Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2017 Nov;21(6):579-589. 10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.6.579.
Genistein attenuates isoflurane-induced neurotoxicity and improves impaired spatial learning and memory by regulating cAMP/CREB and BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Shandong Cancer Hospital, Jinan 250117, Shandong Province, China.
- 2Department of Gynecology, Shandong Cancer Hospital, Jinan 250117, Shandong Province, China. xueliandu@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2395252
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.6.579
Abstract
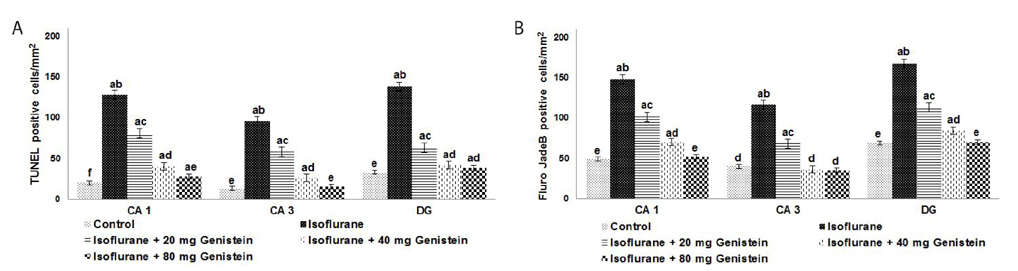
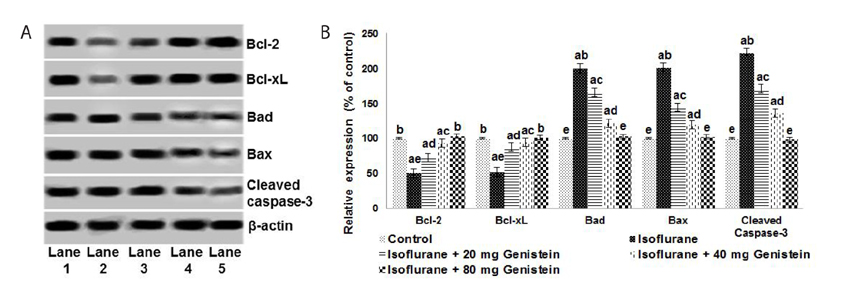
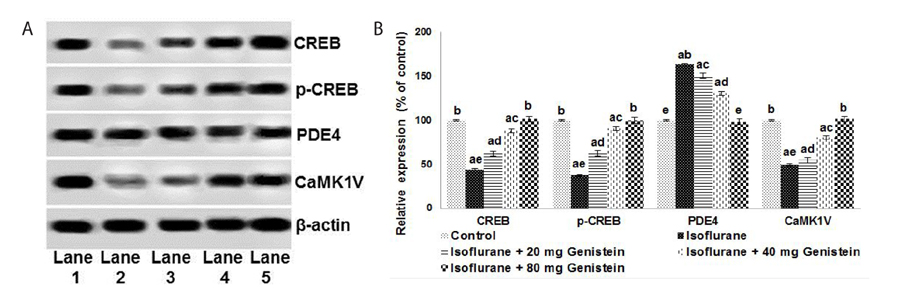
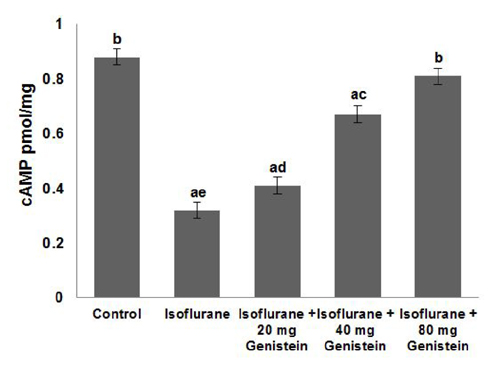
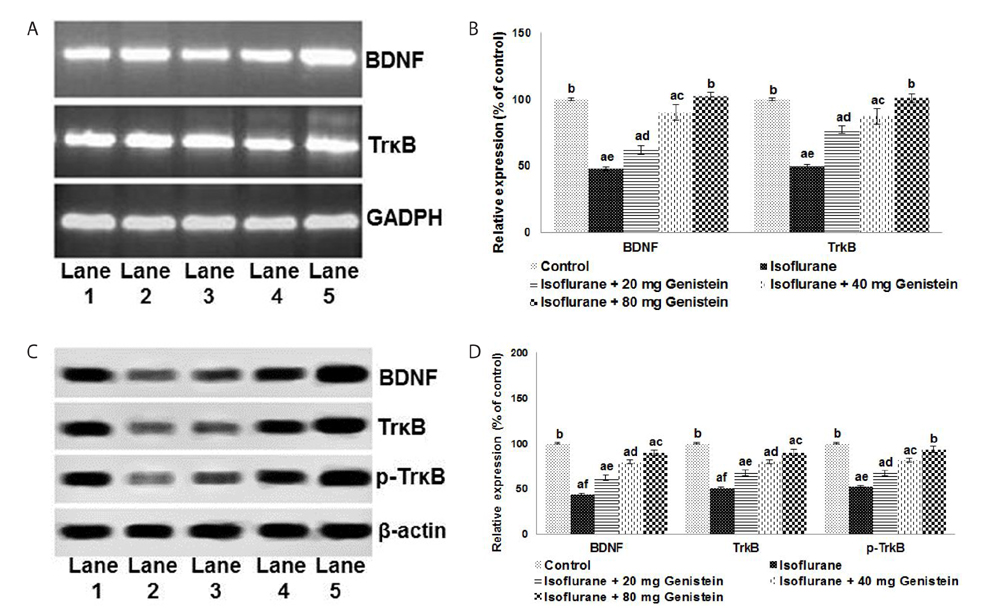
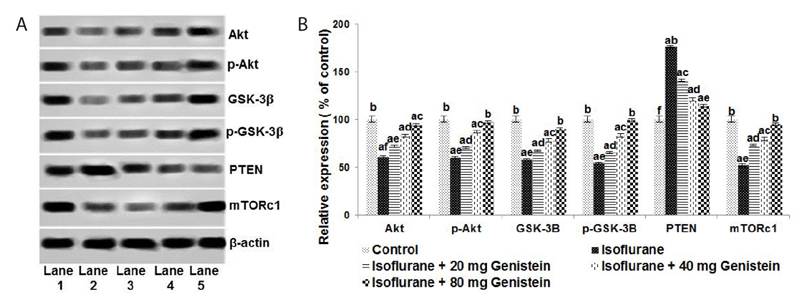
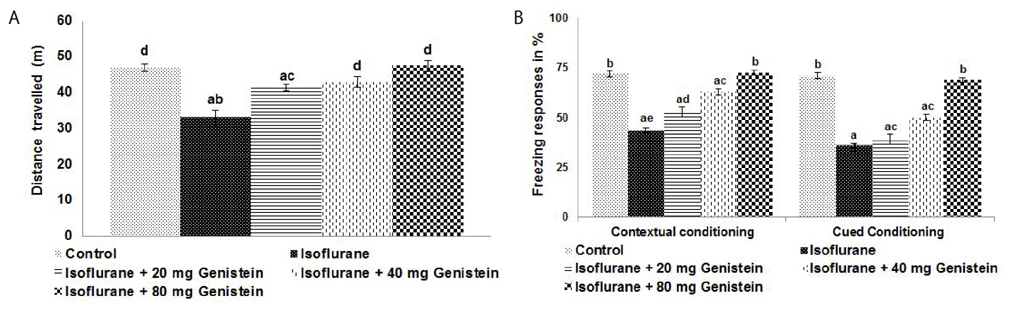
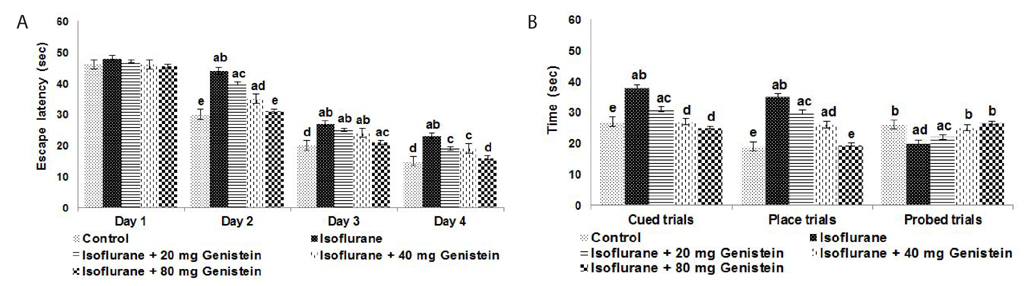
- Anesthetics are used extensively in surgeries and related procedures to prevent pain. However, there is some concern regarding neuronal degeneration and cognitive deficits arising from regular anesthetic exposure. Recent studies have indicated that brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB) are involved in learning and memory processes. Genistein, a plant-derived isoflavone, has been shown to exhibit neuroprotective effects. The present study was performed to examine the protective effect of genistein against isoflurane-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Neonatal rats were exposed to isoflurane (0.75%, 6 hours) on postnatal day 7 (P7). Separate groups of rat pups were orally administered genistein at doses of 20, 40, or 80 mg/kg body weight from P3 to P15 and then exposed to isoflurane anesthesia on P7. Neuronal apoptosis was detected by TUNEL assay and FluoroJade B staining following isoflurane exposure. Genistein significantly reduced apoptosis in the hippocampus, reduced the expression of proapoptotic factors (Bad, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3), and increased the expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. RT-PCR analysis revealed enhanced BDNF and TrkB mRNA levels. Genistein effectively upregulated cAMP levels and phosphorylation of CREB and TrkB, leading to activation of cAMP/CREB-BDNF-TrkB signaling. PI3K/Akt signaling was also significantly activated. Genistein administration improved general behavior and enhanced learning and memory in the rats. These observations suggest that genistein exerts neuroprotective effects by suppressing isoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis and by activating cAMP/CREB-BDNF-TrkB-PI3/Akt signaling.
MeSH Terms
-
Anesthesia
Anesthetics
Animals
Apoptosis
Body Weight
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor
Cognition Disorders
