J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2010 Dec;36(6):481-489.
Effects of all-trans retinoic acid on expression of Toll-like receptor 5 on immune cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1CK Dental Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Pusan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea. ds5nki@hanmail.net
Abstract
- INTRODUCTION
TLR-5, a member of the toll-like receptor (TLR) family, is a element of the type I transmembrane receptors, which are characterized by an intracellular signaling domain homolog to the interleukin-1 receptor. These receptors recognize microbial components, particularly bacterial flagellin. All-trans retinoic acid (atRA, tretinoin), a natural metabolite of vitamin A, acts as a growth and differentiation factor in many tissues, and is also needed for immune functions. In this study, THP-1 human macrophage-monocytes were used to examine the mechanisms by which atRA regulated the expression of TLR-5. Because the molecular mechanism underlying this regulation at the transcriptional level is also unclear, this study examined which putative transcription factors are responsible for TLR-5 expression by atRA in immune cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
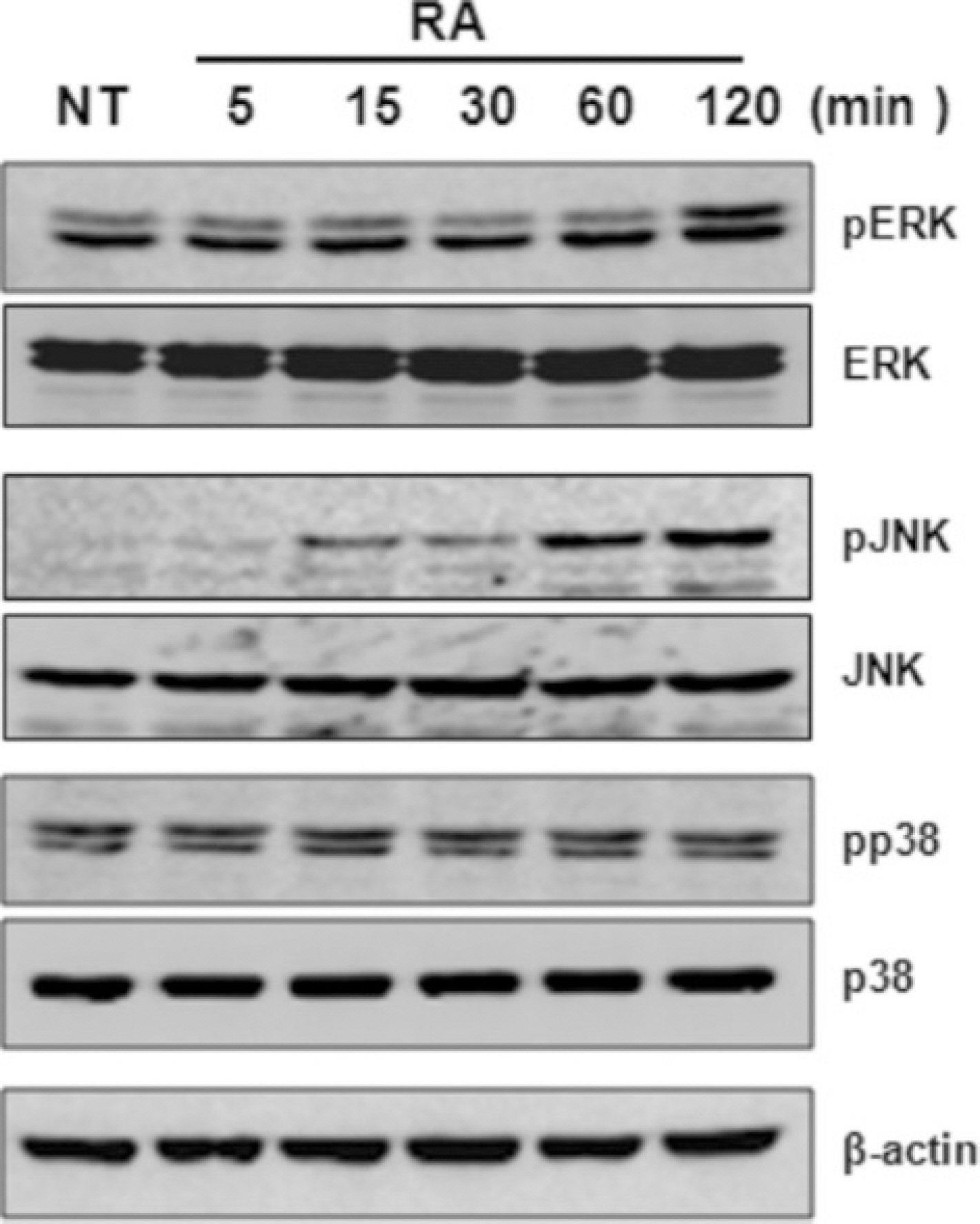
This study examined whether atRA induces the expression of TLR-5 in THP-1 cells using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and which transcription factors are involved in regulating the TLR-5 