Chonnam Med J.
2018 Sep;54(3):159-166. 10.4068/cmj.2018.54.3.159.
Effects of NADPH Oxidase Inhibitors and Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants on Amyloid βâ‚â‚‹â‚„â‚‚-Induced Neuronal Deaths in Mouse Mixed Cortical Cultures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea. jkkim57@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2420883
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2018.54.3.159
Abstract
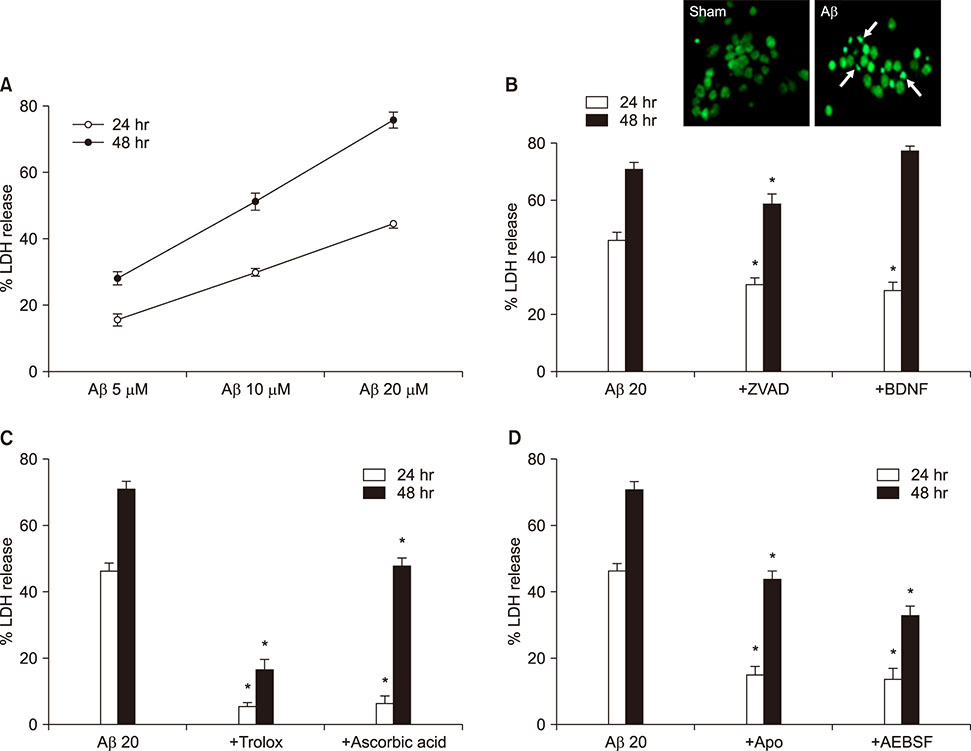
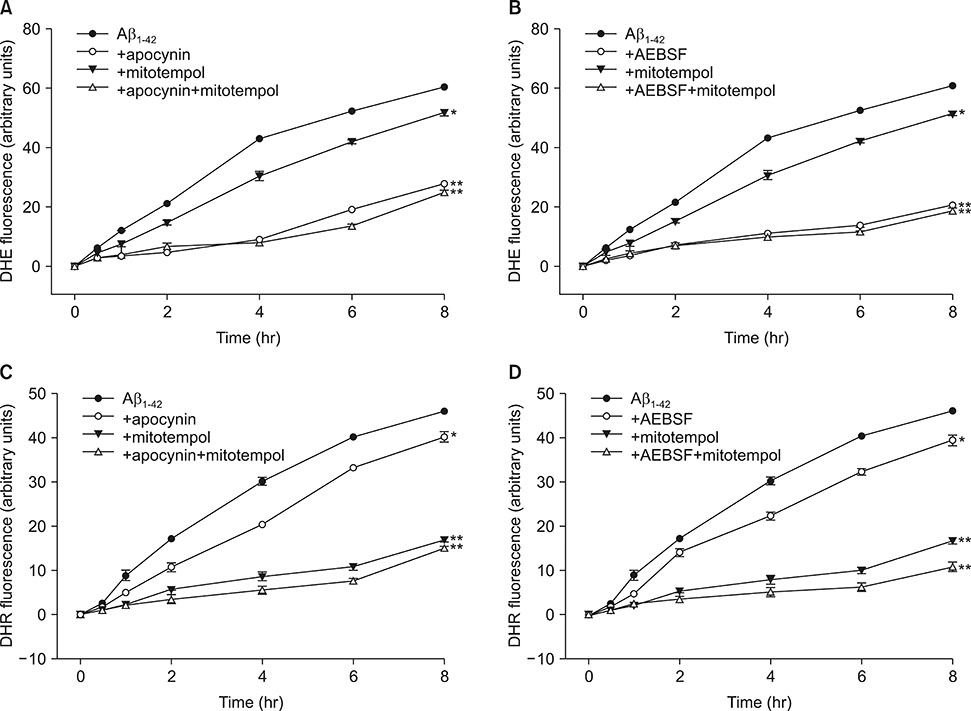
- The Amyloid β peptide (Aβ) is a main component of senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Currently, NADPH oxidase (NOX) and mitochondria are considered as primary sources of ROS induced by Aβ. However, the contribution of NOX and mitochondria to Aβ-induced ROS generation has not been well defined. To delineate the relative involvement of NOX and mitochondria in Aβ-induced ROS generation and neuronal death in mouse cortical cultures, we examined the effect of NOX inhibitors, apocynin and AEBSF, and the mitochondria-targeted antioxidants (MTAs), mitotempol and mitoquinone, on Aβ-induced ROS generation and neuronal deaths. Cell death was assessed by measuring lactate dehydrogenase efflux in bathing media at 24 and 48 hrs after exposure to Aβâ‚â‚‹â‚„â‚‚. Aβâ‚â‚‹â‚„â‚‚ induced dose- and time-dependent neuronal deaths in cortical cultures. Treatment with 20 µM Aβâ‚â‚‹â‚„â‚‚ markedly and continuously increased not only the DHE fluorescence (intracellular ROS signal), but also the DHR123 fluorescence (mitochondrial ROS signal) up to 8 hrs. Treatment with apocynin or AEBSF selectively suppressed the increase in DHE fluorescence, while treatment with mitotempol selectively suppressed the increase in DHR123 fluorescence. Each treatment with apocynin, AEBSF, mitotempol or mitoquinone significantly attenuated the Aβâ‚â‚‹â‚„â‚‚-induced neuronal deaths. However, any combined treatment with apocynin/AEBSF and mitotempol/mitoquinone failed to show additive effects. These findings indicate that 20 µM Aβâ‚â‚‹â‚„â‚‚ induces oxidative neuronal death via inducing mitochondrial ROS as well as NOX activation in mixed cortical cultures, but combined suppression of intracellular and mitochondrial ROS generation fail to show any additive neuroprotective effects against Aβ neurotoxicity.
