cardiovasc Res. 1999; 43:521–531. PMID: 10690324.
Article3. Korhonen R, Lahti A, Kankaanranta H, Moilanen E. Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2005; 4:471–479. PMID: 16101524.
Article4. Albina JE, Cui S, Mateo RB, Reichner JS. Nitric oxide-mediated apoptosis in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1993; 150:5080–5085. PMID: 7684418.5. Tanaka Y, Nakayamada S, Okada Y. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling and inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2005; 4:325–328. PMID: 16101541.
Article6. Son MJ, Lee SB, Byun YJ, Lee HO, Kim HS, Kwon OJ, Jeong SW. Sodium nitroprusside induces autophagic cell death in glutathione-depleted osteoblasts. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2010; 24:313–322. PMID: 20201107.
Article7. Evans DM, Ralston SH. Nitric oxide and bone. J Bone Miner Res. 1996; 11:300–305. PMID: 8852940.
Article8. Collin-Osdoby P, Nickols GA, Osdoby P. Bone cell function, regulation, and communication: a role for nitric oxide. J Cell Biochem. 1995; 57:399–408. PMID: 7539433.
Article9. van't Hof RJ, Ralston SH. Nitric oxide and bone. Immunology. 2001; 103:255–261. PMID: 11454054.10. Damoulis PD, Hauschka PV. Cytokines induce nitric oxide production in mouse osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994; 201:924–931. PMID: 8003032.
Article11. Löwik CW, Nibbering PH, van de Ruit M, Papapoulos SE. Inducible production of nitric oxide in osteoblast-like cells and in fetal mouse bone explants is associated with suppression of osteoclastic bone resorption. J Clin Invest. 1994; 93:1465–1472. PMID: 8163651.
Article12. Ralston SH, Todd D, Helfrich M, Benjamin N, Grabowski PS. Human osteoblast-like cells produce nitric oxide and express inducible nitric oxide synthase. Endocrinology. 1994; 135:330–336. PMID: 7516867.
Article13. Hukkanen M, Hughes FJ, Buttery LD, Gross SS, Evans TJ, Seddon S, Riveros-Moreno V, Macintyre I, Polak JM. Cytokine-stimulated expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase by mouse, rat, and human osteoblast-like cells and its functional role in osteoblast metabolic activity. Endocrinology. 1995; 136:5445–5453. PMID: 7588294.
Article14. Riancho JA, Salas E, Zarrabeitia MT, Olmos JM, Amado JA, Fernández-Luna JL, González-Macías J. Expression and functional role of nitric oxide synthase in osteoblast-like cells. J Bone Miner Res. 1995; 10:439–446. PMID: 7540349.
Article15. Sudo H, Kodama HA, Amagai Y, Yamamoto S, Kasai S. In vitro differentiation and calcification in a new clonal osteogenic cell line derived from newborn mouse calvaria. J Cell Biol. 1983; 96:191–198. PMID: 6826647.
Article16. Brandi ML, Hukkanen M, Umeda T, Moradi-Bidhendi N, Bianchi S, Gross SS, Polak JM, MacIntyre I. Bidirectional regulation of osteoclast function by nitric oxide synthase isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995; 92:2954–2958. PMID: 7535933.
Article17. Ralston SH, Ho LP, Helfrich MH, Grabowski PS, Johnston PW, Benjamin N. Nitric oxide: a cytokine-induced regulator of bone resorption. J Bone Miner Res. 1995; 10:1040–1049. PMID: 7484279.
Article18. Glick D, Barth S, Macleod KF. Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 2010; 221:3–12. PMID: 20225336.
Article19. Tallóczy Z, Jiang W, Virgin HW 4th, Leib DA, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Eskelinen EL, Levine B. Regulation of starvation- and virus-induced autophagy by the eIF2alpha kinase signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002; 99:190–195. PMID: 11756670.20. Kanzawa T, Germano IM, Komata T, Ito H, Kondo Y, Kondo S. Role of autophagy in temozolomide-induced cytotoxicity for malignant glioma cells. Cell Death Differ. 2004; 11:448–457. PMID: 14713959.
