Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2018 Mar;22(2):215-223. 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.2.215.
Hydrogen peroxide inhibits Ca²⺠efflux through plasma membrane Ca²âº-ATPase in mouse parotid acinar cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon 35365, Korea. hspark@konyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Dental Hygiene, College of Medical Science, Konyang University, Daejeon 35365, Korea.
- 3Myunggok Medical Research Institute, Konyang University, Daejeon 35365, Korea.
- KMID: 2410111
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.2.215
Abstract
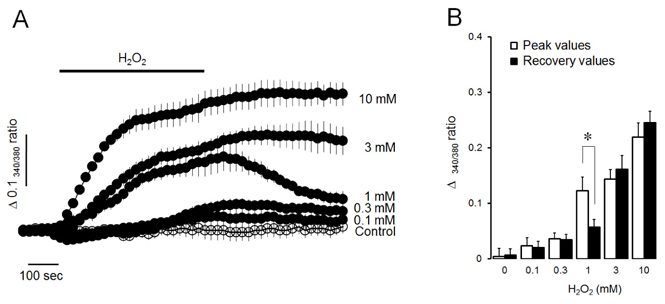
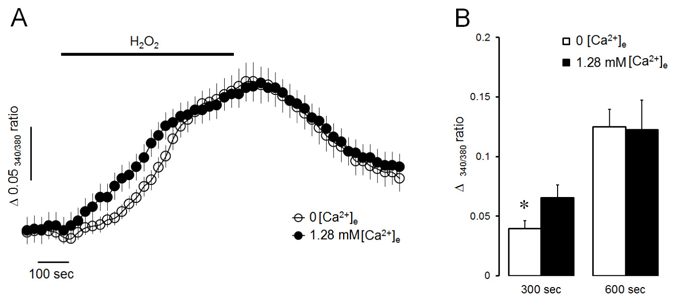
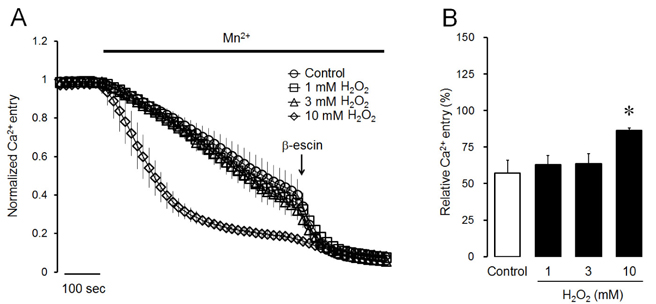
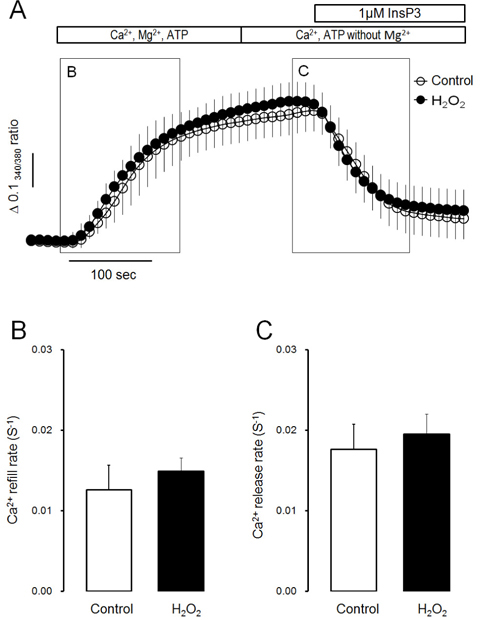
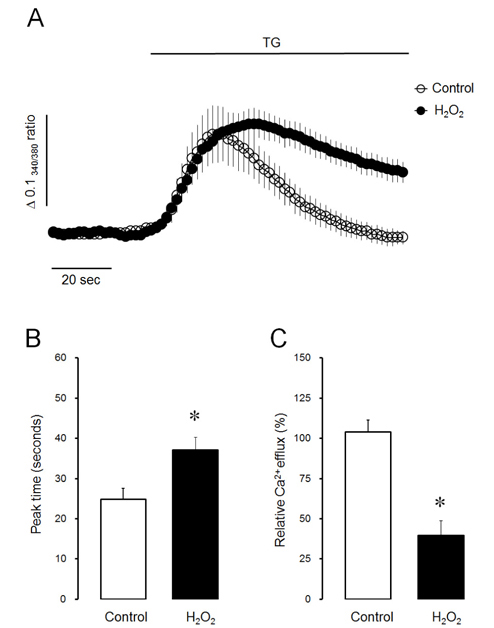
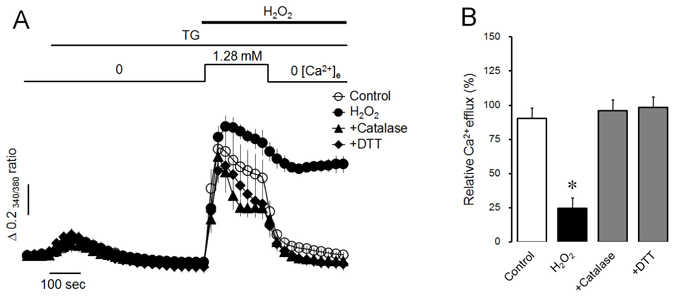
- Intracellular Ca²âº mobilization is closely linked with the initiation of salivary secretion in parotid acinar cells. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are known to be related to a variety of oxidative stress-induced cellular disorders and believed to be involved in salivary impairments. In this study, we investigated the underlying mechanism of hydrogen peroxide (Hâ‚‚Oâ‚‚) on cytosolic Ca²âº accumulation in mouse parotid acinar cells. Intracellular Ca²âº levels were slowly elevated when 1 mM Hâ‚‚Oâ‚‚ was perfused in the presence of normal extracellular Ca²âº. In a Ca²âº-free medium, 1 mM Hâ‚‚Oâ‚‚ still enhanced the intracellular Ca²âº level. Ca²âº entry tested using manganese quenching technique was not affected by perfusion of 1 mM Hâ‚‚Oâ‚‚. On the other hand, 10 mM Hâ‚‚Oâ‚‚ induced more rapid Ca²âº accumulation and facilitated Ca²âº entry from extracellular fluid. Ca²âº refill into intracellular Ca²âº store and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (1 µM)-induced Ca²âº release from Ca²âº store was not affected by 1 mM Hâ‚‚Oâ‚‚ in permeabilized cells. Ca²âº efflux through plasma