Cyclic AMP Response Element-Binding Protein
Genistein*
Hippocampus
In Situ Nick-End Labeling
Isoflurane
Learning
Memory*
Neurons
Neuroprotective Agents
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase
Phosphorylation
Rats
RNA, Messenger
Spatial Learning*
Anesthetics
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor
Cyclic AMP Response Element-Binding Protein
Genistein
Isoflurane
Neuroprotective Agents
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase
RNA, Messenger
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ursolic acid in health and disease
Dae Yun Seo, Sung Ryul Lee, Jun-Won Heo, Mi-Hyun No, Byoung Doo Rhee, Kyung Soo Ko, Hyo-Bum Kwak, Jin Han
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;22(3):235-248. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.3.235.
Reference
-
1. Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Hartman RE, Izumi Y, Benshoff ND, Dikranian K, Zorumski CF, Olney JW, Wozniak DF. Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. J Neurosci. 2003; 23:876–882.2. Brambrink AM, Evers AS, Avidan MS, Farber NB, Smith DJ, Zhang X, Dissen GA, Creeley CE, Olney JW. Isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in the neonatal rhesus macaque brain. Anesthesiology. 2010; 112:834–841.3. Kong F, Xu L, He D, Zhang X, Lu H. Effects of gestational isoflurane exposure on postnatal memory and learning in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011; 670:168–174.4. Li Y, Liu C, Zhao Y, Hu K, Zhang J, Zeng M, Luo T, Jiang W, Wang H. Sevoflurane induces short-term changes in proteins in the cerebral cortices of developing rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2013; 57:380–390.5. Li Y, Wang F, Liu C, Zeng M, Han X, Luo T, Jiang W, Xu J, Wang H. JNK pathway may be involved in isoflurane-induced apoptosis in the hippocampi of neonatal rats. Neurosci Lett. 2013; 545:17–22.6. Flick RP, Katusic SK, Colligan RC, Wilder RT, Voigt RG, Olson MD, Sprung J, Weaver AL, Schroeder DR, Warner DO. Cognitive and behavioral outcomes after early exposure to anesthesia and surgery. Pediatrics. 2011; 128:e1053–e1061.7. Gentry KR, Steele LM, Sedensky MM, Morgan PG. Early developmental exposure to volatile anesthetics causes behavioral defects in Caenorhabditis elegans. Anesth Analg. 2013; 116:185–189.8. Head BP, Patel HH, Niesman IR, Drummond JC, Roth DM, Patel PM. Inhibition of p75 neurotrophin receptor attenuates isoflurane-mediated neuronal apoptosis in the neonatal central nervous system. Anesthesiology. 2009; 110:813–825.9. Xiong WX, Zhou GX, Wang B, Xue ZG, Wang L, Sun HC, Ge SJ. Impaired spatial learning and memory after sevoflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia in aged rats is associated with down-regulated cAMP/CREB signaling. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e79408.10. Wu J, Zhang M, Li H, Sun X, Hao S, Ji M, Yang J, Li K. BDNF pathway is involved in the protective effects of SS-31 on isoflurane-induced cognitive deficits in aging mice. Behav Brain Res. 2016; 305:115–121.11. Bourtchuladze R, Frenguelli B, Blendy J, Cioffi D, Schutz G, Silva AJ. Deficient long-term memory in mice with a targeted mutation of the cAMP-responsive element-binding protein. Cell. 1994; 79:59–68.12. Impey S, Mark M, Villacres EC, Poser S, Chavkin C, Storm DR. Induction of CRE-mediated gene expression by stimuli that generate long-lasting LTP in area CA1 of the hippocampus. Neuron. 1996; 16:973–982.13. Nakagawa S, Kim JE, Lee R, Chen J, Fujioka T, Malberg J, Tsuji S, Duman RS. Localization of phosphorylated cAMP response element-binding protein in immature neurons of adult hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2002; 22:9868–9876.14. Fujioka T, Fujioka A, Duman RS. Activation of cAMP signaling facilitates the morphological maturation of newborn neurons in adult hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2004; 24:319–328.15. Ao H, Ko SW, Zhuo M. CREB activity maintains the survival of cingulate cortical pyramidal neurons in the adult mouse brain. Mol Pain. 2006; 2:15.16. Schneider HH. Brain cAMP response to phosphodiesterase inhibitors in rats killed by microwave irradiation or decapitation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984; 33:1690–1693.17. Li YF, Huang Y, Amsdell SL, Xiao L, O'Donnell JM, Zhang HT. Antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects of the phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor rolipram on behavior depend on cyclic AMP response element binding protein-mediated neurogenesis in the hip pocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009; 34:2404–2419.18. Brightwell JJ, Smith CA, Neve RL, Colombo PJ. Long-term memory for place learning is facilitated by expression of cAMP response element-binding protein in the dorsal hippocampus. Learn Mem. 2007; 14:195–199.19. Rosenegger D, Parvez K, Lukowiak K. Enhancing memory formation by altering protein phosphorylation balance. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2008; 90:544–552.20. Zhang F, Zhu ZQ, Liu DX, Zhang C, Gong QH, Zhu YH. Emulsified isoflurane anesthesia decreases brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and induces cognitive dysfunction in adult rats. Exp Ther Med. 2014; 8:471–477.21. Minichiello L. TrkB signalling pathways in LTP and learning. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009; 10:850–860.22. Park H, Poo MM. Neurotrophin regulation of neural circuit development and function. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013; 14:7–23.23. Huang EJ, Reichardt LF. Trk receptors: roles in neuronal signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003; 72:609–642.24. Reichardt LF. Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2006; 361:1545–1564.25. Takei N, Kawamura M, Hara K, Yonezawa K, Nawa H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances neuronal translation by activating multiple initiation processes: comparison with the effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:42818–42825.26. Horwood JM1, Dufour F, Laroche S, Davis S. Signalling mechanisms mediated by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt cascade in synaptic plasticity and memory in the rat. Eur J Neurosci. 2006; 23:3375–3384.27. Chiang HC, Wang L, Xie Z, Yau A, Zhong Y. PI3 kinase signaling is involved in Abeta-induced memory loss in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:7060–7065.28. Mizuno M, Yamada K, Takei N, Tran MH, He J, Nakajima A, Nawa H, Nabeshima T. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: a molecule mediating BDNF-dependent spatial memory formation. Mol Psychiatry. 2003; 8:217–224.29. Pontén E, Fredriksson A, Gordh T, Eriksson P, Viberg H. Neonatal exposure to propofol affects BDNF but not CaMKII, GAP-43, synaptophysin and tau in the neonatal brain and causes an altered behavioural response to diazepam in the adult mouse brain. Behav Brain Res. 2011; 223:75–80.30. Gętek M, Czech N, Muc-Wierzgoń M, Grochowska-Niedworok E, Kokot T, Nowakowska-Zajdel E. The active role of leguminous plant components in type 2 diabetes. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014; 2014:293961.31. Xu SZ, Zhong W, Ghavideldarestani M, Saurabh R, Lindow SW, Atkin SL. Multiple mechanisms of soy isoflavones against oxidative stress-induced endothelium injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009; 47:167–175.32. Behloul N, Wu G. Genistein: a promising therapeutic agent for obesity and diabetes treatment. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013; 698:31–38.33. Ganai AA, Khan AA, Malik ZA, Farooqi H. Genistein modulates the expression of NF-κB and MAPK (p-38 and ERK1/2), thereby attenuating d-Galactosamine induced fulminant hepatic failure in Wistar rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015; 283:139–146.34. Su P, Zhang J, Wang S, Aschner M, Cao Z, Zhao F, Wang D, Chen J, Luo W. Genistein alleviates lead-induced neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo: Involvement of multiple signaling pathways. Neurotoxicology. 2016; 53:153–164.35. Spoerlein C, Mahal K, Schmidt H, Schobert R. Effects of chrysin, apigenin, genistein and their homoleptic copper(II) complexes on the growth and metastatic potential of cancer cells. J Inorg Biochem. 2013; 127:107–115.36. Orliaguet G, Vivien B, Langeron O, Bouhemad B, Coriat P, Riou B. Minimum alveolar concentration of volatile anesthetics in rats during postnatal maturation. Anesthesiology. 