Tuberc Respir Dis.
2015 Jul;78(3):218-226. 10.4046/trd.2015.78.3.218.
EphA2 Receptor Signaling Mediates Inflammatory Responses in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lung Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pms70@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2320646
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2015.78.3.218
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
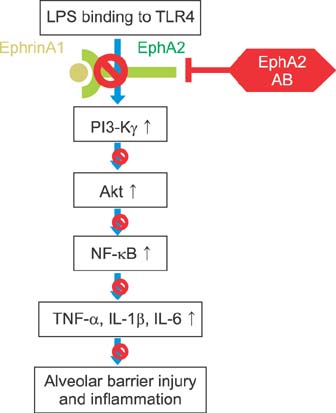
Eph receptors and ephrin ligands have several functions including angiogenesis, cell migration, axon guidance, fluid homeostasis, oncogenesis, inflammation and injury repair. The EphA2 receptor potentially mediates the regulation of vascular permeability and inflammation in response to lung injury.
METHODS
Mice were divided into 3 experimental groups to study the role of EphA2 signaling in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced lung injury model i.e., IgG+phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) group (IgG instillation before PBS exposure), IgG+LPS group (IgG instillation before LPS exposure) and EphA2 monoclonal antibody (mAb)+LPS group (EphA2 mAb pretreatment before LPS exposure).
RESULTS
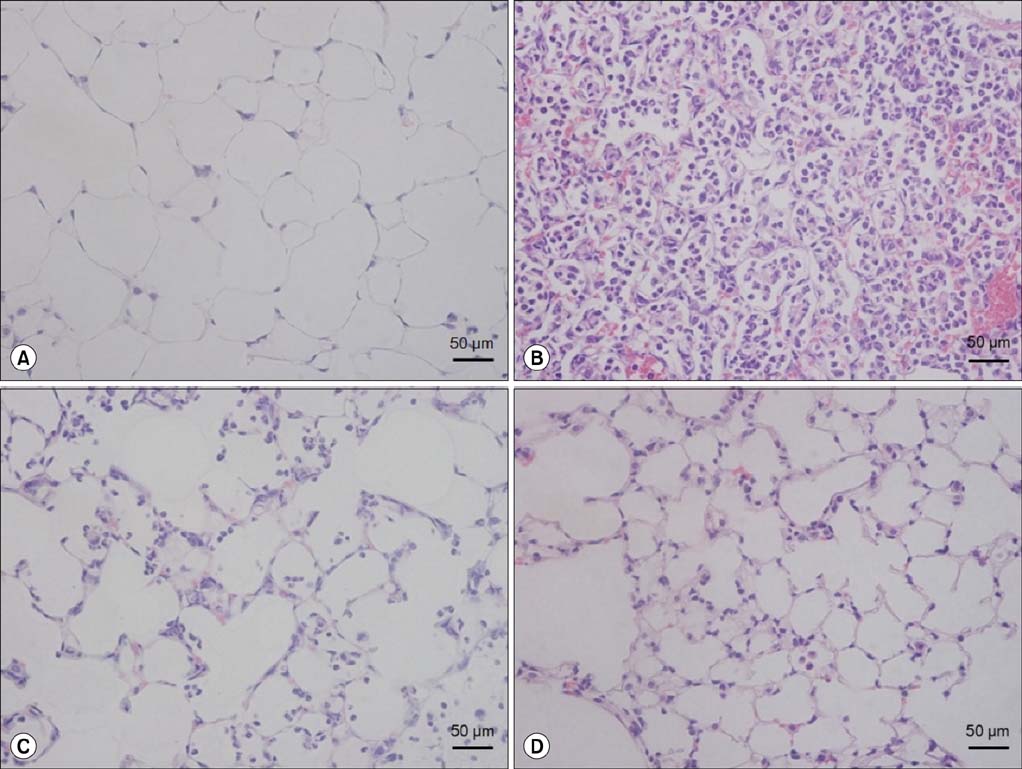
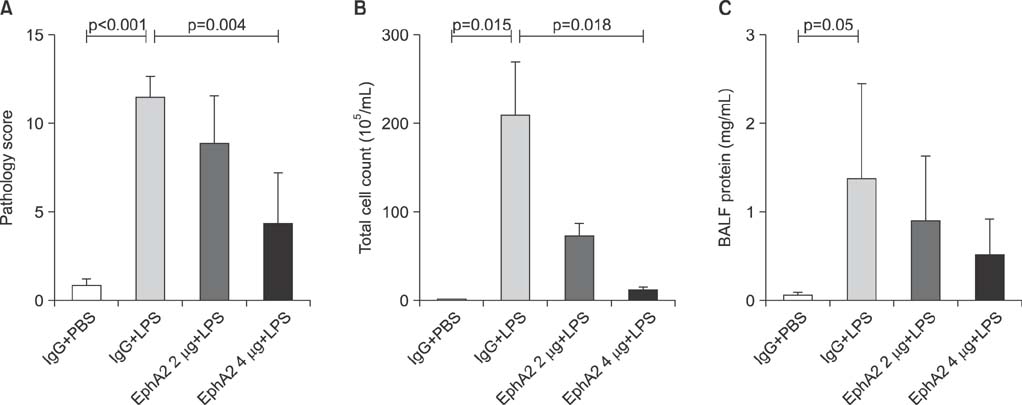
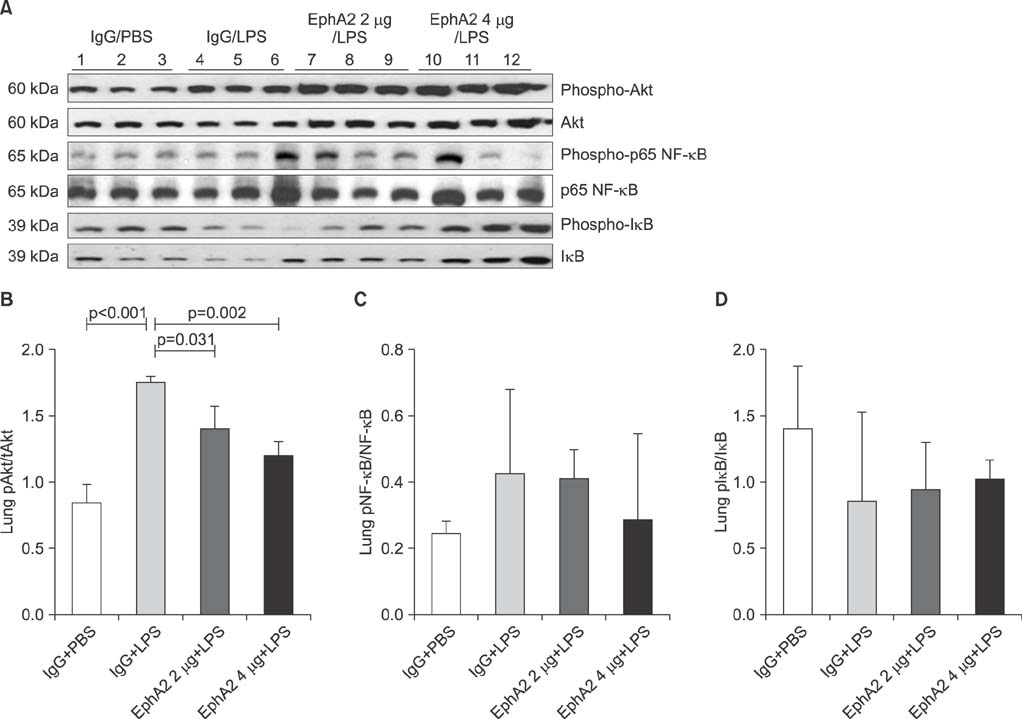
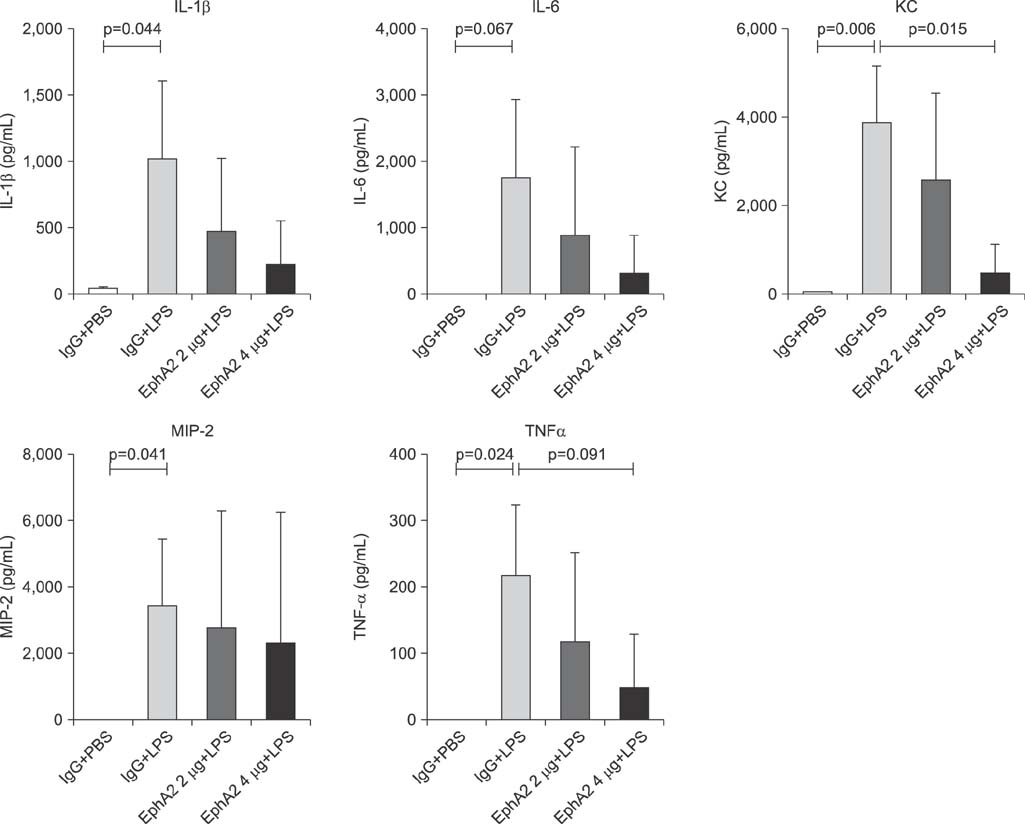
EphA2 and ephrinA1 were upregulated in LPS-induced lung injury. The lung injury score of the EphA2 mAb+LPS group was lower than that of the IgG+LPS group (4.30+/-2.93 vs. 11.45+/-1.20, respectively; p=0.004). Cell counts (EphA2 mAb+LPS: 11.33x10(4)+/-8.84x10(4) vs. IgG+LPS: 208.0x10(4)+/-122.6x10(4); p=0.018) and total protein concentrations (EphA2 mAb+LPS: 0.52+/-0.41 mg/mL vs. IgG+LPS: 1.38+/-1.08 mg/mL; p=0.192) were decreased in EphA2 mAb+LPS group, as compared to the IgG+LPS group. In addition, EphA2 antagonism reduced the expression of phospho-p85, phosphoinositide 3-kinase 110gamma, phospho-Akt, nuclear factor kappaB, and proinflammatory cytokines.
CONCLUSION
