Cancer Res Treat.
2006 Feb;38(1):54-60.
Arsenic Trioxide Induces A poptosis in Human Colorectal Adenocarcinoma HT-29 Cells Through ROS
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea. jhykim@med.yu.ac.kr
- 2Aging-Associated Vascular Disease Research Center, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Treatment with arsenic trioxide (As2O3) results in a wide range of cellular effects that includes induction of apoptosis, inhibition of cell growth, promotion or inhibition of cellular differentiation, and inhibition of angiogenesis through a variety of mechanisms. The mechanisms of As2O3-induced cell death have been mainly studied in hematological cancers, and those mechanisms in solid cancers have yet to be clearly defined. In this study, the mechanisms by which As2O3 induces apoptosis in human colorectal adenocarcinoma HT-29 cells were investigated.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
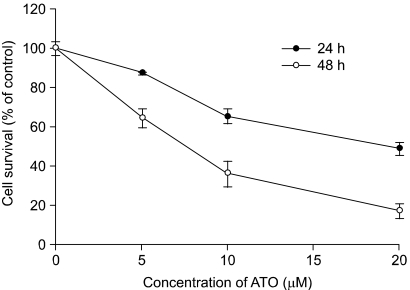
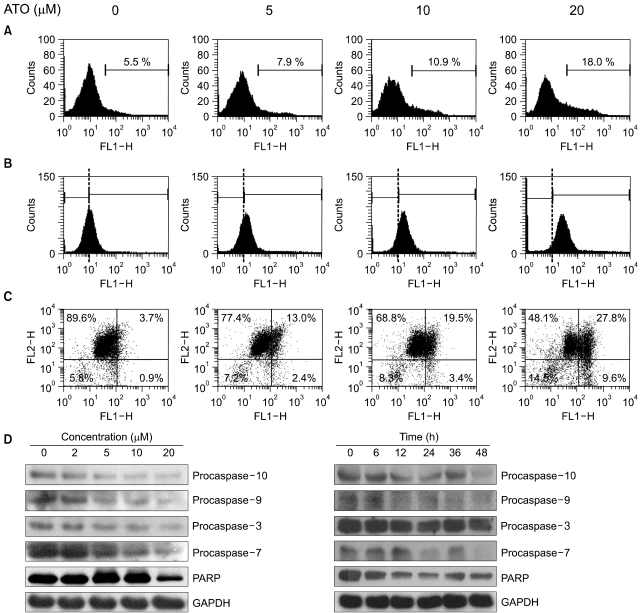
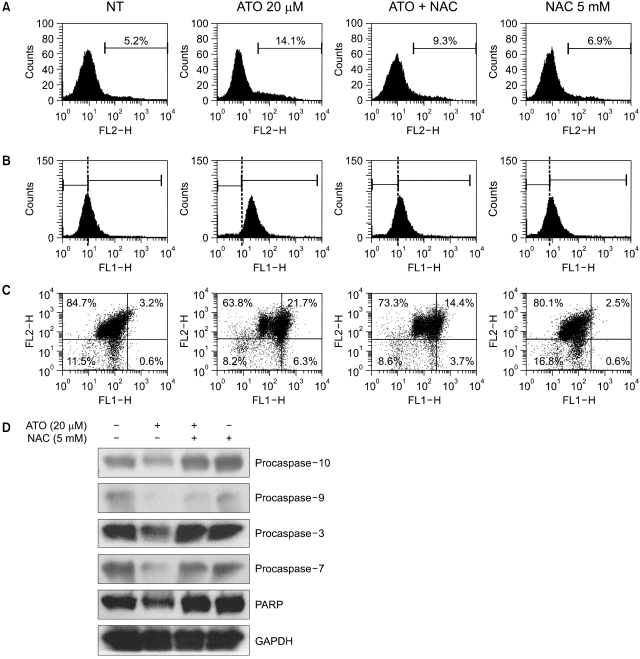
To examine the levels of apoptosis, HT-29 cells were treated with As2O3 and then we measured the percentage of Annexin V binding cells, the amount of ROS production and the mitochondrial membrane potential. Western blot analysis was performe to identify the activated caspases after As2O3 exposure, and we compared the possible target molecules of apoptosis. As2O3 treatment induced the loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential and an increase of ROS, as well as activation of caspase-3, -7, -9 and -10.
RESULTS
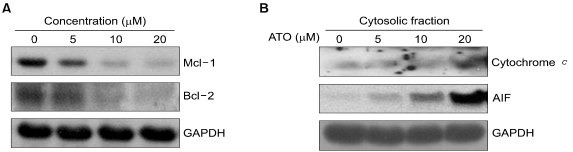
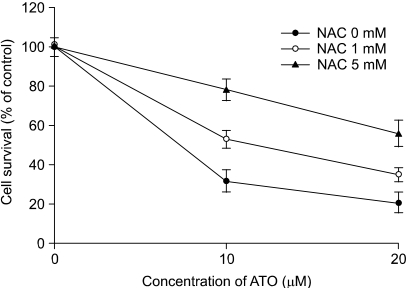
As2O3 induced apoptosis via the production of reactive oxygen species and the loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential. As2O3 induced the activation of caspase-3, -7, -9 and -10. Furthermore, As2O3 treatment downregulates the Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 expressions, and the release of cytochrome c and an apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF). Pretreating the HT-29 cells with N-acetyl-L-cysteine, which is a thiol-containing antioxidant, inhibited the As2O3- Induced Apoptosis and Caspase Activation.