membrane Ca²âº-ATPase (PMCA) was markedly blocked by 1 mM Hâ‚‚Oâ‚‚ in thapsigargin-treated intact acinar cells. Antioxidants, either catalase or dithiothreitol, completely protected Hâ‚‚Oâ‚‚-induced Ca²âº accumulation through PMCA inactivation. From the above results, we suggest that excessive production of Hâ‚‚Oâ‚‚ under pathological conditions may lead to cytosolic Ca²âº accumulation and that the primary mechanism of Hâ‚‚Oâ‚‚-induced Ca²âº accumulation is likely to inhibit Ca²âº efflux through PMCA rather than mobilize Ca²âº ions from extracellular medium or intracellular stores in mouse parotid acinar cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acinar Cells*
Animals
Antioxidants
Calcium
Catalase
Cell Membrane*
Cytosol
Dithiothreitol
Extracellular Fluid
Hand
Hydrogen Peroxide*
Hydrogen*
Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate
Ions
Manganese
Mice*
Perfusion
Plasma Membrane Calcium-Transporting ATPases
Plasma*
Reactive Oxygen Species
Antioxidants
Calcium
Catalase
Dithiothreitol
Hydrogen
Hydrogen Peroxide
Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate
Ions
Manganese
Plasma Membrane Calcium-Transporting ATPases
Reactive Oxygen Species
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ca2+ entry through reverse Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in NCI-H716, glucagon-like peptide-1 secreting cells
Kyung Jin Choi, Jin Wook Hwang, Se Hoon Kim, Hyung Seo Park
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2022;26(3):219-225. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2022.26.3.219.
Reference
-
1. Ambudkar IS. Calcium signalling in salivary gland physiology and dysfunction. J Physiol. 2016; 594:2813–2824.
Article2. Petersen OH. Stimulus-secretion coupling: cytoplasmic calcium signals and the control of ion channels in exocrine acinar cells. J Physiol. 1992; 448:1–51.
Article3. Fox PC. Acquired salivary dysfunction. Drugs and radiation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998; 842:132–137.