promoter in RAW264.7 cells using a reporter assay system. Western blot analysis was used to determine which signal pathway is involved in the expression of TLR-5 in atRA-treated THP-1 cells.
RESULTS
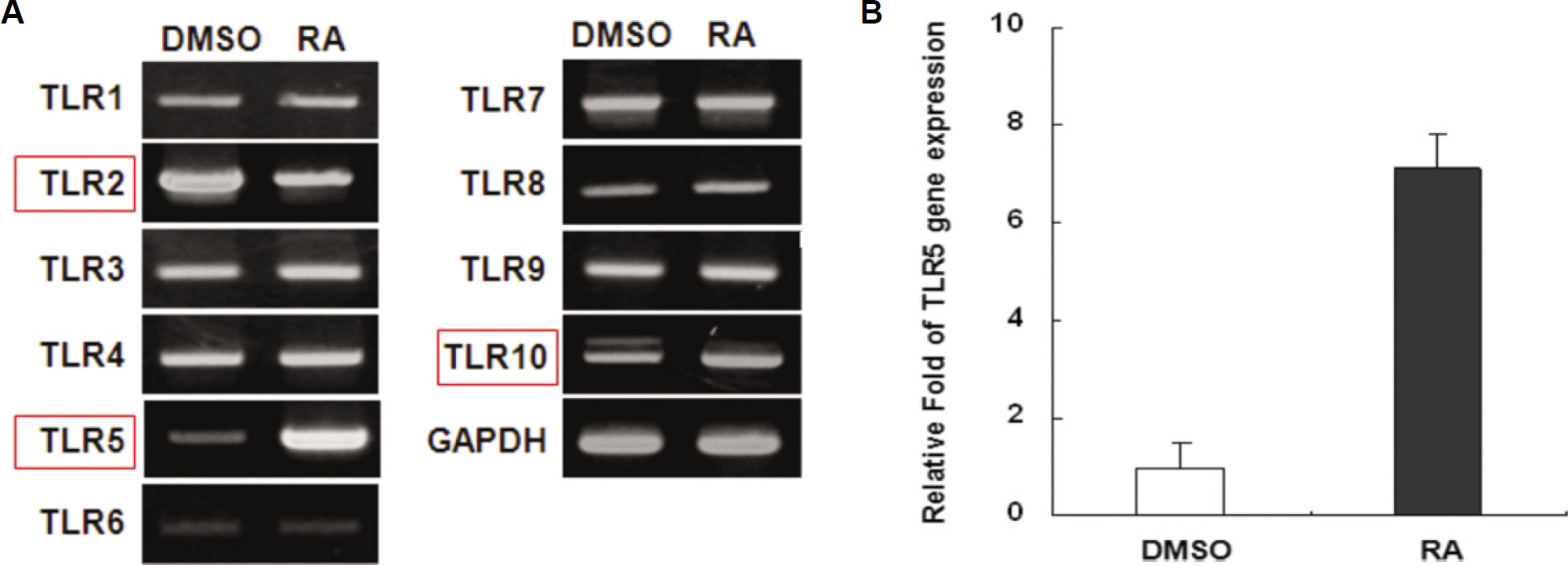
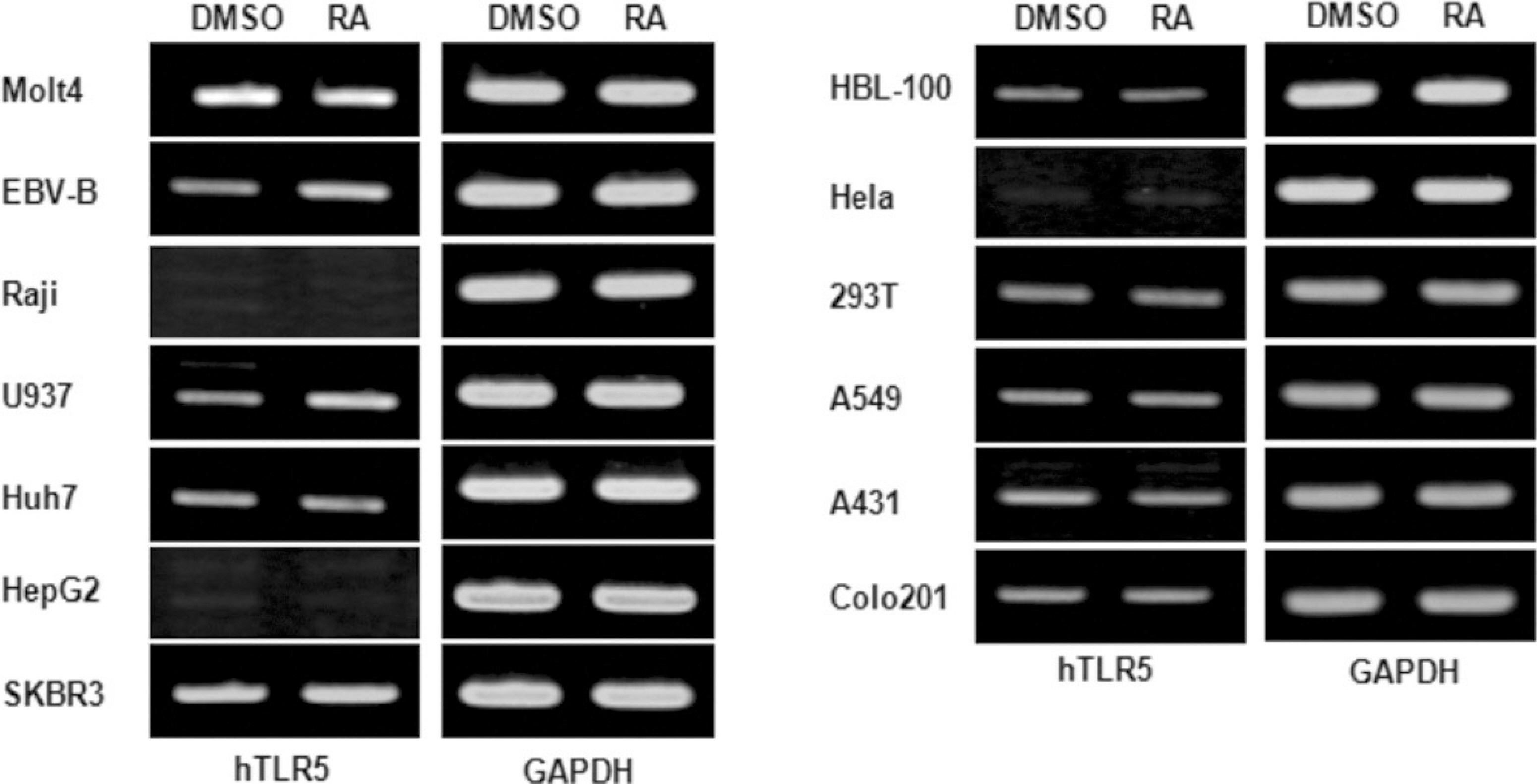
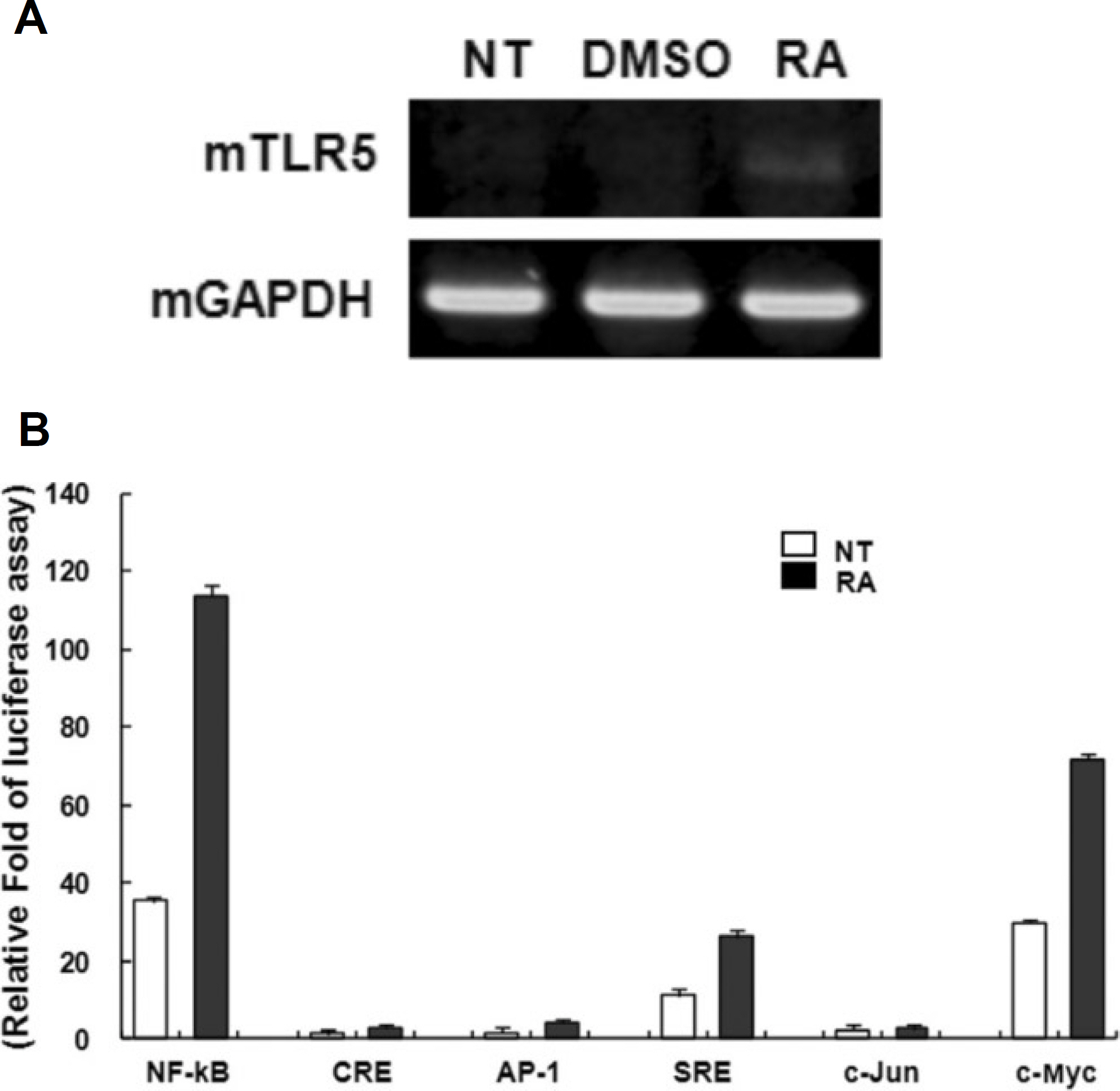
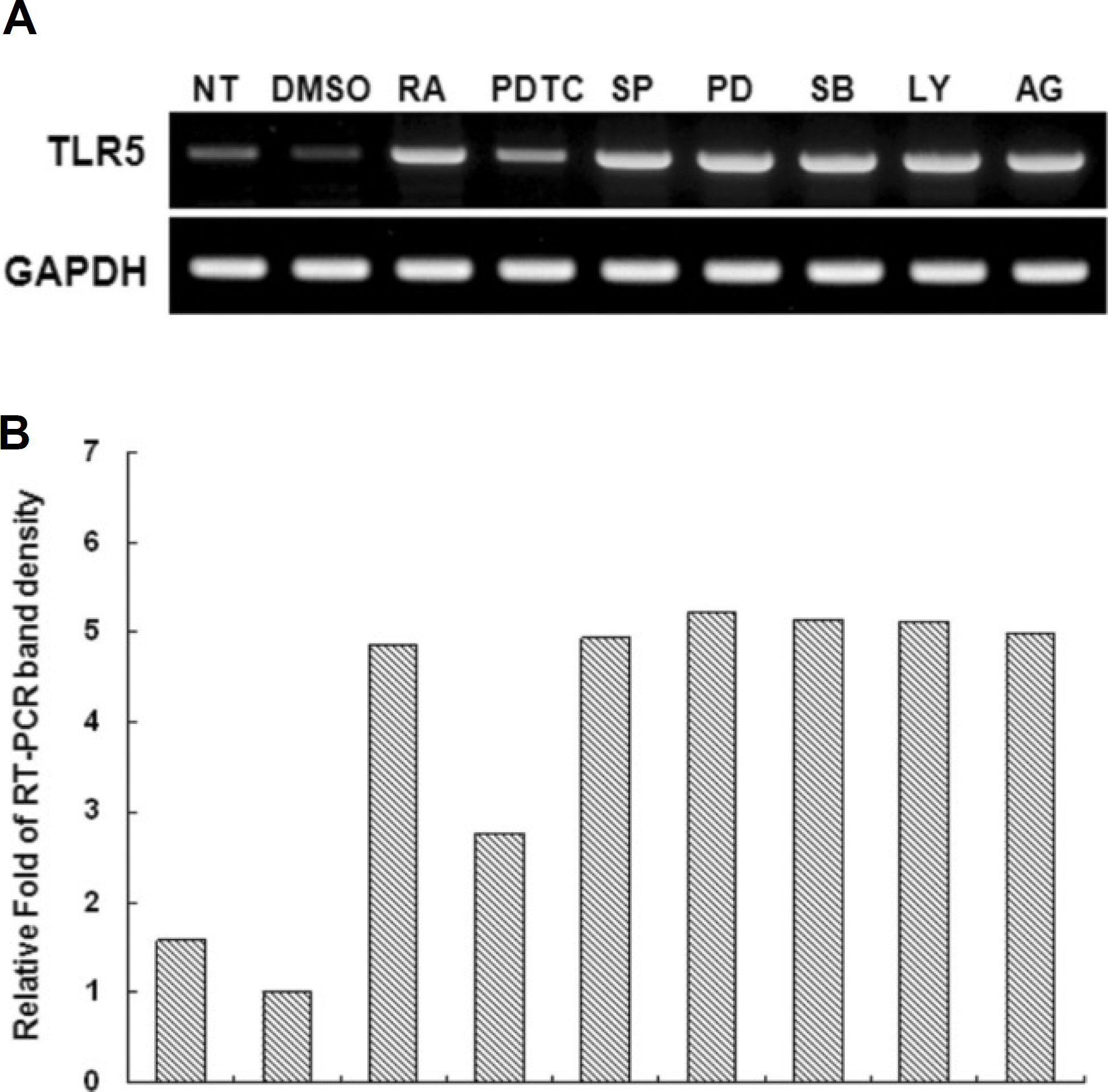
atRA at a concentration of 10 nM greatly induced the expression of TLR-5 in THP-1 cells. Human TLR-5 promoter contains three Sp-1/GC binding sites around -50 bp and two NF-kB binding sites at -380 bp and -160 bp from the transcriptional start site of the TLR-5 gene. Sp-1/GC is primarily responsible for the constitutive TLR-5 expression, and may also contribute to NF-kB at -160 bp to induce TLR-5 after atRA stimulation in THP-1 cells. The role of NF-kB in TLR-5 expression was further confirmed by inhibitor pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) experiments, which greatly reduced the TLR-5 transcription by 70-80%.