CONCLUSION
Taken together, these results suggest that the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by As2O3 might play an important role in the regulation of As2O3-induced apoptosis. This cytotoxicity is mediated through a mitochondria-dependent apoptotic signal pathway in HT-29 cells.
MeSH Terms
-
Acetylcysteine
Adenocarcinoma*
Annexin A5
Apoptosis
Apoptosis Inducing Factor
Arsenic*
Blotting, Western
Caspase 3
Caspases
Cell Death
Cytochromes c
HT29 Cells*
Humans*
Membrane Potential, Mitochondrial
Mitochondria
Reactive Oxygen Species
Signal Transduction
Acetylcysteine
Annexin A5
Apoptosis Inducing Factor
Arsenic
Caspase 3
Caspases
Cytochromes c
Reactive Oxygen Species
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhang TD, Chen GQ, Wang ZG, Wang ZY, Chen SJ, Chen Z. Arsenic trioxide, a therapeutic agent for APL. Oncogene. 2001; 20:7146–7153. PMID: 11704843.
Article2. Antman KH. Introduction: the history of arsenic trioxide in cancer therapy. Oncologist. 2001; 6(Suppl 2):1–2. PMID: 11331433.
Article3. Soignet SL, Frankel SR, Douer D, Tallman MS, Kantarjian H, Calleja E, et al. United States multicenter study of arsenic trioxide in relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2001; 19:3852–3860. PMID: 11559723.
Article4. Kang YH, Yi MJ, Kim MJ, Park MT, Bae S, Kang CM, et al. Caspase-independent cell death by arsenic trioxide in human cervical cancer cells: reactive oxygen species-mediated poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation signals apoptosis-inducing factor release from mitochondria. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:8960–8967. PMID: 15604259.5. Bortner CD, Cidlowski JA. Cellular mechanisms for the repression of apoptosis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002; 42:259–281. PMID: 11807173.
Article7. Fischer U, Schulze-Osthoff K. New approaches and therapeutics targeting apoptosis in disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2005; 57:187–215. PMID: 15914467.
Article8. Ferrari R, Guardigli G, Mele D, Percoco GF, Ceconi C, Curello S. Oxidative stress during myocardial ischaemia and heart failure. Curr Pharm Des. 2004; 10:1699–1711. PMID: 15134567.
Article9. Honda K, Casadesus G, Petersen RB, Perry G, Smith MA. Oxidative stress and redox-active iron in Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004; 1012:179–182. PMID: 15105265.
Article10. Brown NS, Bicknell R. Hypoxia and oxidative stress in breast cancer. Oxidative stress: its effects on the growth, metastatic potential and response to therapy of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2001; 3:323–327. PMID: 11597322.
Article11. Pelicano H, Carney D, Huang P. ROS stress in cancer cells and therapeutic implications. Drug Resist Updat. 2004; 7:97–110. PMID: 15158766.
Article12. Salvioli S, Ardizzoni A, Franceschi C, Cossarizza A. JC-1, but not DiOC6 (3) or rhodamine 123, is a reliable fluorescent probe to assess delta psi changes in intact cells: implications for studies on mitochondrial functionality during apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 1997; 411:77–82. PMID: 9247146.13. Buzard GS, Kasprzak KS. Possible roles of nitric oxide and redox cell signaling in metal-induced toxicity and carcinogenesis: a review. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2000; 19:179–199. PMID: 10983886.14. Susin SA, Zamzami N, Castedo M, Hirsch T, Marchetti P, Macho A, et al. Bcl-2 inhibits the mitochondrial release of an apoptogenic protease. J Exp Med. 1996; 184:1331–1341. PMID: 8879205.
Article15. Cho SG, Choi EJ. Apoptotic signaling pathways: caspases and stress-activated protein kinases. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2002; 35:24–27. PMID: 16248966.
Article16. Kaufmann SH, Hengartner MO. Programmed cell death: alive and well in the new millennium. Trends Cell Biol. 2001; 11:526–534. PMID: 11719060.
Article17. Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, et al. Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 1997; 91:479–489. PMID: 9390557.
Article18. Hockenbery DM, Giedt CD, O'Neill JW, Manion MK, Banker DE. Mitochondria and apoptosis: new therapeutic targets. Adv Cancer Res. 2002; 85:203–242. PMID: 12374287.
Article19. Henry-Mowatt J, Dive C, Martinou JC, James D. Role of mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in apoptosis and cancer. Oncogene. 2004; 23:2850–2860. PMID: 15077148.
Article20. Constantini P, Jacotot E, Decaudin D, Kroemer G. Mitochondrion as a novel target of anticancer chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000; 92:1042–1053. PMID: 10880547.21. Adams JM, Cory S. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 1998; 281:1322–1326. PMID: 9735050.
Article22. Michels J, Johnson PW, Packham G. Mcl-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005; 37:267–271. PMID: 15474972.
Article23. Jabs T. Reactive oxygen intermediates as mediators of programmed cell death in plants and animals. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999; 57:231–245. PMID: 9890550.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Osteomyelitis on Maxilla Caused by Arsenic Trioxide
- Combination Treatment with Arsenic Trioxide and Sulindac Induces Apoptosis of NCI-H157 Human Lung Carcinoma Cells via ROS Generation with Mitochondrial Dysfunction
- A Case of Relapsed Acute Promyleocytic Leukemia Induced Remission with Arsenic Trioxide(As2O3)
- Inducing Apoptosis of NCI-H157 Human Lung Carcinoma Cells via Activation of Caspase Cascade by Combination Treatment with Arsenic Trioxide and Sulindac
- Antitumor Effects of Arsenic Trioxide on Neuroblastoma