Cancer Res Treat.
2012 Sep;44(3):195-201.
Constitutive Expression of MAP Kinase Phosphatase-1 Confers Multi-drug Resistance in Human Glioblastoma Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea. cchoi@kaist.ac.kr
- 2KAIST Institute for the BioCentury, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Current treatment of glioblastoma after surgery consists of a combination of fractionated radiotherapy and temozolomide. However, it is difficult to completely remove glioblastoma because it has uncertain boundaries with surrounding tissues. Moreover, combination therapy is not always successful because glioblastoma has diverse resistances. To overcome these limitations, we examined the combined effects of chemotherapy and knockdown of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
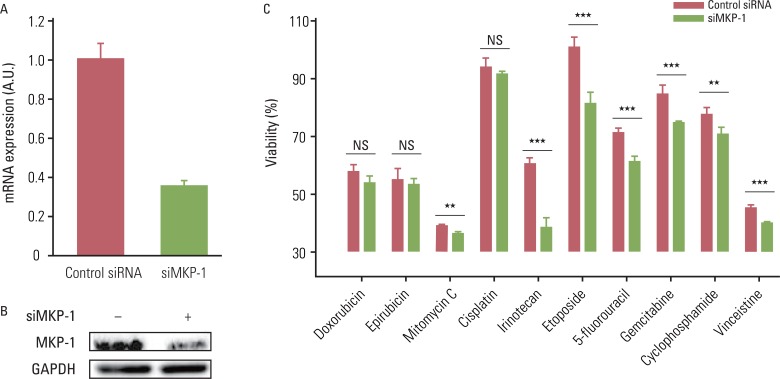
We used ten different anti-cancer drugs (cisplatin, cyclophosphoamide, doxorubicin, epirubicin, etoposide, 5-fluorouracil, gemcitabine, irinotecan, mitomycin C, and vincristine) to treat glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells. Knockdown of MKP-1 was performed using siRNA and lipofectamine. The basal level of MKP-1 in GBM was analyzed based on cDNA microarray data obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases.
RESULTS
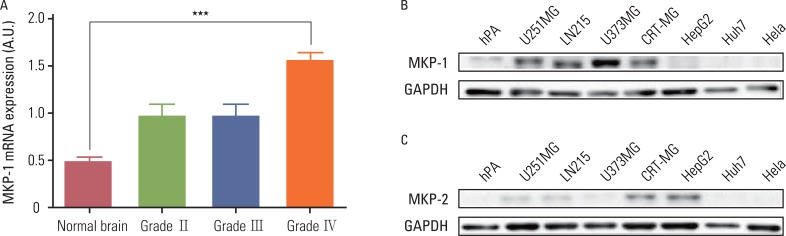
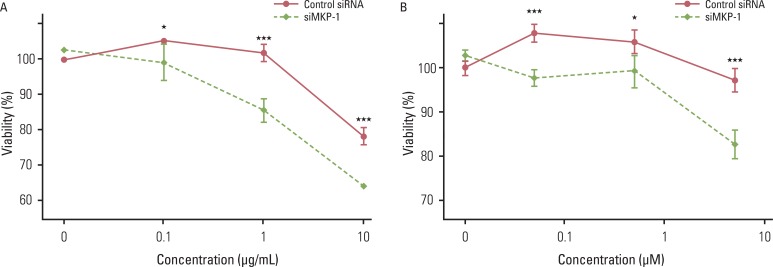
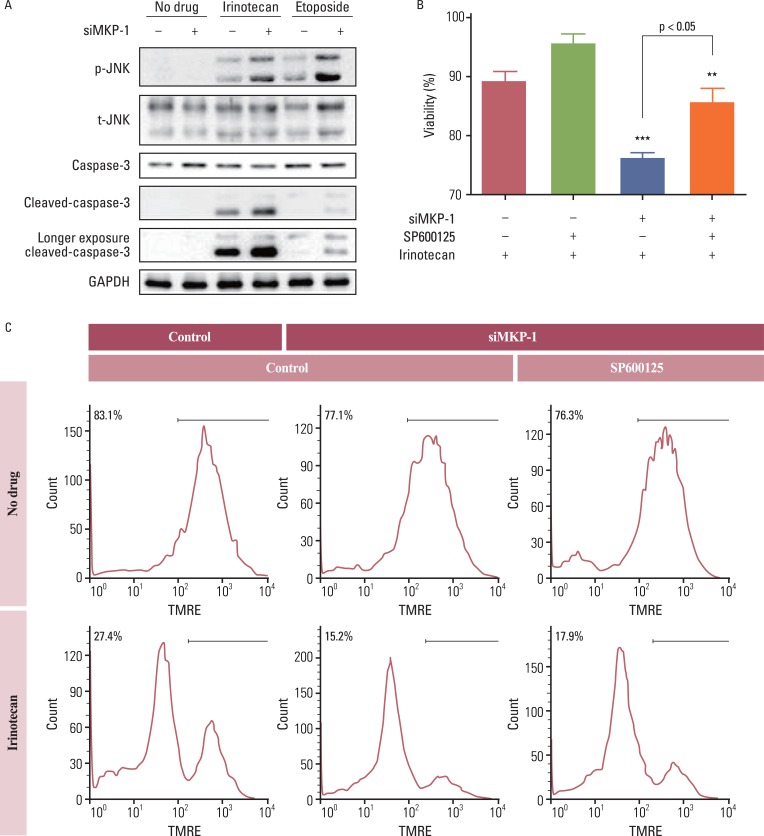
Anti-cancer drug-induced cell death was significantly enhanced by knockdown of MKP-1, and this effect was most prominent in cells treated with irinotecan and etoposide. Treatment with these two drugs led to significantly increased phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in a time-dependent manner, while pharmacological inhibition of JNK partially inhibited drug-induced cell death. Knockdown of MKP-1 also enhanced drug-induced phosphorylation of JNK.