MeSH Terms
-
Alzheimer Disease
Amyloid beta-Peptides
Amyloid*
Animals
Antioxidants*
Baths
Cell Death
Fluorescence
L-Lactate Dehydrogenase
Mice*
Mitochondria
NADP*
NADPH Oxidase*
Neurons*
Neuroprotective Agents
Oxidative Stress
Plaque, Amyloid
Amyloid
Amyloid beta-Peptides
Antioxidants
L-Lactate Dehydrogenase
NADP
NADPH Oxidase
Neuroprotective Agents
Figure
Reference
-
1. Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM. Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:329–344.
Article2. Butterfield DA. beta-amyloid-associated free radical oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: implications for Alzheimer's disease. Chem Res Toxicol. 1997; 10:495–506.
Article3. Butterfield DA, Swomley AM, Sultana R. Amyloid β-peptide (1-42)-induced oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease: importance in disease pathogenesis and progression. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013; 19:823–835.
Article4. Sorce S, Stocker R, Seredenina T, Holmdahl R, Aguzzi A, Chio A, et al. NADPH oxidases as drug targets and biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases: what is the evidence? Free Radic Biol Med. 2017; 112:387–396.
Article5. Cifuentes-Pagano ME, Meijles DN, Pagano PJ. Nox inhibitors & therapies: rational design of peptidic and small molecule inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des. 2015; 21:6023–6035.
Article6. Bruce-Keller AJ, Gupta S, Parrino TE, Knight AG, Ebenezer PJ, Weidner AM, et al. NOX activity is increased in mild cognitive impairment. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010; 12:1371–1382.
Article7. Abramov AY, Jacobson J, Wientjes F, Hothersall J, Canevari L, Duchen MR. Expression and modulation of an NADPH oxidase in mammalian astrocytes. J Neurosci. 2005; 25:9176–9184.
Article8. Chay KO, Nam Koong KY, Hwang S, Kim JK, Bae CS. NADPH oxidase mediates β-amyloid peptide-induced neuronal death in mouse cortical cultures. Chonnam Med J. 2017; 53:196–202.