Article21. Kanzawa T, Kondo Y, Ito H, Kondo S, Germano I. Induction of autophagic cell death in malignant glioma cells by arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res. 2003; 63:2103–2108. PMID: 12727826.22. Paglin S, Hollister T, Delohery T, Hackett N, McMahill M, Sphicas E, Domingo D, Yahalom J. A novel response of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy and formation of acidic vesicles. Cancer Res. 2001; 61:439–444. PMID: 11212227.23. Debnath J, Baehrecke EH, Kroemer G. Does autophagy contribute to cell death? Autophagy. 2005; 1:66–74. PMID: 16874022.
Article24. Yang J, Wu LJ, Tashino S, Onodera S, Ikejima T. Reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide regulate mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and autophagy in evodiamine-treated human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells. Free Radic Res. 2008; 42:492–504. PMID: 18484413.
Article25. Mizushima N, Komatsu M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 2011; 147:728–741. PMID: 22078875.
Article26. Gutierrez MG, Master SS, Singh SB, Taylor GA, Colombo MI, Deretic V. Autophagy is a defense mechanism inhibiting BCG and Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival in infected macrophages. Cell. 2004; 119:753–766. PMID: 15607973.
Article27. Bjørkøy G, Lamark T, Pankiv S, Øvervatn A, Brech A, Johansen T. Monitoring autophagic degradation of p62/SQSTM1. Methods Enzymol. 2009; 452:181–197. PMID: 19200883.28. Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A, Kroemer G. Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007; 8:741–752. PMID: 17717517.
Article29. Fimia GM, Piacentini M. Regulation of autophagy in mammals and its interplay with apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010; 67:1581–1588. PMID: 20165902.
Article30. Rubinstein AD, Kimchi A. Life in the balance - a mechanistic view of the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. J Cell Sci. 2012; 125:5259–5268. PMID: 23377657.
Article31. Kaminskyy VO, Zhivotovsky B. Free radicals in cross talk between autophagy and apoptosis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014; 21:86–102. PMID: 24359220.
Article32. Zeng R, He J, Peng J, Chen Y, Yi S, Zhao F, Cui G. The time-dependent autophagy protects against apoptosis with possible involvement of Sirt1 protein in multiple myeloma under nutrient depletion. Ann Hematol. 2012; 91:407–417. PMID: 21915620.
Article33. Thorburn J, Andrysik Z, Staskiewicz L, Gump J, Maycotte P, Oberst A, Green DR, Espinosa JM, Thorburn A. Autophagy controls the kinetics and extent of mitochondrial apoptosis by regulating PUMA levels. Cell Rep. 2014; 7:45–52. PMID: 24685133.
Article34. Cervia D, Perrotta C, Moscheni C, De Palma C, Clementi E. Nitric oxide and sphingolipids control apoptosis and autophagy with a significant impact on Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013; 27(2 Suppl):11–22. PMID: 24813312.35. Shen C, Yan J, Erkocak OF, Zheng XF, Chen XD. Nitric oxide inhibits autophagy via suppression of JNK in meniscal cells. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014; 53:1022–1033. PMID: 24501244.
Article36. Cui S, Reichner JS, Mateo RB, Albina JE. Activated murine macrophages induce apoptosis in tumor cells through nitric oxide-dependent or -independent mechanisms. Cancer Res. 1994; 54:2462–2467. PMID: 8162595.37. Chen RM, Liu HC, Lin YL, Jean WC, Chen JS, Wang JH. Nitric oxide induces osteoblast apoptosis through the de novo synthesis of Bax protein. J Orthop Res. 2002; 20:295–302. PMID: 11918309.
Article38. Wu GJ, Chen TG, Chang HC, Chiu WT, Chang CC, Chen RM. Nitric oxide from both exogenous and endogenous sources activates mitochondria-dependent events and induces insults to human chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2007; 101:1520–1531. PMID: 17492650.
Article39. Scherz-Shouval R, Elazar Z. ROS, mitochondria and the regulation of autophagy. Trends Cell Biol. 2007; 17:422–427. PMID: 17804237.
Article40. Murad F. Shattuck Lecture. Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP in cell signaling and drug development. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:2003–2011. PMID: 17093251.41. da Silva LP, Issa JP, Del Bel EA. Action of nitric oxide on healthy and inflamed human dental pulp tissue. Micron. 2008; 39:797–801. PMID: 18337111.
