J Bacteriol Virol.
2010 Jun;40(2):67-75. 10.4167/jbv.2010.40.2.67.
Analysis of Low Molecular Weight Proteome from H. pylori Cell Extract Using the High Performance Liquid Chromatography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Institute for Subtropical Horticulture, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea.
- 2Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. khrhee1@gnu.ac.kr
- 3Deaprtment of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 1456269
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2010.40.2.67
Abstract
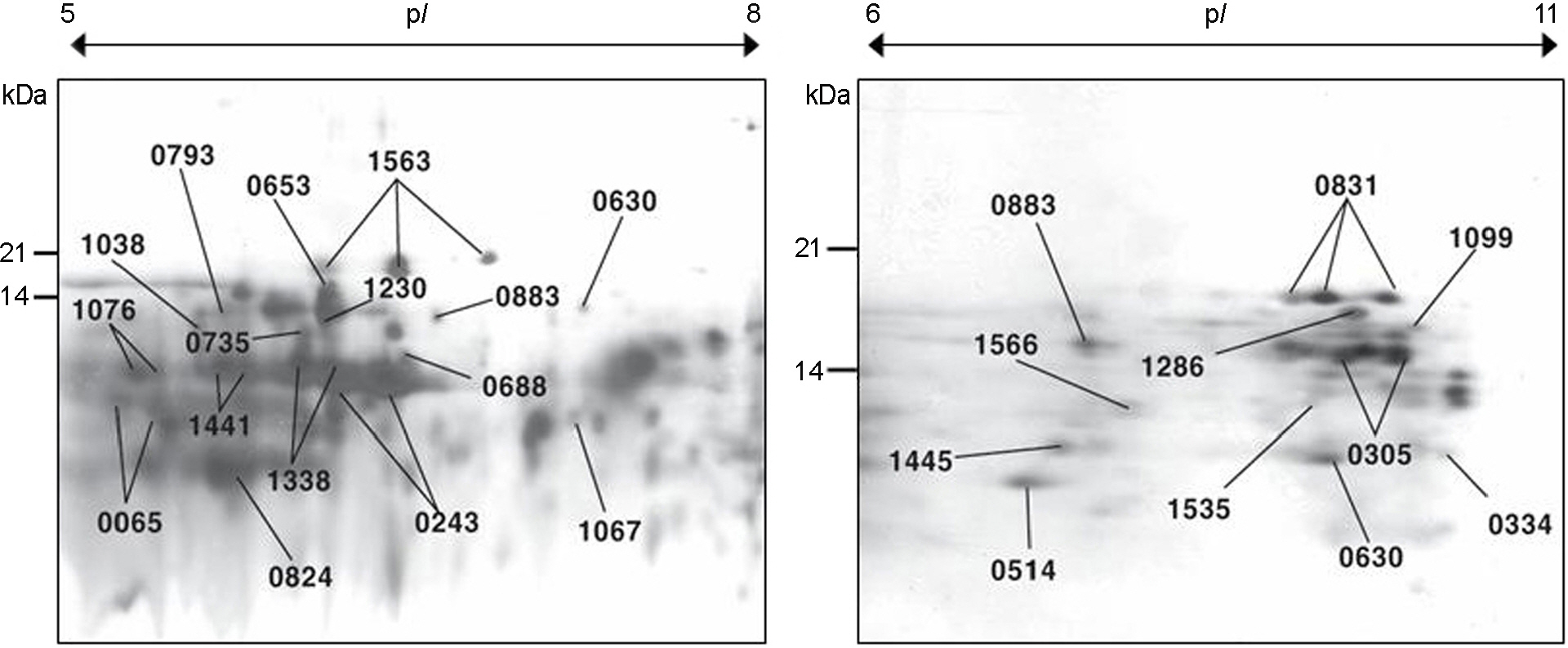
- Low molecular proteins (LMPs) which are smaller than 20 kDa are difficult to visible on a standard two-dimensional SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2-D SDS-PAGE) map. LMPs must be enriched appropriately to be analyzed. We isolated LMPs of Helicobacter pylori 26695 from 1-D polyacrylamide gel and digested by pepsin. Pepsin-digested LMPs were separated by HPLC and each fraction was analyzed by hybrid tandem mass spectrometer. Seventy nine peptides, representing 27 genes, including copper ion binding protein (CopP, 7 kDa), thioredoxin (TrxA, 11.9 kDa) and ribosomal protein L23 (Rpl23, 10.5 kDa) were identified. Some proteins larger than 40 kDa including Omp2, Omp21, Omp27, Omp30, Omp32, catalase and HP1083 were also identified. This work may give researchers a useful way to analyse the expressed LMPs which could not be identified on the conventional 2-D SDS-PAGE.