CONCLUSION
atRA induces the expression of the human TLR-5 gene and NF-kB is a critical transcription factor for the atRA-induced expression of TLR-5. Accordingly, it is conceivable that retinoids are required for adequate innate and adaptive immune responses to agents of infectious diseases. atRA and various synthetic retinoids have been used therapeutically in human diseases, such as leukemia and other cancers due to the antiproliferative and apoptosis inducing effects of retinoids. Therefore, understanding the molecular regulatory mechanism of TLR-5 may assist in the design of alternative strategies for the treatment of infectious diseases, leukemia and cancers.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis
Binding Sites
Blotting, Western
Communicable Diseases
Flagellin
Humans
Immunity, Cellular
Interleukin-1
Leukemia
NF-kappa B
Pyrrolidines
Retinoids
Signal Transduction
Thiocarbamates
Toll-Like Receptor 5
Toll-Like Receptors
Transcription Factors
Tretinoin
Vitamin A
Flagellin
Interleukin-1
NF-kappa B
Pyrrolidines
Retinoids
Thiocarbamates
Toll-Like Receptor 5
Toll-Like Receptors
Transcription Factors
Tretinoin
Vitamin A
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hashimoto C, Hudson KL, Anderson KV. The Toll gene of Drosophila, required for dorsal-ventral embryonic polarity, appears to encode a transmembrane protein. Cell. 1988; 52:269–79.
Article2. Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA Jr. A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature. 1997; 388:394–7.
Article3. Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptor function and signaling. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:979–87. quiz 988.
Article4. Lee SJ, Lee S. Toll-like receptors and inflammation in the CNS. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002; 1:181–91.5. Goodman DS. Vitamin A and retinoids in health and disease. N Engl J Med. 1984; 310:1023–31.
Article6. Lotan R. Immunomodulatory effects of retinoids. J Nutr Growth Cancer. 1986; 3:57–65.7. Lotan R. Retinoids in cancer chemoprevention. FASEB J. 1996; 10:1031–9.
Article8. Hofmann C, Eichele G. Retinoids in development. Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Goodman DS, editors. The retinoids: biology, chemistry and medicine. 2nd ed.New York, NY: Raven Press;1994. 387-442.9. Israel H, Odziemiec C, Ballow M. The effects of retinoic acid on immunoglobulin synthesis by human cord blood mononuclear cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991; 59:417–25.
Article10. Wang W, Ballow M. The effects of retinoic acid on in vitro immunoglobulin synthesis by cord blood and adult peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cell Immunol. 1993; 148:291–300.11. Ballow M, Wang W, Xiang S. Modulation of B-cell immunoglobulin synthesis by retinoic acid. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1996; 80:S73–81.
