Korean Diabetes J.
2008 Dec;32(6):477-487. 10.4093/kdj.2008.32.6.477.
Protective Effects of Glucagon Like Peptide-1 on HIT-T15 beta Cell Apoptosis via ER Stress Induced by 2-deoxy-D-glucose
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Eulji University School of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 2222455
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.6.477
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The characteristic feature of pancreatic beta cells is highly developed endoplasmic reticulum (ER) due to a heavy engagement in insulin secretion. The ER serves several important function, including post-translational modification, folding, and assembly of newly synthesized secretory proteins, and its proper function is essential to cell survival. Various stress conditions can interfere with ER function. Pancreatic beta cells may be particularly vulnerable to ER stress that causes to impair insulin biosynthesis and beta cell survival through apoptosis. Glucagon like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a new drug for treatment of type 2 diabetes and has effects on stimulation of insulin secretion and beta cell preservation. Also, it may have an antiapoptotic effect on beta cells, but detailed mechanisms are not proven. Therefore, we investigated the protective mechanism of GLP-1 in beta cells through ER stress response induced by 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2DG).
METHODS
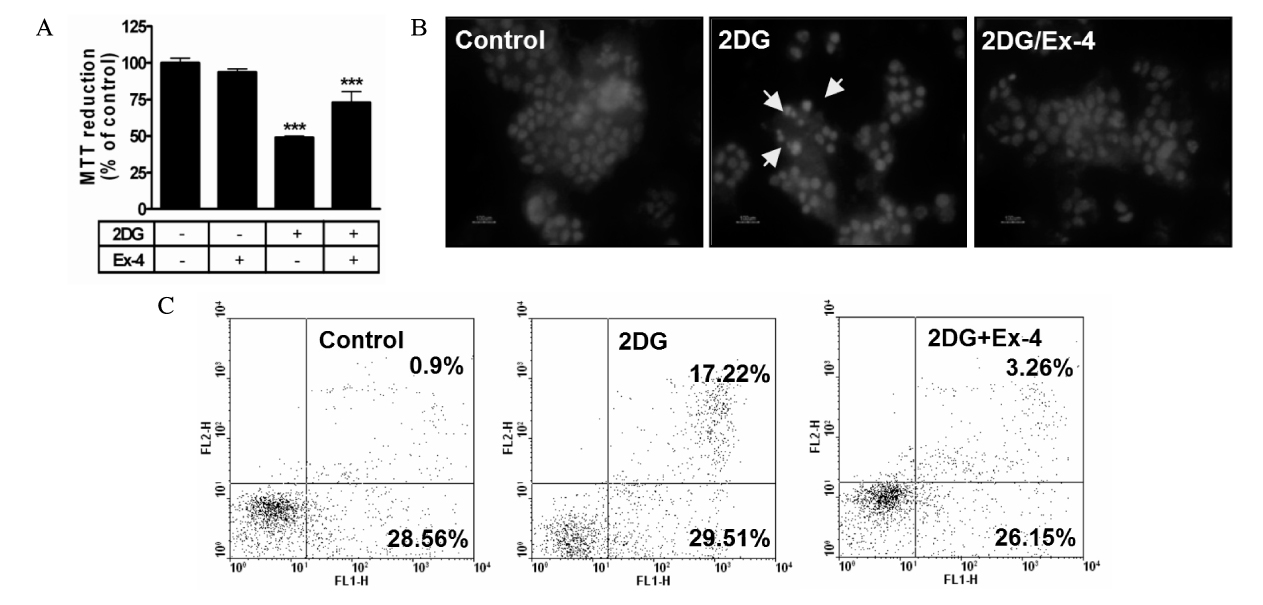
For induction of the ER stress, HIT-T15 cells (hamster beta cell line) were treated with 2DG (10 mM). Apoptosis was evaluated with MTT assay, hoechst 33342 staining and Annexin/PI flow cytometry. Expression of ER stress-related molecules was determined by real-time PCR or western blot. For blocking ER stress, we pretreated HIT-T15 cells with exendin-4 (Ex-4; GLP-1 receptor agonist) for 1 hour before stress induction.