Article4. Abdollahi M, Fooladian F, Emami B, Zafari K, Bahreini-Moghadam A. Protection by sildenafil and theophylline of lead acetate-induced oxidative stress in rat submandibular gland and saliva. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2003; 22:587–592.5. Acauan MD, Figueiredo MA, Cherubini K, Gomes AP, Salum FG. Radiotherapy-induced salivary dysfunction: Structural changes, pathogenetic mechanisms and therapies. Arch Oral Biol. 2015; 60:1802–1810.
Article6. Yamada T, Ryo K, Tai Y, Tamaki Y, Inoue H, Mishima K, Tsubota K, Saito I. Evaluation of therapeutic effects of astaxanthin on impairments in salivary secretion. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010; 47:130–137.
Article7. Abedi SM, Yarmand F, Motallebnejad M, Seyedmajidi M, Moslemi D, Ashrafpour M, Bijani A, Moghadamnia A, Mardanshahi A, Hosseinimehr SJ. Vitamin E protects salivary glands dysfunction induced by ionizing radiation in rats. Arch Oral Biol. 2015; 60:1403–1409.
Article8. Ryo K, Yamada H, Nakagawa Y, Tai Y, Obara K, Inoue H, Mishima K, Saito I. Possible involvement of oxidative stress in salivary gland of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Pathobiology. 2006; 73:252–260.9. Pagano G, Castello G, Pallardó FV. Sjøgren's syndrome-associated oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction: prospects for chemoprevention trials. Free Radic Res. 2013; 47:71–73.
Article10. Gardner AM, Xu FH, Fady C, Jacoby FJ, Duffey DC, Tu Y, Lichtenstein A. Apoptotic vs. nonapoptotic cytotoxicity induced by hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic Biol Med. 1997; 22:73–83.
Article11. Aruoma OI. Free radicals, oxidative stress, and antioxidants in human health and disease. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1998; 75:199–212.
Article12. Kourie JI. Interaction of reactive oxygen species with ion transport mechanisms. Am J Physiol. 1998; 275:C1–24.13. Kiselyov K, Muallem S. ROS and intracellular ion channels. Cell Calcium. 2016; 60:108–114.
Article14. Yu BP. Cellular defenses against damage from reactive oxygen species. Physiol Rev. 1994; 74:139–162.
Article15. Dröge W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev. 2002; 82:47–95.
Article16. Roveri A, Coassin M, Maiorino M, Zamburlini A, van Amsterdam FT, Ratti E, Ursini F. Effect of hydrogen peroxide on calcium homeostasis in smooth muscle cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992; 297:265–270.
Article17. Gen W, Tani M, Takeshita J, Ebihara Y, Tamaki K. Mechanisms of Ca2+ overload induced by extracellular H2O2 in quiescent isolated rat cardiomyocytes. Basic Res Cardiol. 2001; 96:623–629.18. Sun L, Yau HY, Lau OC, Huang Y, Yao X. Effect of hydrogen peroxide and superoxide anions on cytosolic Ca2+: comparison of endothelial cells from large-sized and small-sized arteries. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e25432.19. Giambelluca MS, Gende OA. Hydrogen peroxide activates calcium influx in human neutrophils. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008; 309:151–156.
Article20. Liu X, Cotrim A, Teos L, Zheng C, Swaim W, Mitchell J, Mori Y, Ambudkar I. Loss of TRPM2 function protects against irradiation-induced salivary gland dysfunction. Nat Commun. 2013; 4:1515.
Article21. Kozai D, Ogawa N, Mori Y. Redox regulation of transient receptor potential channels. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014; 21:971–986.
Article22. Santiago E, Climent B, Muñoz M, García-Sacristán A, Rivera L, Prieto D. Hydrogen peroxide activates store-operated Ca2+ entry in coronary arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 2015; 172:5318–5332.23. Zaidi A, Barŕon L, Sharov VS, Schöneich C, Michaelis EK, Michaelis ML. Oxidative inactivation of purified plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase by hydrogen peroxide and protection by calmodulin. Biochemistry. 2003; 42:12001–12010.24. Bruce JI, Elliott AC. Oxidant-impaired intracellular Ca2+ signaling in pancreatic acinar cells: role of the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007; 293:C938–C950.25. Yoon MN, Kim DK, Kim SH, Park HS. Hydrogen peroxide attenuates refilling of intracellular calcium store in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017; 21:233–239.
Article26. Park HS, Betzenhauser MJ, Zhang Y, Yule DI. Regulation of Ca2+ release through inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors by adenine nucleotides in parotid acinar cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012; 302:G97–G104.27. Choi KJ, Kim KS, Kim SH, Kim DK, Park HS. Caffeine and 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) have different ability to inhibit intracellular calcium mobilization in pancreatic acinar cell. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010; 14:105–111.