Article12. Cantorna MT, Nashold FE, Hayes CE. In vitamin A deficiency multiple mechanisms establish a regulatory T helper cell imbalance with excess Th1 and insufficient Th2 function. J Immunol. 1994; 152:1515–22.13. Racke MK, Burnett D, Pak SH, Albert PS, Cannella B, Raine CS, et al. Retinoid treatment of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis IL-4 production correlates with improved disease course. J Immunol. 1995; 154:450–8.14. Stephensen C, Rasooly R, Jiang X, Ceddia M, Weaver C, Chandraratna R, et al. Vitamin A enhances in vitro Th2 development via retinoid X receptor pathway. J Immunol. 2002; 168:4495–503.15. Lee HY, Dohi DF, Kim YH, Walsh GL, Consoli U, Andreeff M, et al. All-trans retinoic acid converts E2F into a transcriptional suppressor and inhibits the growth of normal human bronchial epithelial cells through a retinoic acid receptor-dependent signaling pathway. J Clin Invest. 1998; 101:1012–9.16. Sun SY, Yue P, Lotan R. Implication of multiple mechanisms in apoptosis induced by the synthetic retinoid CD437 in human prostate carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2000; 19:4513–22.
Article17. Wan YJ, Cai Y, Magee TR. Retinoic acid differentially regulates retinoic acid receptor-mediated pathways in the Hep3B cell line. Exp Cell Res. 1998; 238:241–7.
Article18. Agadir A, Shealy YF, Hill DL, Zhang X. Retinyl methyl ether down-regulates activator protein 1 transcriptional activation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1997; 57:3444–50.19. Liu PT, Krutzik SR, Kim J, Modlin RL. All-trans Retinoic acid down-regulates TLR2 expression and function. J Immunol. 2005; 174:2467–70.20. Gudas LJ, Sporn MB, Roberts AB. Cellular biology and biochemistry of the retinoids. Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Goodman DS, editors. The retinoids: biology, chemistry and medicine. 2nd ed.New York, NY: Raven Press;1994. p. 443–50.21. Ross AC, Stephensen CB. Vitamin A and retinoids in antiviral responses. FASEB J. 1996; 10:979–85.
Article22. Ross AC, Ha¨mmerling UG. Retinoids and the immune system. Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Goodman DS, editors. The retinoids: biology, chemistry and medicine. 2nd ed.New York, NY: Raven Press;1994. p. 521–43.23. Ballow M, Xiang S, Wang W, Brodsky L. The effects of retinoic acid on immunoglobulin synthesis: role of interleukin 6. J Clin Immunol. 1996; 16:171–9.
Article24. Ballow M, Wang W. Retinoic acid (RA) induced enhancing effects on immunoglobulin (Ig) synthesis of human B-cells. Pediatr Res. 1993; 33:151A.25. Ballow M, Xiang S, Greenberg SJ, Brodsky L, Allen C, Rich G. Retinoic acid-induced modulation of IL-2mRNA production and IL-2 receptor expression on T Cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997; 113:167–9.26. Matikainen S, Serkkola E, Hurme M. Retinoic acid enhances IL-1βexpression in myeloid leukemia cells and in human monocytes. J Immunol. 1991; 147:162–7.27. Blomhoff HK, Smeland EB, Erikstein B, Rasmussen AM, Skrede B, Skj � nsberg C, et al. Vitamin A is a key regulator for cell growth, cytokine production, and differentiation in normal B cells. J Biol Chem. 1992; 267:23988–92.
Article28. Chen Q, Ross AC. Retinoic acid regulates cell cycle progression and cell differentiation in human monocytic THP-1 cells. Exp Cell Res. 2004; 297:68–81.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of All-Trans-Retinoic Acid on the Activity and the Gene Expression of Drug Metabolizing Enzymes in Rat Skin
- The Effect of Retinoids in Medulloblastoma Cell Culture
- All-trans Retinoic Acid induced Myositis in a Patient with Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
- Anticancer Effect and Apoptosis of All-trans-retinoic Acid on the Human Ovarian Epithelial Carcinoma Cell Lines
- The Effect of All-trans and 13-cis-retinoic Acid in Medulloblastoma and Glioblastoma Cell Culture