This results of the study indicated a role for EphA2-ephrinA1 signaling in the pathogenesis of LPS-induced lung injury. Furthermore, EphA2 antagonism inhibits the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt pathway and attenuates inflammation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kullander K, Klein R. Mechanisms and functions of Eph and ephrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002; 3:475–486.2. Pasquale EB. Eph-ephrin bidirectional signaling in physiology and disease. Cell. 2008; 133:38–52.3. Coulthard MG, Morgan M, Woodruff TM, Arumugam TV, Taylor SM, Carpenter TC, et al. Eph/Ephrin signaling in injury and inflammation. Am J Pathol. 2012; 181:1493–1503.4. Beauchamp A, Debinski W. Ephs and ephrins in cancer: ephrin-A1 signalling. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012; 23:109–115.5. Surawska H, Ma PC, Salgia R. The role of ephrins and Eph receptors in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004; 15:419–433.6. Pratt RL, Kinch MS. Activation of the EphA2 tyrosine kinase stimulates the MAP/ERK kinase signaling cascade. Oncogene. 2002; 21:7690–7699.7. Miao H, Burnett E, Kinch M, Simon E, Wang B. Activation of EphA2 kinase suppresses integrin function and causes focaladhesion-kinase dephosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol. 2000; 2:62–69.8. Liu DP, Wang Y, Koeffler HP, Xie D. Ephrin-A1 is a negative regulator in glioma through down-regulation of EphA2 and FAK. Int J Oncol. 2007; 30:865–871.9. Carpenter TC, Schroeder W, Stenmark KR, Schmidt EP. Eph-A2 promotes permeability and inflammatory responses to bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012; 46:40–47.10. Cercone MA, Schroeder W, Schomberg S, Carpenter TC. EphA2 receptor mediates increased vascular permeability in lung injury due to viral infection and hypoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009; 297:L856–L863.11. Ivanov AI, Steiner AA, Scheck AC, Romanovsky AA. Expression of Eph receptors and their ligands, ephrins, during lipopolysaccharide fever in rats. Physiol Genomics. 2005; 21:152–160.12. Hedrich HJ. The laboratory mouse. