Chonnam Med J.
2017 Sep;53(3):196-202. 10.4068/cmj.2017.53.3.196.
NADPH Oxidase Mediates β-Amyloid Peptide-Induced Neuronal Death in Mouse Cortical Cultures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Anatomy, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. csbae@jnu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Pharmacology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2390433
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2017.53.3.196
Abstract
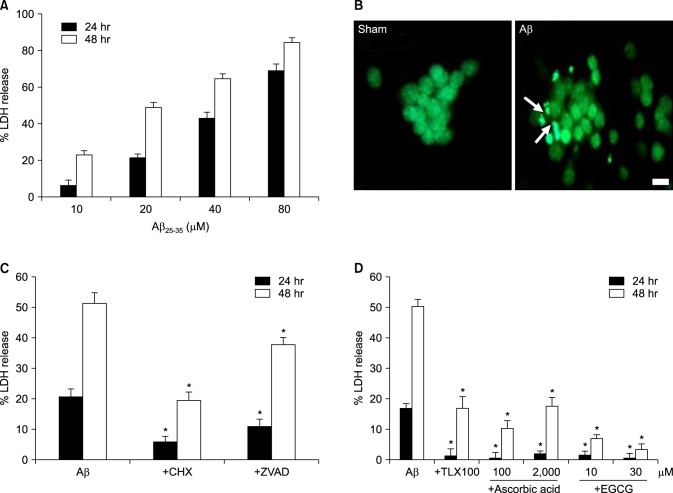
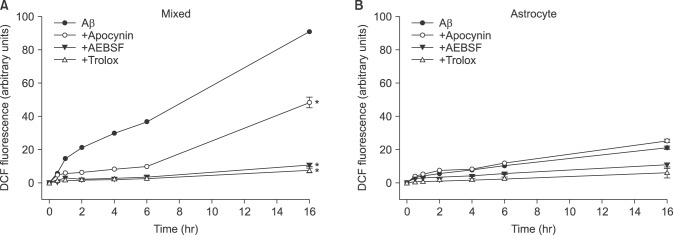
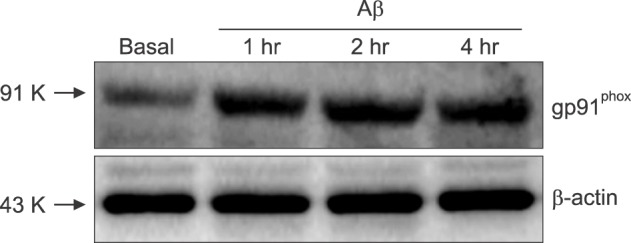
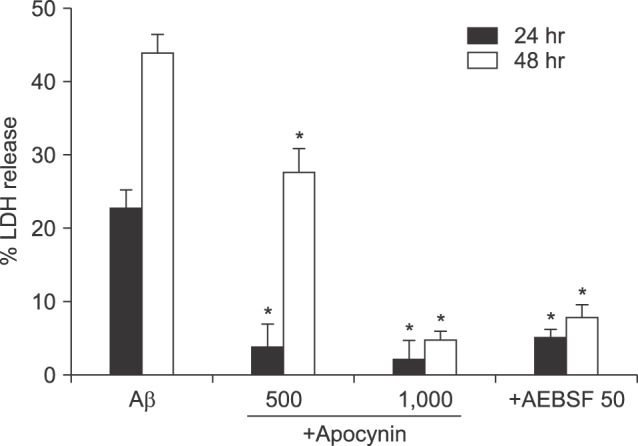
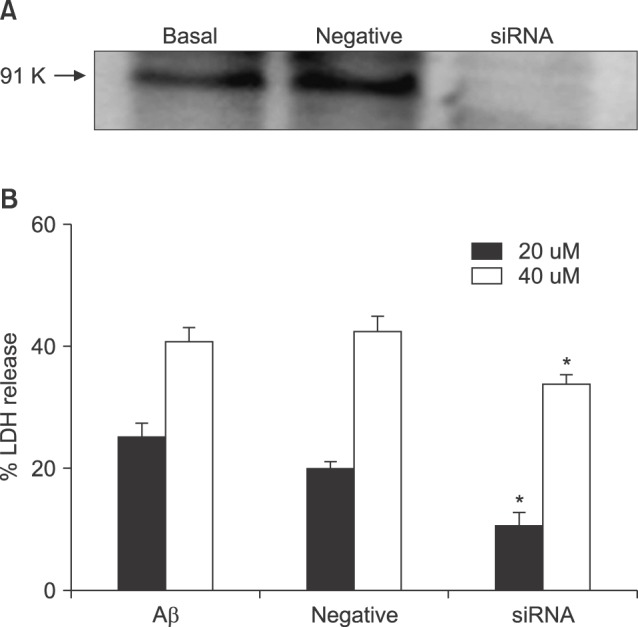
- β-Amyloid peptide (Aβ) is the main component of senile plaques in patients with Alzheimer's disease, and is known to be a main pathogenic factor of the disease. Recent evidence indicates that activation of NADPH oxidase (NOX) in microglia or astrocytes may be a source of Aβ-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS). We investigated the role of neuronal NOX in Aβ-induced neuronal death in mouse mixed cortical cultures. Cell death was assessed by measuring lactate dehydrogenase efflux to bathing media 24 or 48 hr after exposure to Aβ₂₅₋₃₅, a fragment of Aβ with an equivalent neurotoxic effect. Aβ₂₅₋₃₅ induced neuronal death in concentration- and time- dependent manners with apoptotic features. Neuronal death was significantly attenuated, not only by anti-apoptotic drugs, such as z-VAD-fmk and cycloheximide, but also by antioxidants, such as trolox, ascorbic acid, and epigallocatethin gallate. We also demonstrated that treatment with 20 µM Aβ₂₅₋₃₅ increased fluorescent signals in mixed cortical cultures, but produced only weak signals in pure astrocyte cultures in the presence of 2',7'-dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCF-DA), an indicator for intracellular ROS. Increased DCF-DA fluorescence was markedly inhibited, not only by trolox, but also by selective NOX inhibitors, such as apocynin and AEBSF. Western blot analyses revealed that Aβ₂₅₋₃₅ increased the expression of gp91phox, a main subunit of NOX in cells. The above antioxidants, apocynin, and AEBSF significantly attenuated neuronal death induced by Aβ₂₅₋₃₅. Furthermore, the gp91phox-specific siRNA-based knockdown of NOX significantly inhibited neuronal death. These results suggest that activation of neuronal NOX is involved in Aβ25-35-induced neuronal death.
MeSH Terms
-
Alzheimer Disease
Amyloid beta-Peptides
Animals
Antioxidants
Ascorbic Acid
Astrocytes
Baths
Blotting, Western
Cell Death
Cycloheximide
Fluorescence
Humans
L-Lactate Dehydrogenase
Mice*
Microglia
NADP*
NADPH Oxidase*
Neurons*
Plaque, Amyloid
Reactive Oxygen Species
Amyloid beta-Peptides
Antioxidants
Ascorbic Acid
Cycloheximide
L-Lactate Dehydrogenase
NADP
NADPH Oxidase
Reactive Oxygen Species
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effects of NADPH Oxidase Inhibitors and Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants on Amyloid β1-42-Induced Neuronal Deaths in Mouse Mixed Cortical Cultures
Shinae Hwang, Jong-Keun Kim
Chonnam Med J. 2018;54(3):159-166. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2018.54.3.159.
Reference
-