2001; 95:734–739.37. Wu J, Dong L, Zhang M, Jia M, Zhang G, Qiu L, Ji M, Yang J. Class I histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid reverses cognitive deficits in a mouse model of septic encephalopathy. Neurochem Res. 2013; 38:2440–2449.38. Ji M, Dong L, Jia M, Liu W, Zhang M, Ju L, Yang J, Xie Z, Yang J. Epigenetic enhancement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling pathway improves cognitive impairments induced by isoflurane exposure in aged rats. Mol Neurobiol. 2014; 50:937–944.39. Kim JJ, Fanselow MS. Modality-specific retrograde amnesia of fear. Science. 1992; 256:675–677.40. Lin D, Zuo Z. Isoflurane induces hippocampal cell injury and cognitive impairments in adult rats. Neuropharmacology. 2011; 61:1354–1359.41. Satomoto M, Satoh Y, Terui K, Miyao H, Takishima K, Ito M, Imaki J. Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane induces abnormal social behaviors and deficits in fear conditioning in mice. Anesthesiology. 2009; 110:628–637.42. Istaphanous GK, Howard J, Nan X, Hughes EA, McCann JC, McAuliffe JJ, Danzer SC, Loepke AW. Comparison of the neuroapoptotic properties of equipotent anesthetic concentrations of desflurane, isoflurane, or sevoflurane in neonatal mice. Anesthesiology. 2011; 114:578–587.43. Dong Y, Zhang G, Zhang B, Moir RD, Xia W, Marcantonio ER, Culley DJ, Crosby G, Tanzi RE, Xie Z. The common inhalational anesthetic sevoflurane induces apoptosis and increases beta-amyloid protein levels. Arch Neurol. 2009; 66:620–631.44. Culley DJ, Baxter MG, Yukhananov R, Crosby G. Long-term impairment of acquisition of a spatial memory task following isoflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia in rats. Anesthesiology. 2004; 100:309–314.45. DiMaggio CJ, Sun L, Kakavouli A, Li G. Exposure to anesthesia and the risk of developmental and behavioral disorders in young children. Anesthesiology. 2008; 109:A1415.46. Wilder RT, Flick RP, Sprung J, Katusic SK, Barbaresi WJ, Mickelson C, Gleich SJ, Schroeder DR, Weaver AL, Warner DO. Early exposure to anesthesia and learning disabilities in a population-based birth cohort. Anesthesiology. 2009; 110:796–804.47. Sakamoto K, Karelina K, Obrietan K. CREB: a multifaceted regulator of neuronal plasticity and protection. J Neurochem. 2011; 116:1–9.48. Kida S, Serita T. Functional roles of CREB as a positive regulator in the formation and enhancement of memory. Brain Res Bull. 2014; 105:17–24.49. Gonzalez GA, Montminy MR. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989; 59:675–680.50. Gonzalez GA, Yamamoto KK, Fischer WH, Karr D, Menzel P, Biggs W 3rd, Vale WW, Montminy MR. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989; 337:749–752.51. Carlezon WA Jr, Duman RS, Nestler EJ. The many faces of CREB. Trends Neurosci. 2005; 28:436–445.52. Yamashima T. 'PUFA-GPR40-CREB signaling' hypothesis for the adult primate neurogenesis. Prog Lipid Res. 2012; 51:221–231.53. Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, Birnbaum MJ, Yao R, Cooper GM, Segal RA, Kaplan DR, Greenberg ME. Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt. Science. 1997; 275:661–665.54. Brunet A, Datta SR, Greenberg ME. Transcription-dependent and -independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001; 11:297–305.55. Ma D, Williamson P, Januszewski A, Nogaro MC, Hossain M, Ong LP, Shu Y, Franks NP, Maze M. Xenon mitigates isoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis in the developing rodent brain. Anesthesiology. 2007; 106:746–753.56. Hsu SY, Kaipia A, Zhu L, Hsueh AJ. Interference of BAD (Bcl-xL/ Bcl-2-associated death promoter)-induced apoptosis in mammalian cells by 14-3-3 isoforms and P11. Mol Endocrinol. 1997; 11:1858–1867.57. Zhu YM, Wang CC, Chen L, Qian LB, Ma LL, Yu J, Zhu MH, Wen CY, Yu LN, Yan M. Both PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways participate in the protection by dexmedetomidine against transient focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Brain Res. 2013; 1494:1–8.58. Koh PO. Nicotinamide attenuates the ischemic brain injury-induced decrease of Akt activation and Bad phosphorylation. Neurosci Lett. 2011; 498:105–109.59. Amano H, Maruyama IN. Aversive olfactory learning and associative long-term memory in Caenorhabditis elegans. Learn Mem. 2011; 18:654–665.60. Kandel ER. The molecular biology of memory: cAMP, PKA, CRE, CREB-1, CREB-2, and CPEB. Mol Brain. 2012; 5:14.61. Merz K, Herold S, Lie DC. CREB in adult neurogenesis--master and partner in the development of adult-born neurons? Eur J Neurosci. 2011; 33:1078–1086.62. Sheng M, Thompson MA, Greenberg ME. CREB: a Ca2+-regulated transcription factor phosphorylated by calmodulin-dependent kinases. Science. 1991; 252:1427–1430.63. Finkbeiner S, Tavazoie SF, Maloratsky A, Jacobs KM, Harris KM, Greenberg ME. CREB: a major mediator of neuronal neurotrophin responses. Neuron. 1997; 19:1031–1047.64. Henriksson BG, Söderström S, Gower AJ, Ebendal T, Winblad B, Mohammed AH. Hippocampal nerve growth factor levels are related to spatial learning ability in aged rats. Behav Brain Res. 1992; 48:15–20.65. Bromley-Brits K, Deng Y, Song W. Morris water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease model mice. J Vis Exp. 2011; DOI: 10.3791/2920.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Exploring amygdala structural changes and signaling pathways in postmortem brains: consequences of long-term methamphetamine addiction
- A Neuroprotective Action of Quercetin and Apigenin through Inhibiting Aggregation of Aβ and Activation of TRKB Signaling in a Cellular Experiment
- A Functional Role for CREB as a Positive Regulator of Memory Formation and LTP
- Long-term Surgical and Chemical Castration Deteriorates Memory Function Through Downregulation of PKA/CREB/BDNF and c-Raf/MEK/ERK Pathways in Hippocampus
- Neuroprotective Effect of β-Lapachone against Glutamate-Induced Injury in HT22 Cells