CONCLUSION
Increased MKP-1 expression levels could be the cause of the high resistance to conventional chemotherapeutics in human GBM. Therefore, MKP-1 is an attractive target for overcoming drug resistance in this highly refractory malignancy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis
Camptothecin
Cell Death
Dacarbazine
Deoxycytidine
Doxorubicin
Drug Resistance
Drug Resistance, Multiple
Dual Specificity Phosphatase 1
Epirubicin
Etoposide
Fluorouracil
Gene Expression
Glioblastoma
Humans
JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Lipids
Mitomycin
Oligonucleotide Array Sequence Analysis
Phosphorylation
Phosphotransferases
Protein Kinases
RNA, Small Interfering
Camptothecin
Dacarbazine
Deoxycytidine
Doxorubicin
Dual Specificity Phosphatase 1
Epirubicin
Etoposide
Fluorouracil
JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Lipids
Mitomycin
Phosphotransferases
Protein Kinases
RNA, Small Interfering
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:492–507. PMID: 18669428.
Article3. Krakstad C, Chekenya M. Survival signalling and apoptosis resistance in glioblastomas: opportunities for targeted therapeutics. Mol Cancer. 2010; 9:135. PMID: 20515495.
Article4. Reijneveld JC, Voest EE, Taphoorn MJ. Angiogenesis in malignant primary and metastatic brain tumors. J Neurol. 2000; 247:597–608. PMID: 11041327.
Article5. Bredel M, Zentner J. Brain-tumour drug resistance: the bare essentials. Lancet Oncol. 2002; 3:397–406. PMID: 12142169.
Article6. Wick W, Weller M, Weiler M, Batchelor T, Yung AW, Platten M. Pathway inhibition: emerging molecular targets for treating glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2011; 13:566–579. PMID: 21636705.
Article7. Riemenschneider MJ, Hegi ME, Reifenberger G. MGMT promoter methylation in malignant gliomas. Target Oncol. 2010; 5:161–165. PMID: 20725792.
Article8. Bredel M. Anticancer drug resistance in primary human brain tumors. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001; 35:161–204. PMID: 11336781.
Article9. Patterson KI, Brummer T, O'Brien PM, Daly RJ. Dual-specificity phosphatases: critical regulators with diverse cellular targets. Biochem J. 2009; 418:475–489. PMID: 19228121.
Article10. Bermudez O, Pages G, Gimond C. The dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases: critical roles in development and cancer. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010; 299:C189–C202. PMID: 20463170.
Article11. Keyse SM. Dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs) and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008; 27:253–261. PMID: 18330678.
Article12. Small GW, Somasundaram S, Moore DT, Shi YY, Orlowski RZ. Repression of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase-1 by anthracyclines contributes to their antiapoptotic activation of p44/42-MAPK. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003; 307:861–869. PMID: 14557375.
Article13. Small GW, Shi YY, Edmund NA, Somasundaram S, Moore DT, Orlowski RZ. Evidence that mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 induction by proteasome inhibitors plays an antiapoptotic role. Mol Pharmacol. 2004; 66:1478–1490. PMID: 15448190.
Article14. Wang J, Zhou JY, Wu GS. ERK-dependent MKP-1-mediated cisplatin resistance in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:11933–11941. PMID: 18089824.15. Loda M, Capodieci P, Mishra R, Yao H, Corless C, Grigioni W, et al. Expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in the early phases of human epithelial carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1996; 149:1553–1564. PMID: 8909245.16. Haigis KM, Kendall KR, Wang Y, Cheung A, Haigis MC, Glickman JN, et al. Differential effects of oncogenic K-Ras and N-Ras on proliferation, differentiation and tumor progression in the colon. Nat Genet. 2008; 40:600–608. PMID: 18372904.
Article17. Szakacs G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA, Booth-Genthe C, Gottesman MM. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006; 5:219–234. PMID: 16518375.
Article18. Wang Z, Xu J, Zhou JY, Liu Y, Wu GS. Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 is required for cisplatin resistance. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:8870–8877. PMID: 16951204.
Article19. Small GW, Shi YY, Higgins LS, Orlowski RZ. Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 is a mediator of breast cancer chemoresistance. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:4459–4466. PMID: 17483361.
Article20. Chamberlain MC. Bevacizumab for the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma. Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2011; 5:117–129. PMID: 21603247.
Article21. Jakobsen JN, Hasselbalch B, Stockhausen MT, Lassen U, Poulsen HS. Irinotecan and bevacizumab in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011; 12:825–833. PMID: 21385110.
Article22. Watanabe K, Kanaya H, Fujiyama Y, Kim P. Combination chemotherapy using carboplatin (JM-8) and etoposide (JET therapy) for recurrent malignant gliomas: a phase II study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2002; 144:1265–1270. PMID: 12478337.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- IL-1beta Induces Lysozyme Overexpression through a Mechanism Involving ERK/p38 Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Activation in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Molecular biologic mechanism of drug resistance in cancer chemotherapy
- RANKL expression is mediated by p38 MAPK in rat periodontal ligament cells
- Inhibitory effect of Hsp70 on angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cell hypertrophy
- Effects of Sense and Antisense Expression of Protein Kinase Calpha on the Proliferation and Radiosensitization of U-87 Human Glioblastoma Cells