MeSH Terms
-
Acrylic Resins
Carrier Proteins
Catalase
Chimera
Chromatography, High Pressure Liquid
Chromatography, Liquid
Copper
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis, Polyacrylamide Gel
Helicobacter pylori
Molecular Weight
Pepsin A
Peptides
Proteins
Proteome
Ribosomal Proteins
Thioredoxins
Acrylic Resins
Carrier Proteins
Catalase
Copper
Pepsin A
Peptides
Proteins
Proteome
Ribosomal Proteins
Thioredoxins
Figure
Reference
-
1). Marshall BJ., Warren JR. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984. 16:1311–5.
Article2). Rhee KH., Cho MJ., Kim JB., Choi SK., Park CK., Kim YC, et al. A prospective study on the Campylobacter pylori isolated from patients of gastroduodenal inflammatory conditions. J Kor Soc Microbiol. 1988. 23:9–16.3). Rhee KH. Campylobacter and Helicobacter. Ko GG, editor. Recent clinical microbiology. 3rd. Seoul: Seoheung Publishing Company;1992. .p.p. 283–90.4). Blaser MJ. Helicobacter pylori; its role in disease. Clin Infect Dis. 1992. 15:386–91.5). Langenberg ML., Tytgat GNJ., Schipper MEI., Rietra PJG., Zanen HC., Burnett RA, et al. Campylobacter-like organisms in the stomach of patients and healthy individuals. Lancet. 1984. 323:1348–9.6). Rauws EA., Langenberg W., Houthoff HJ., Zanen HC., Tytgat GN. Campylobacter pyloridis-associated chronic active antral gastritis. A prospective study of its prevalence and the effects of antibacterial and antiulcer treatment. Gastroenterology. 1988. 94:33–40.7). Price AB., Levi J., Dolby JM., Dunscombe PL., Smith A., Clark J, et al. Campylobacter pyloridis in peptic ulcer disease: microbiology, pathology, and scanning electron microscopy. Gut. 1985. 26:1183–8.8). Peterson W. Helicobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. N Engl J Med. 1991. 324:1043–8.9). World Health Organization. Schistosomes, liver flukes and Helicobacter pylori. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 1994. 61:177–240.10). Petersen AM., Krogfelt KA. Helicobacter pylori: an invading microorganism? A review. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003. 36:117–26.11). Baik SC., Kim JB., Cho MJ., Kim YC., Park CK., Ryou HH, et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection among normal Korean adults. J Kor Soc Microbiol. 1990. 25:455–62.12). Rhee KH., Youn HS., Baik SC., Lee WK., Cho MJ., Choi HJ, et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in Korea. J Kor Soc Microbiol. 1990. 25:475–90.13). Youn HS., Baik SC., Lee WK., Cho MJ., Ryou HH., Choi HJ, et al. Serodiagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection. J Kor Soc Microbiol. 1990. 25:463–74.14). Alm RA., Ling LS., Moir DT., King BL., Brown ED., Doig PC, et al. Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature. 1999. 397:176–80.15). Tomb JF., White O., Kerlavage AR., Clayton RA., Sutton GG., Fleischmann RD, et al. The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature. 1997. 388:539–47.16). Oh JD., Kling-Bäckhed H., Giannakis M., Xu J., Fulton RS., Fulton LA, et al. The complete genome sequence of a chronic atrophic gastritis Helicobacter pylori strain: evolution during disease progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006. 103:9999–10004.17). Cho MJ., Jeon BS., Park JW., Jung TS., Song JY., Lee WK, et al. Identifying the major proteome components of Helicobacter pylori strain 26695. Electrophoresis. 2002. 23:1161–73.18). Jungblut PR., Bumann D., Haas G., Zimny-Arndt U., Holland P., Lamer S, et al. Comparative proteome analysis of Helicobacter pylori. Mol Microbiol. 2000. 36:710–25.19). Baik SC., Kim KM., Song SM., Kim DS., Jun JS., Lee SG, et al. Proteomic analysis of the sarcosine-insoluble outer membrane fraction of Helicobacter pylori strain 26695. J Bacteriol. 2004. 186:949–55.20). Bumann D., Aksu S., Wendland M., Janek K., Zimny-Arndt U., Sabarth N, et al. Proteome analysis of secreted proteins of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 2002. 70:3396–403.21). Jungblut PR., Bumann D. Immunoproteome of Helicobacter pylori. Methods Enzymol. 2002. 358:307–16.22). Cash P. Proteomics in medical microbiology. Electrophoresis. 2000. 21:1187–201.