RESULTS
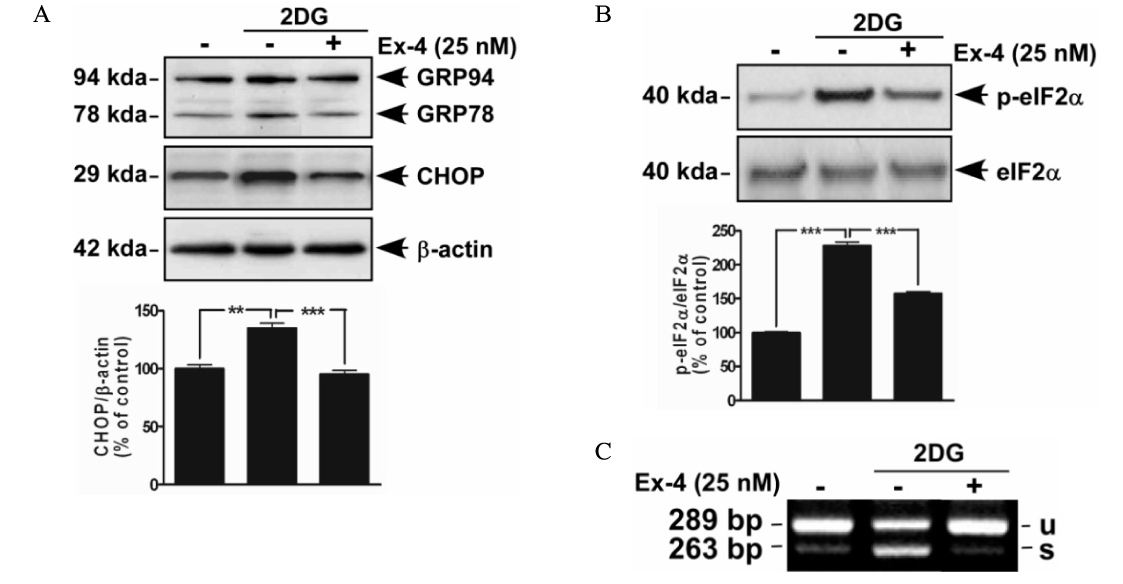
After induction with ER stress (2DG), beta cells were lost by apoptosis. We found that Ex-4 had a protective effect through ER stress related molecules (GRP78, GRP94, XBP-1, eIF2alpha, CHOP) modulation. Also, Ex-4 recovered the expression of insulin2 mRNA in beta cells.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that GLP-1 may protect beta cells apoptosis through ER stress modulation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis
Benzimidazoles
Blotting, Western
Cell Survival
Deoxyglucose
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Flow Cytometry
Glucagon
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor
HSP70 Heat-Shock Proteins
Insulin
Insulin-Secreting Cells
Membrane Proteins
Peptides
Protein Processing, Post-Translational
Proteins
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Receptors, Glucagon
RNA, Messenger
Venoms
Benzimidazoles
Deoxyglucose
Glucagon
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1
HSP70 Heat-Shock Proteins
Insulin
Membrane Proteins
Peptides
Proteins
RNA, Messenger
Receptors, Glucagon
Venoms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weir GC, Laybutt DR, Kaneto H, Bonner-Weir S, Sharma A. Beta-cell adaptation and decompensation during the progression of diabetes. Diabetes. 2001; 50 Suppl 1:S154–S159.
Article2. Poitout V, Robertson RP. Minireview: Secondary beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes-a convergence of glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity. Endocrinology. 2002; 143:339–342.3. Lorenzo A, Razzaboni B, Weir GC, Yankner BA. Pancreatic islet cell toxicity of amylin associated with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1994; 368:756–760.
Article4. Harding HP, Ron D. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the development of diabetes: a review. Diabetes. 2002; 51 Suppl 3:S455–S461.
Article5. Oyadomari S, Araki E, Mori M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells. Apoptosis. 2002; 7:335–345.6. Schröder M, Kaufman RJ. The mammalian unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005; 74:739–789.
Article7. Harding HP, Calfon M, Urano F, Novoa I, Ron D. Transcriptional and translational control in the Mammalian unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2002; 18:575–599.
Article8. Araki E, Oyadomari S, Mori M. Impact of endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway on pancreatic beta-cells and diabetes mellitus. Exp Biol Med. 2003; 228:1213–1217.9. Orskov C. Glucagon-like peptide-1, a new hormone of the entero-insular axis. Diabetologia. 1992; 35:701–711.
Article10. Stoffers DA, Kieffer TJ, Hussain MA, Drucker DJ, Bonner-Weir S, Habener JF, Egan JM. Insulinotropic glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists stimulate expression of homeodomain protein IDX-1 and increase islet size in mouse pancreas. Diabetes. 2000; 49:741–748.
