Intest Res.
2014 Apr;12(2):90-95. 10.5217/ir.2014.12.2.90.
Lipopolysaccharide: Basic Biochemistry, Intracellular Signaling, and Physiological Impacts in the Gut
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Digestive Diseases, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA. shrhee@mednet.ucla.edu
- KMID: 2284892
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2014.12.2.90
Abstract
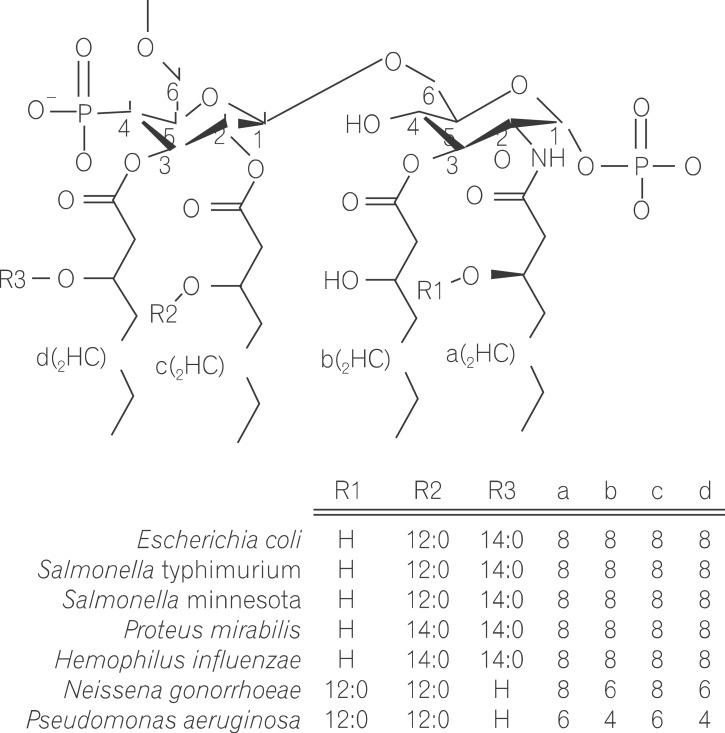
- Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a main constituent of Gram-negative bacterial membrane, specifically activates Toll-like receptor 4, leading to the production of pleiotropic cytokines/chemokines which in turn regulate inflammatory and innate and subsequent adaptive immune responses. Given that human gut harbors a large collection of commensal bacteria, LPS released by gut microbes is able to make the great impact on gut homeostasis through the intracellular signaling pathways engaged by host-microbial interaction. Emerging evidence indicates that LPS in the gut has a potency to elicit the pathogenesis of intestinal inflammatory diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease and necrotizing enterocolitis. In this review, we discuss the current understanding of the basic biochemistry of LPS, LPS-induced intracellular signaling, and physiological impacts of LPS in the intestine.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Can Proton Pump Inhibitors Increase Incidence of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Druginduced Small Bowel Injury?
Seong Ran Jeon
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2016;68(2):123-125. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2016.68.2.123.Changes in serum levels of lipopolysaccharides and CD26 in patients with Crohn's disease
Daniéla Oliveira Magro, Paulo Gustavo Kotze, Carlos Augusto Real Martinez, Michel Gardere Camargo, Dioze Guadagnini, Antonio Ramos Calixto, Ana Carolina Junqueira Vasques, Maria de Lourdes Setsuko Ayrizono, Bruno Geloneze, José Carlos Pareja, Mario José Saad, Claudio Saddy Rodrigues Coy
Intest Res. 2017;15(3):352-357. doi: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.352.
Reference
-
2. Raetz CR, Ulevitch RJ, Wright SD, Sibley CH, Ding A, Nathan CF. Gram-negative endotoxin: an extraordinary lipid with profound effects on eukaryotic signal transduction. FASEB J. 1991; 5:2652–2660. PMID: 1916089.
Article4. Murakami A, Ohigashi H. Targeting NOX, INOS and COX-2 in inflammatory cells: chemoprevention using food phytochemicals. Int J Cancer. 2007; 121:2357–2363. PMID: 17893865.
Article5. Murray PJ, Smale ST. Restraint of inflammatory signaling by interdependent strata of negative regulatory pathways. Nat Immunol. 2012; 13:916–924. PMID: 22990889.
Article6. Rhee SH, Hwang D. Murine TOLL-like receptor 4 confers lipopolysaccharide responsiveness as determined by activation of NF kappa B and expression of the inducible cyclooxygenase. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:34035–34040. PMID: 10952994.
Article7. Bosshart H, Heinzelmann M. Targeting bacterial endotoxin: two sides of a coin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007; 1096:1–17. PMID: 17405910.8. Ziegler-Heitbrock HW, Ulevitch RJ. CD14: cell surface receptor and differentiation marker. Immunol Today. 1993; 14:121–125. PMID: 7682078.
Article9. Sultzer BM. Genetic control of leucocyte responses to endotoxin. Nature. 1968; 219:1253–1254. PMID: 4877918.