Article42. Kawanishi HN, Kawashima N, Suzuki N, Suda H, Takagi M. Effects of an inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on experimentally induced rat pulpitis. Eur J Oral Sci. 2004; 112:332–337. PMID: 15279652.
Article43. Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, Behrmann I, Germer M, Pawlita M, Krammer PH, Peter ME. Cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor. EMBO J. 1995; 14:5579–5588. PMID: 8521815.
Article44. He H, Feng YS, Zang LH, Liu WW, Ding LQ, Chen LX, Kang N, Hayashi T, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Qiu F, Ikejima T. Nitric oxide induces apoptosis and autophagy; autophagy down-regulates NO synthesis in physalin A-treated A375-S2 human melanoma cells. Food Chem Toxi. 2014; 71:128–135.
Article45. Paglin S, Hollister T, Delohery T, Hackett N, McMahill M, Sphicas E, Domingo D, Yahalom J. A novel response of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy and formation of acidic vesicles. Cancer Res. 2001; 61:439–444. PMID: 11212227.46. Jones RG. The roles, mechanisms, and controversies of autophagy in mammalian biology. F1000 Biol Rep. 2009; 1:68–73. PMID: 20948619.
Article47. Hamacher-Brady A, Brady NR, Gottlieb RA. Enhancing macroautophagy protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:29776–29787. PMID: 16882669.
Article48. Ravikumar B, Vacher C, Berger Z, Davies JE, Luo S, Oroz LG, Scaravilli F, Easton DF, Duden R, O'Kane CJ, Rubinsztein DC. Inhibition of mTOR induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease. Nat Genet. 2004; 36:585–595. PMID: 15146184.
Article49. Hardie DG. The AMP-activated protein kinase pathway--new players upstream and downstream. J Cell Sci. 2004; 117:5479–5487. PMID: 15509864.50. Mihaylova MM, Shaw RJ. The AMPK signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 2011; 13:1016–1023. PMID: 21892142.
Article51. Wang RC, Wei Y, An Z, Zou Z, Xiao G, Bhagat G, White M, Reichelt J, Levine B. Akt-mediated regulation of autophagy and tumorigenesis through Beclin 1 phosphorylation. Science. 2012; 338:956–959. PMID: 23112296.
Article52. Zhang J, Xie Z, Dong Y, Wang S, Liu C, Zou MH. Identification of nitric oxide as an endogenous activator of the AMP-activated protein kinase in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:27452–27461. PMID: 18693249.
Article53. She C, Zhu LQ, Zhen YF, Wang XD, Dong QR. Activation of AMPK protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced osteoblast apoptosis through autophagy induction and NADPH maintenance: new implications for osteonecrosis treatment? Cell Signal. 2014; 26:1–8. PMID: 24080159.
Article54. Guo L, Xie B, Mao Z. Autophagy in premature senescent cells is activated via AMPK pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2012; 13:3563–3582. PMID: 22489168.
Article55. Liu X, Chhipa RR, Nakano I, Dasgupta B. The AMPK inhibitor compound C is a potent AMPK-independent antiglioma agent. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014; 13:596–605. PMID: 24419061.
Article56. Bess E, Fisslthaler B, Fromel T, Fleming I. Nitric oxide-induced activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase α2 subunit attenuates IκB kinase activity and inflammatory responses in endothelial cells. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e20848. PMID: 21673972.
Article57. Kato K, Tokuda H, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Natsume H, Kondo A, Ito Y, Kozawa O, Otsuka T. AMPK limits IL-1-stimulated IL-6 synthesis in osteoblasts: involvement of Iκ B/NF-κB pathway. Cell Signal. 2012; 24:1706–1712. PMID: 22560875.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effects of vanadium oxide & sodium orthovanadate on murin osteoblast-like (MC3T3-E1) cells
- Induction of cytoprotective autophagy by morusin via AMP-activated protein kinase activation in human non-small cell lung cancer cells
- Spironolactone Attenuates Methylglyoxal-induced Cellular Dysfunction in MC3T3-E1 Osteoblastic Cells
- Expression of Constitutive Nitric Oxide Synthase by Gastrointestinal Epithelial Cells
- The effect of static magnetic fields on molecular and cellular activities