1. Mattson MP. Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000; 1:120–129. PMID: 11253364.2. Small DH, McLean CA. Alzheimer's disease and the amyloid beta protein: what is the role of amyloid? J Neurochem. 1999; 73:443–449. PMID: 10428038.3. Small DH, Mok SS, Bornstein JC. Alzheimer's disease and Abeta toxicity: from top to bottom. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001; 2:595–598. PMID: 11484003.4. Verdier Y, Zarándi M, Penke B. Amyloid beta-peptide interactions with neuronal and glial cell plasma membrane: binding sites and implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Pept Sci. 2004; 10:229–248. PMID: 15160835.5. Mattson MP. Cellular actions of beta-amyloid precursor protein and its soluble and fibrillogenic derivatives. Physiol Rev. 1997; 77:1081–1132. PMID: 9354812.6. Behl C, Moosmann B. Antioxidant neuroprotection in Alzheimer's disease as preventive and therapeutic approach. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002; 33:182–191. PMID: 12106814.7. Onyango IG, Khan SM. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and stress signaling in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2006; 3:339–349. PMID: 17017864.8. Praticò D. Evidence of oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease brain and antioxidant therapy: lights and shadows. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008; 1147:70–78. PMID: 19076432.9. Goodman Y, Steiner MR, Steiner SM, Mattson MP. Nordihydroguaiaretic acid protects hippocampal neurons against amyloid beta-peptide toxicity, and attenuates free radical and calcium accumulation. Brain Res. 1994; 654:171–176. PMID: 7982093.10. Bruce AJ, Malfroy B, Baudry M. Beta-amyloid toxicity in organotypic hippocampal cultures: protection by EUK-8, a synthetic catalytic free radical scavenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996; 93:2312–2316. PMID: 8637869.11. Bastianetto S, Ramassamy C, Doré S, Christen Y, Poirier J, Quirion R. The Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects hippocampal neurons against cell death induced by beta-amyloid. Eur J Neurosci. 2000; 12:1882–1890. PMID: 10886329.12. Ajith TA, Padmajanair G. Mitochondrial pharmaceutics: a new therapeutic strategy to ameliorate oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Aging Sci. 2015; 8:235–240. PMID: 25986626.13. Groemping Y, Rittinger K. Activation and assembly of the NADPH oxidase: a structural perspective. Biochem J. 2005; 386:401–416. PMID: 15588255.14. Shimohama S, Tanino H, Kawakami N, Okamura N, Kodama H, Yamaguchi T, et al. Activation of NADPH oxidase in Alzheimer's disease brains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000; 273:5–9. PMID: 10873554.15. Jang HJ, Hwang S, Cho KY, Kim DK, Chay KO, Kim JK. Taxol induces oxidative neuronal cell death by enhancing the activity of NADPH oxidase in mouse cortical cultures. Neurosci Lett. 2008; 443:17–22. PMID: 18672029.16. Sun GY, Horrocks LA, Farooqui AA. The roles of NADPH oxidase and phospholipases A2 in oxidative and inflammatory responses in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurochem. 2007; 103:1–16. PMID: 17561938.17. Wilkinson BL, Landreth GE. The microglial NADPH oxidase complex as a source of oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2006; 3:30. PMID: 17094809.18. Neniskyte U, Fricker M, Brown GC. Amyloid β induces microglia to phagocytose neurons via activation of protein kinase Cs and NADPH oxidase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016; 81:346–355. PMID: 27267660.19. Abramov AY, Canevari L, Duchen MR. Beta-amyloid peptides induce mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in astrocytes and death of neurons through activation of NADPH oxidase. J Neurosci. 