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press;2004.13. Fang WF, Cho JH, He Q, Lin MC, Wu CC, Voelkel NF, et al. Lipid A fraction of LPS induces a discrete MAPK activation in acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007; 293:L336–L344.14. Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, Weaver J, Martin DP, Neff M, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:1685–1693.15. Nasreen N, Khodayari N, Sriram PS, Patel J, Mohammed KA. Tobacco smoke induces epithelial barrier dysfunction via receptor EphA2 signaling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014; 306:C1154–C1166.16. Kustermans G, El Benna J, Piette J, Legrand-Poels S. Perturbation of actin dynamics induces NF-kappaB activation in myelomonocytic cells through an NADPH oxidase-dependent pathway. Biochem J. 2005; 387(Pt 2):531–540.17. Nemeth ZH, Deitch EA, Davidson MT, Szabo C, Vizi ES, Hasko G. Disruption of the actin cytoskeleton results in nuclear factor-kappaB activation and inflammatory mediator production in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2004; 200:71–81.18. Kustermans G, El Mjiyad N, Horion J, Jacobs N, Piette J, Legrand-Poels S. Actin cytoskeleton differentially modulates NF-kappaB-mediated IL-8 expression in myelomonocytic cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008; 76:1214–1228.19. Ardeshna KM, Pizzey AR, Devereux S, Khwaja A. The PI3 kinase, p38 SAP kinase, and NF-kappaB signal transduction pathways are involved in the survival and maturation of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Blood. 2000; 96:1039–1046.20. Beraud C, Henzel WJ, Baeuerle PA. Involvement of regulatory and catalytic subunits of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in NF-kappaB activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:429–434.21. Kane LP, Shapiro VS, Stokoe D, Weiss A. Induction of NF-kappaB by the Akt/PKB kinase. Curr Biol. 1999; 9:601–604.22. Manna SK, Aggarwal BB. Wortmannin inhibits activation of nuclear transcription factors NF-kappaB and activated protein-1 induced by lipopolysaccharide and phorbol ester. FEBS Lett. 2000; 473:113–118.23. Yum HK, Arcaroli J, Kupfner J, Shenkar R, Penninger JM, Sasaki T, et al. Involvement of phosphoinositide 3-kinases in neutrophil activation and the development of acute lung injury. J Immunol. 