Article23). O'Connell KL., Stults JT. Identification of mouse liver proteins on two-dimensional electrophoresis gels by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of in situ enzymatic digests. Electrophoresis. 1997. 18:349–59.24). Lee HW., Choe YH., Kim DK., Jung SY., Lee NG. Proteomic analysis of a ferric uptake regulator mutant of Helicobacter pylori: regulation of Helicobacter pylori gene expression by ferric uptake regulator and iron. Proteomics. 2004. 4:2014–27.25). Lock RA., Cordwell SJ., Coombs GW., Walsh BJ., Forbes GM. Proteome analysis of Helicobacter pylori: major proteins of type strain NCTC 11637. Pathology. 2001. 33:365–74.26). McAtee CP., Hoffman PS., Berg DE. Identification of differentially regulated proteins in metronidozole resistant Helicobacter pylori by proteome techniques. Proteomics. 2001. 1:516–21.27). Hood BL., Lucas DA., Kim G., Chan KC., Blonder J., Issaq HJ, et al. Quantitative analysis of the low molecular weight serum proteome using 18O stable isotope labeling in a lung tumor xenograft mouse model. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2005. 16:1221–30.28). Wang G., Alamuri P., Maier RJ. The diverse antioxidant systems of Helicobacter pylori. Mol Microbiol. 2006. 61:847–60.29). Cooksley C., Jenks PJ., Green A., Cockayne A., Logan RP., Hardie KR. NapA protects Helicobacter pylori from oxidative stress damage, and its production is influenced by the ferric uptake regulator. J Med Microbiol. 2003. 52:461–9.30). Yang HB., Sheu BS., Wang JT., Lin ST., Wu JJ. Serological responses of FldA and small-molecular-weight proteins of Helicobacter pylori: correlation with the presence of the gastric MALT tissue. Helicobacter. 2004. 9:81–6.31). Harper RG., Workman SR., Schuetzner S., Timperman AT., Sutton JN. Low-molecular-weight human serum proteome using ultrafiltration, isoelectric focusing, and mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis. 2004. 25:1299–306.
Article32). Keller BO., Wang Z., Li L. Low-mass proteome analysis based on liquid chromatography fractionation, nanoliter protein concentration/digestion, and microspot matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002. 782:317–29.
Article33). Dunlop KY., Li L. Automated mass analysis of low-molecularmass bacterial proteome by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2001. 925:123–32.
Article34). Lollo BA., Harvey S., Liao J., Stevens AC., Wagenknecht R., Sayen R, et al. Improved two-dimensional gel electrophoresis representation of serum proteins by using Protoclear™. Electrophoresis. 1999. 20:854–9.
Article35). Kang HL., Baik SC. Application of hemin-agarose affinity chromatography to enrich proteome components of Helicobacter pylori strain 26695. J Bacteriol Virol. 2005. 35:77–85.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficient Isolation of Dihydrophaseic acid 3′-O-β-D-Glucopyranoside from Nelumbo nucifera Seeds Using High-performance Countercurrent Chromatography and Reverse-phased High-performance Liquid Chromatography
- Proteomics Approach in Helicobacter pylori Researches
- Application of Hemin-Agarose Affinity Chromatography to Enrich Proteome Components of Helicobacter pylori Strain 26695
- Development of high-performance liquid chromatography methods for the anticoccidials: toltrazuril and diclazuril
- Identification and partial purification of antibacterial compounds against Streptococcus mutans from Galla Rhois