2004; 24:565–575. PMID: 14724257.20. Angelova PR, Abramov AY. Interaction of neurons and astrocytes underlies the mechanism of Aβ-induced neurotoxicity. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014; 42:1286–1290. PMID: 25233405.21. Bruce-Keller AJ, Gupta S, Parrino TE, Knight AG, Ebenezer PJ, Weidner AM, et al. NOX activity is increased in mild cognitive impairment. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010; 12:1371–1382. PMID: 19929442.22. Choi SM, Kim BC, Cho YH, Choi KH, Chang J, Park MS, et al. Effects of flavonoid compounds on β-amyloid-peptide-induced neuronal death in cultured mouse cortical neurons. Chonnam Med J. 2014; 50:45–51. PMID: 25229015.23. Selkoe DJ. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1991; 6:487–498. PMID: 1673054.24. Rush DK, Aschmies S, Merriman MC. Intracerebral beta-amyloid(25-35) produces tissue damage: is it neurotoxic. Neurobiol Aging. 1992; 13:591–594. PMID: 1281289.25. Roth KA. Caspases, apoptosis, and Alzheimer disease: causation, correlation, and confusion. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2001; 60:829–838. PMID: 11556539.26. Kim MJ, Shin KS, Chung YB, Jung KW, Cha CI, Shin DH. Immunohistochemical study of p47Phox and gp91Phox distributions in rat brain. Brain Res. 2005; 1040:178–186. PMID: 15804439.27. Infanger DW, Sharma RV, Davisson RL. NADPH oxidases of the brain: distribution, regulation, and function. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006; 8:1583–1596. PMID: 16987013.28. Ferreira AP, Rodrigues FS, Della-Pace ID, Mota BC, Oliveira SM, Velho Gewehr Cde C, et al. The effect of NADPH-oxidase inhibitor apocynin on cognitive impairment induced by moderate lateral fluid percussion injury: role of inflammatory and oxidative brain damage. Neurochem Int. 2013; 63:583–593. PMID: 24076474.29. Diatchuk V, Lotan O, Koshkin V, Wikstroem P, Pick E. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation by 4-(2-aminoethyl)-benzenesulfonyl fluoride and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272:13292–13301. PMID: 9148950.30. Citron M, Diehl TS, Capell A, Haass C, Teplow DB, Selkoe DJ. Inhibition of amyloid beta-protein production in neural cells by the serine protease inhibitor AEBSF. Neuron. 1996; 17:171–179. PMID: 8755488.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of NADPH Oxidase Inhibitors and Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants on Amyloid βâ‚â‚‹â‚„â‚‚-Induced Neuronal Deaths in Mouse Mixed Cortical Cultures
- Protective effect of the aerial parts of Silybum marianum against amyloid β protein (25-35)-induced neuronal death in cultured neurons
- Effects of Flavonoid Compounds on beta-amyloid-peptide-induced Neuronal Death in Cultured Mouse Cortical Neurons
- N-Acetylcysteine Induces Apoptotic, Oxidative and Excitotoxic Neuronal Death in Mouse Cortical Cultures
- Spectrin Cleavage Induced by LLP-1 Lentivirus Lytic Peptide Domain in the Intracytoplasmic Tail of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 GP41 in Rat Organotypic Hippocampal Slice Cultures