Article28. Gallacher DV, Petersen OH. Stimulus-secretion coupling in mammalian salivary glands. Int Rev Physiol. 1983; 28:1–52.29. Yule DI, Straub SV, Bruce JI. Modulation of Ca2+ oscillations by phosphorylation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptors. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003; 31:954–957.30. Melvin JE, Yule D, Shuttleworth T, Begenisich T. Regulation of fluid and electrolyte secretion in salivary gland acinar cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 2005; 67:445–469.
Article31. Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003; 4:517–529.
Article32. Won JH, Cottrell WJ, Foster TH, Yule DI. Ca2+ release dynamics in parotid and pancreatic exocrine acinar cells evoked by spatially limited flash photolysis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007; 293:G1166–G1177.33. Clapham DE. Calcium signaling. Cell. 2007; 131:1047–1058.
Article34. Petersen OH. Calcium signalling and secretory epithelia. Cell Calcium. 2014; 55:282–289.
Article35. Pariente JA, Camello C, Camello PJ, Salido GM. Release of calcium from mitochondrial and nonmitochondrial intracellular stores in mouse pancreatic acinar cells by hydrogen peroxide. J Membr Biol. 2001; 179:27–35.
Article36. Baggaley EM, Elliott AC, Bruce JI. Oxidant-induced inhibition of the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase in pancreatic acinar cells: role of the mitochondria. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008; 295:C1247–C1260.37. Strehler EE, Caride AJ, Filoteo AG, Xiong Y, Penniston JT, Enyedi A. Plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPases as dynamic regulators of cellular calcium handling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007; 1099:226–236.38. Bellomo G, Mirabelli F, Richelmi P, Orrenius S. Critical role of sulfhydryl group(s) in ATP-dependent Ca2+ sequestration by the plasma membrane fraction from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1983; 163:136–139.39. Zaidi A, Barŕon L, Sharov VS, Schöneich C, Michaelis EK, Michaelis ML. Oxidative inactivation of purified plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase by hydrogen peroxide and protection by calmodulin. Biochemistry. 2003; 42:12001–12010.40. Pengpanichpakdee N, Thadtapong T, Auparakkitanon S, Wilairat P. Plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase sulfhydryl modifications: implication for oxidized red cell. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2012; 43:1252–1257.41. Strehler EE, Zacharias DA. Role of alternative splicing in generating isoform diversity among plasma membrane calcium pumps. Physiol Rev. 2001; 81:21–50.
Article42. Grover AK, Samson SE, Misquitta CM. Sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump isoform SERCA3 is more resistant than SERCA2b to peroxide. Am J Physiol. 1997; 273:C420–C425.43. Barnes KA, Samson SE, Grover AK. Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-pump isoform SERCA3a is more resistant to superoxide damage than SERCA2b. Mol Cell Biochem. 2000; 203:17–21.44. Yin D, Kuczera K, Squier TC. The sensitivity of carboxyl-terminal methionines in calmodulin isoforms to oxidation by H2O2 modulates the ability to activate the plasma membrane Ca-ATPase. Chem Res Toxicol. 2000; 13:103–110.45. Baggaley E, McLarnon S, Demeter I, Varga G, Bruce JI. Differential regulation of the apical plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase by protein kinase A in parotid acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:37678–37693.46. Belan PV, Gerasimenko OV, Tepikin AV, Petersen OH. Localization of Ca2+ extrusion sites in pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:7615–7619.47. Lee MG, Xu X, Zeng W, Diaz J, Kuo TH, Wuytack F, Racymaekers L, Muallem S. Polarized expression of Ca2+ pumps in pancreatic and salivary gland cells. Role in initiation and propagation of [Ca2+]i waves. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272:15771–15776.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hydrogen peroxide attenuates refilling of intracellular calcium store in mouse pancreatic acinar cells
- Calcium Signaling of Lysophosphatidylethanolamine through LPA1 in Human SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells
- Calcium Signaling in Salivary Secretion
- Alteration of Expression of Ca(2+) Signaling Proteins and Adaptation of Ca(2+) Signaling in SERCA2(+/-) Mouse Parotid Acini
- N-acetyl-L-cysteine and cysteine increase intracellular calcium concentration in human neutrophils