2001; 167:6601–6608.24. Holen HL, Shadidi M, Narvhus K, Kjosnes O, Tierens A, Aasheim HC. Signaling through ephrin-A ligand leads to activation of Src-family kinases, Akt phosphorylation, and inhibition of antigen receptor-induced apoptosis. J Leukoc Biol. 2008; 84:1183–1191.25. Cheng N, Brantley DM, Liu H, Lin Q, Enriquez M, Gale N, et al. Blockade of EphA receptor tyrosine kinase activation inhibits vascular endothelial cell growth factor-induced angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 2002; 1:2–11.26. Pandey A, Shao H, Marks RM, Polverini PJ, Dixit VM. Role of B61, the ligand for the Eck receptor tyrosine kinase, in TNF-alpha-induced angiogenesis. Science. 1995; 268:567–569.27. Tandon M, Vemula SV, Mittal SK. Emerging strategies for EphA2 receptor targeting for cancer therapeutics. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011; 15:31–51.28. Chee CE, Krishnamurthi S, Nock CJ, Meropol NJ, Gibbons J, Fu P, et al. Phase II study of dasatinib (BMS-354825) in patients with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Oncologist. 2013; 18:1091–1092.29. Annunziata CM, Kohn EC, LoRusso P, Houston ND, Coleman RL, Buzoianu M, et al. Phase 1, open-label study of MEDI-547 in patients with relapsed or refractory solid tumors. Invest New Drugs. 2013; 31:77–84.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- EphrinA1/EphA2 Promotes Epithelial Hyperpermeability Involving in Lipopolysaccharide-induced Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction
- Lipopolysaccharide: Basic Biochemistry, Intracellular Signaling, and Physiological Impacts in the Gut
- Growth Factor-mediated Tumor Progression and Metastasis in Cholangiocarcinoma
- The effects of BMS-470539 on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
- Oligomeric proanthocyanidin ameliorates sepsis-associated renal tubular injury: involvement of oxidative stress, inflammation, PI3K/AKT and NFκκB signaling pathways