Article11. Yusta B, Baggio LL, Estall JL, Koehler JA, Holland DP, Li H, Pipeleers D, Ling Z, Drucker DJ. GLP-1 receptor activation improves beta cell function and survival following induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Metab. 2006; 4:391–406.12. De León DD, Deng S, Madani R, Ahima RS, Drucker DJ, Stoffers DA. Role of endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 in islet regeneration after partial pancreatectomy. Diabetes. 2003; 52:365–371.
Article13. Perfetti R, Merkel P. Glucagon-like peptide-1: a major regulator of pancreatic beta-cell function. Eur J Endocrinol. 2000; 143:717–725.
Article14. Xu G, Stoffers DA, Habener JF, Bonner-Weir S. Exendin-4 stimulates both beta-cell replication and neogenesis, resulting in increased beta-cell mass and improved glucose tolerance in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1999; 48:2270–2276.
Article15. Wajchenberg BL. beta-cell failure in diabetes and preservation by clinical treatment. Endocr Rev. 2007; 28:187–218.16. Kang HT, Hwang ES. 2-Deoxyglucose: an anticancer and antiviral therapeutic, but not any more a low glucose mimetic. Life Sci. 2006; 78:1392–1399.
Article17. Twentyman PR, Luscombe M. A study of some variables in a tetrazolium dye (MTT) based assay for cell growth and chemosensitivity. Br J Cancer. 1987; 56:279–285.
Article18. Steensma DP, Timm M, Witzig TE. Flow cytometric methods for detection and quantification of apoptosis. Methods Mol Med. 2003; 85:323–332.19. Lin JH, Li H, Yasumura D, Cohen HR, Zhang C, Panning B, Shokat KM, Lavail MM, Walter P. IRE1 signaling affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science. 2007; 318:944–949.
Article20. Polonsky KS, Sturis J, Bell GI. Seminars in Medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus-a genetically programmed failure of the beta cell to compensate for insulin resistance. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:777–783.21. Ortsäter H, Sjöholm A. A busy cell-endoplasmic reticulum stress in the pancreatic beta-cell. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007; 277:1–5.22. Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ. The unfolded protein response: a pathway that links insulin demand with beta-cell failure and diabetes. Endocr Rev. 2008; 29:317–333.23. Wang H, Kouri G, Wollheim CB. ER stress and SREBP-1 activation are implicated in beta-cell glucolipotoxicity. J Cell Sci. 2005; 118:3905–3915.24. Lipson KL, Fonseca SG, Ishigaki S, Nguyen LX, Foss E, Bortell R, Rossini AA, Urano F. Regulation of insulin biosynthesis in pancreatic beta cells by an endoplasmic reticulum-resident protein kinase IRE1. Cell Metab. 2006; 4:245–254.
Article25. Kharroubi I, Ladrière L, Cardozo AK, Dogusan Z, Cnop M, Eizirik DL. Free fatty acids and cytokines induce pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis by different mechanisms: role of nuclear factor-kappaB and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Endocrinology. 2004; 145:5087–5096.26. Laybutt DR, Preston AM, Akerfeldt MC, Kench JG, Busch AK, Biankin AV, Biden TJ. Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to beta cell apoptosis in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007; 50:752–763.
Article27. Kaufman RJ. Stress signaling from the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: coordination of gene transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev. 1999; 13:1211–1233.
Article28. Mori K. Tripartite management of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 2000; 101:451–454.
Article29. Kaufman RJ, Scheuner D, Schröder M, Shen X, Lee K, Liu CY, Arnold SM. The unfolded protein response in nutrient sensing and differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002; 3:411–421.
Article30. Hui H, Nourparvar A, Zhao X, Perfetti R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits apoptosis of insulin-secreting cells via a cyclic 5\'-adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase A- and a phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway. Endocrinology. 2003; 144:1444–1455.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- GLP-1 Can Protect Proinflammatory Cytokines Induced Beta Cell Apoptosis through the Ubiquitination
- Beta Cells Preservation in Diabetes using GLP-1 and Its Analog
- Protective mechanism of glucose against alloxan-induced beta-cell damage: pivotal role of ATP
- Mechanism of 2-Deoxy-D-ribose-induced Damage in Pancreatic beta-cells
- Protective Mechanism of Glucose against Alloxan-Indeved HIT-T15 Cell Damage