Article10. Glode LM, Jacques A, Mergenhagen SE, Rosenstreich DL. Resistance of macrophages from C3H/HeJ mice to the in vitro cytotoxic effects of endotoxin. J Immunol. 1977; 119:162–166. PMID: 326955.11. Watson J, Riblet R. Genetic control of responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharides in mice. II. A gene that influences a membrane component involved in the activation of bone marrow-derived lymphocytes by lipipolysaccharides. J Immunol. 1975; 114:1462–1468. PMID: 123543.12. Ryan JL, McAdam KP. Genetic non-responsiveness of murine fibroblasts to bacterial endotoxin. Nature. 1977; 269:153–155. PMID: 333293.13. Watson J, Kelly K, Largen M, Taylor BA. The genetic mapping of a defective LPS response gene in C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1978; 120:422–424. PMID: 202651.14. Coutinho A, Meo T. Genetic basis for unresponsiveness to lipopolysaccharide in C57BL/10Cr mice. Immunogenetics. 1978; 7:17–24. PMID: 21302052.15. Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998; 282:2085–2088. PMID: 9851930.16. Qureshi ST, Lariviere L, Leveque G, et al. Endotoxin-tolerant mice have mutations in Toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4). J Exp Med. 1999; 189:615–625. PMID: 9989976.17. Choi YJ, Im E, Chung HK, Pothoulakis C, Rhee SH. TRIF mediates Toll-like receptor 5-induced signaling in intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:37570–37578. PMID: 20855887.18. Zanoni I, Granucci F. Role of CD14 in host protection against infections and in metabolism regulation. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013; 3:32. PMID: 23898465.19. Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K. TLR accessory molecules. Curr Opin Immunol. 2008; 20:420–425. PMID: 18625310.20. Kagan JC, Su T, Horng T, Chow A, Akira S, Medzhitov R. TRAM couples endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4 to the induction of interferon-beta. Nat Immunol. 2008; 9:361–368. PMID: 18297073.21. Kenny EF, O'Neill LA. Signalling adaptors used by Toll-like receptors: an update. Cytokine. 2008; 43:342–349. PMID: 18706831.22. Choi YJ, Jung J, Chung HK, Im E, Rhee SH. PTEN regulates TLR5-induced intestinal inflammation by controlling Mal/TIRAP recruitment. FASEB J. 2013; 27:243–254. PMID: 23038756.23. Goldman MJ, Anderson GM, Stolzenberg ED, Kari UP, Zasloff M, Wilson JM. Human beta-defensin-1 is a salt-sensitive antibiotic in lung that is inactivated in cystic fibrosis. Cell. 1997; 88:553–560. PMID: 9038346.24. Smith JJ, Travis SM, Greenberg EP, Welsh MJ. Cystic fibrosis airway epithelia fail to kill bacteria because of abnormal airway surface fluid. Cell. 1996; 85:229–236. PMID: 8612275.25. Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA. The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell. 1996; 86:973–983. PMID: 8808632.26. Williams MJ, Rodriguez A, Kimbrell DA, Eldon ED. The 18-wheeler mutation reveals complex antibacterial gene regulation in Drosophila host defense. EMBO J. 1997; 16:6120–6130. PMID: 9321392.27. Zhao L, Lu W. Defensins in innate immunity. Curr Opin Hematol. 2014; 21:37–42. PMID: 24275690.28. Kahlenberg JM, Kaplan MJ. Little peptide, big effects: the role of LL-37 in inflammation and autoimmune disease. J Immunol. 2013; 191:4895–4901. PMID: 24185823.29. Minton K. Innate immunity: the inside story on complement activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014; 14:61. PMID: 24378841.30. Leaphart CL, Cavallo J, Gribar SC, et al. A critical role for TLR4 in the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis by modulating intestinal injury and repair. J Immunol. 2007; 179:4808–4820. PMID: 17878380.31. Sodhi CP, Shi XH, Richardson WM, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 inhibits enterocyte proliferation via impaired beta-catenin signaling in necrotizing enterocolitis. Gastroenterology. 2010; 138:185–196. PMID: 19786028.32. De Palma G, Nadal I, Medina M, et al. Intestinal dysbiosis and reduced immunoglobulin-coated bacteria associated with coeliac disease in children. BMC Microbiol. 2010; 10:63. PMID: 20181275.33. Martin HM, Campbell BJ, Hart CA, et al. Enhanced Escherichia coli adherence and invasion in Crohn's disease and colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 2004; 127:80–93. PMID: 15236175.34. Seksik P, Rigottier-Gois L, Gramet G, et al. Alterations of the dominant faecal bacterial groups in patients with Crohn's disease of the colon. Gut. 2003; 52:237–242. PMID: 12524406.35. Swidsinski A, Weber J, Loening-Baucke V, Hale LP, Lochs H. Spatial organization and composition of the mucosal flora in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:3380–3389. PMID: 16000463.36. Heimesaat MM, Bereswill S, Fischer A, et al. Gram-negative bacteria aggravate murine small intestinal Th1-type immunopathology following oral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 2006; 177:8785–8795. PMID: 17142781.37. Im E, Riegler FM, Pothoulakis C, Rhee SH. Elevated lipopolysaccharide in the colon evokes intestinal inflammation, aggravated in immune modulator-impaired mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012; 303:G490–G497. PMID: 22723263.38. Cario E, Podolsky DK. Differential alteration in intestinal epithelial cell expression of toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and TLR4 in inflammatory bowel disease. Infect Immun. 2000; 68:7010–7017. PMID: 11083826.39. Fort MM, Mozaffarian A, Stover AG, et al. A synthetic TLR4 antagonist has anti-inflammatory effects in two murine models of inflammatory bowel disease. J Immunol. 2005; 174:6416–6423. PMID: 15879143.40. Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J, Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S, Medzhitov R. Recognition of commensal microflora by tolllike receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell. 2004; 118:229–241. PMID: 15260992.41. Abreu MT, Arnold ET, Thomas LS, et al. TLR4 and MD-2 expression is regulated by immune-mediated signals in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:20431–20437. PMID: 11923281.42. Otte JM, Cario E, Podolsky DK. Mechanisms of cross hyporesponsiveness to Toll-like receptor bacterial ligands in intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:1054–1070. PMID: 15057745.