Cancer Res Treat.
2006 Dec;38(4):224-228.
p53 Prevents Immature Escaping from Cell Cycle G2 Checkpoint Arrest through Inhibiting cdk2-dependent NF-Y Phosphorylation
- Affiliations
-
- 1National Research Laboratory of Cell Cycle Regulation, Department of Microbiology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. dreamer@dku.edu
- 2Department of Food Science and Technology, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Recent studies have suggested that p53 regulates the G2 checkpoint in the cell cycle and this function is required for the maintenance of genomic integrity. In this study, we addressed a role of p53 in escaping from cell cycle G2 arrest following DNA damage.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell cycle checkpoint arrest in the human colon cancer cell line HCT116 and its derivatives carry p53 or p21 deletions, were examined by FACS analysis, immunoprecipitation, Western blot and IP-kinase assay.
RESULTS
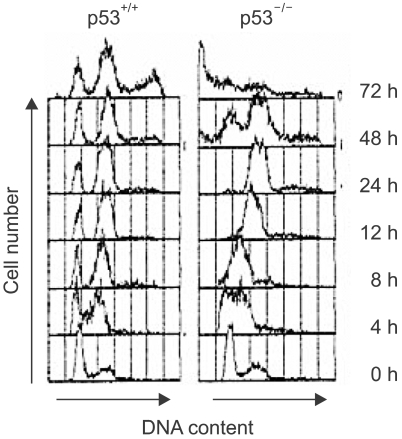
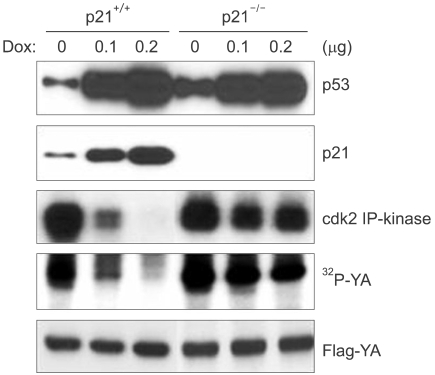
While the cells with functional p53 were arrested at both the G1 and G2 checkpoints, the p53-deficient cells failed to arrest at G1, but they were arrested at G2. However, the p53-deficient cells failed to sustain G2 checkpoint arrest and they entered mitosis earlier than did the p53-positive cells and so this resulted in extensive cell death. Cdc2 kinase becomes reactivated in p53-deficient cells in association with entry into mitosis, but not in the p53-positive cells. Upon DNA damage, the p21-deficient cells, like the p53-negative cells, not only failed to repress cdk2- dependent NF-Y phosphorylation, but they also failed to repress the expression of such cell cycle G2-regulatory genes as cdc2, cyclin B, RNR-R2 and cdc25C, which have all been previously reported as targets of NF-Y transcription factor.
CONCLUSION
p53 is essential to prevent immature escaping from cell cycle G2 checkpoint arrest through p21-mediated cdk2 inactivation, and this leads to inhibition of cdk2-dependent NF-Y phosphorylation and NF-Y dependent transcription of the cell cycle G2-rgulatory genes, including cdc2 and cyclin B.
MeSH Terms
-
Blotting, Western
CCAAT-Binding Factor
CDC2 Protein Kinase
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Cell Cycle*
Cell Death
Cell Line
Colonic Neoplasms
Cyclin B
DNA Damage
G2 Phase
Humans
Immunoprecipitation
Mitosis
Phosphorylation*
Phosphotransferases
Transcription Factors
Tumor Suppressor Protein p53
United Nations*
CCAAT-Binding Factor
CDC2 Protein Kinase
Cyclin B
Phosphotransferases
Transcription Factors
Tumor Suppressor Protein p53
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hartwell LH, Weinert TA. Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science. 1989; 246:629–634. PMID: 2683079.
Article2. Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Harris CC. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991; 253:49–53. PMID: 1905840.
Article3. Kuerbitz SJ, Plunkett BS, Walsh WV, Kastan MB. Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992; 89:7491–7495. PMID: 1323840.
Article4. Bunz F, Dutriaux A, Lengauer C, Waldman T, Zhou S, Brown JP, et al. Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science. 1998; 282:1497–1501. PMID: 9822382.5. el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, et al. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993; 75:817–825. PMID: 8242752.
Article6. Waldman T, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Uncoupling of S phase and mitosis induced by anticancer agents in cells lacking p21. Nature. 1996; 381:713–716. PMID: 8649519.
Article7. Agarwal ML, Agarwal A, Taylor WR, Stark GR. p53 controls both the G2/M and the G1 cell cycle checkpoints and mediates reversible growth arrest in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995; 92:8493–8497. PMID: 7667317.
Article8. Shin DY, Sugrue MM, Lee SW, Aaronson SA. Wild-type p53 triggers a rapid senescence program in human tumor cells lacking functional p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997; 94:9648–9653. PMID: 9275177.9. Park MS, Chae HD, Yun J, Jung M, Kim YS, Kim SH, et al. Constitutive activation of cyclin B1-associated cdc2 kinase overrides p53-mediated G2-M arrest. Cancer Res. 2000; 60:542–545. PMID: 10676633.10. Yun J, Chae HD, Choy HE, Chung J, Yoo HS, Han MH, et al. p53 negatively regulates cdc2 transcription via the CCAAT-binding NF-Y transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:29677–29682. PMID: 10514438.
Article11. Manni J, Mazzaro G, Gurtner A, Mantovani R, Haugwitz U, Krause K, et al. NF-Y mediates the transcriptional inhibition of the cyclin B1, cyclin B2, and cdc25C promoters upon induced G2 arrest. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:5570–5576. PMID: 11096075.12. Jung MS, Yun J, Chae HD, Kim JM, Kim SC, Choi TS, et al. p53 and its homologues, p63 and p73, induce a replicative senescence through inactivation of NF-Y transcription factor. Oncogene. 2001; 20:5818–5825. PMID: 11593387.
Article13. Yun J, Chae HD, Choi TS, Kim EH, Bang YJ, Chung J, et al. Cdk2-dependent phosphorylation of the NF-Y transcription factor and its involvement in the p53-p21 signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:36966–36972. PMID: 12857729.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transcription repression of a CCAAT-binding transcription factor CBF/HSP70 by p53
- Kaempferol induced the apoptosis via cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer MDA-MB-453 cells
- Molecular Aspects of Radiotherapy
- The effects of gamma-radiation on cyclin-dependent kinases and their inhibitors in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells
- The Combined Effect of Gamma Knife Irradiation and p53 Gene Transfection in Human Malignant Glioma Cell Lines