Article9. Picone P, Nuzzo D, Caruana L, Scafidi V, Di Carlo M. Mitochondrial dysfunction: different routes to Alzheimer's disease therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014; 2014:780179.
Article10. Smith RA, Murphy MP. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants as therapies. Discov Med. 2011; 11:106–114.11. Oyewole AO, Birch-Machin MA. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants. FASEB J. 2015; 29:4766–4771.
Article12. Wang Q, Tompkins KD, Simonyi A, Korthuis RJ, Sun AY, Sun GY. Apocynin protects against global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative stress and injury in the gerbil hippocampus. Brain Res. 2006; 1090:182–189.
Article13. Diatchuk V, Lotan O, Koshkin V, Wikstroem P, Pick E. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation by 4-(2-aminoethyl)-benzenesulfonyl fluoride and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272:13292–13301.
Article14. Trnka J, Blaikie FH, Logan A, Smith RA, Murphy MP. Antioxidant properties of MitoTEMPOL and its hydroxylamine. Free Radic Res. 2009; 43:4–12.
Article15. Doughan AK, Dikalov SI. Mitochondrial redox cycling of mitoquinone leads to superoxide production and cellular apoptosis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007; 9:1825–1836.
Article16. Choi SM, Kim BC, Cho YH, Choi KH, Chang J, Park MS, et al. Effects of flavonoid compounds on β-amyloid-peptide-induced neuronal death in cultured mouse cortical neurons. Chonnam Med J. 2014; 50:45–51.
Article17. Kalyanaraman B, Darley-Usmar V, Davies KJ, Dennery PA, Forman HJ, Grisham MB, et al. Measuring reactive oxygen and nitrogen species with fluorescent probes: challenges and limitations. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012; 52:1–6.
Article18. Nagahara Y, Shiina I, Nakata K, Sasaki A, Miyamoto T, Ikekita M. Induction of mitochondria-involved apoptosis in estrogen receptor-negative cells by a novel tamoxifen derivative, ridaifen-B. Cancer Sci. 2008; 99:608–614.
Article19. Naslund J, Schierhorn A, Hellman U, Lannfelt L, Roses AD, Tjernberg LO, et al. Relative abundance of Alzheimer a beta amyloid peptide variants in Alzheimer disease and normal aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994; 91:8378–8382.
Article20. Ferreira ST, Vieira MN, De Felice FG. Soluble protein oligomers as emerging toxins in Alzheimer's and other amyloid diseases. IUBMB Life. 2007; 59:332–345.
Article21. Han XJ, Hu YY, Yang ZJ, Jiang LP, Shi SL, Li YR, et al. Amyloid β-42 induces neuronal apoptosis by targeting mitochondria. Mol Med Rep. 2017; 16:4521–4528.
Article22. Kienlen-Campard P, Miolet S, Tasiaux B, Octave JN. Intracellular amyloid-beta 1-42, but not extracellular soluble amyloid-beta peptides, induces neuronal apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:15666–15670.
Article23. Bastianetto S, Ramassamy C, Dore S, Christen Y, Poirier J, Quirion R. The ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects hippocampal neurons against cell death induced by β-amyloid. Eur J Neurosci. 2000; 12:1882–1890.
Article24. Shimohama S, Tanino H, Kawakami N, Okamura N, Kodama H, Yamaguchi T, et al. Activation of NADPH oxidase in Alzheimer's disease brains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000; 273:5–9.
Article25. Abramov AY, Duchen MR. The role of an astrocytic NADPH oxidase in the neurotoxicity of amyloid beta peptides. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005; 360:2309–2314.
Article26. Bordt EA, Polster BM. NADPH oxidase-and mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species in proinflammatory microglial activation: a bipartisan affair? Free Radic Biol Med. 2014; 76:34–46.
Article27. Wang K, Yao Y, Zhu X, Zhang K, Zhou F, Zhu L. Amyloid β induces NLRP3 inflammasome activation in retinal pigment epithelial cells via NADPH oxidase- and mitochondria-dependent ROS production. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2017; 31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- NADPH Oxidase Mediates β-Amyloid Peptide-Induced Neuronal Death in Mouse Cortical Cultures
- Anti-oxidative neuroprotection by estrogens in mouse cortical cultures
- Effects of Flavonoid Compounds on beta-amyloid-peptide-induced Neuronal Death in Cultured Mouse Cortical Neurons
- Cilostazol Attenuates 4-hydroxynonenal-enhanced CD36 Expression on Murine Macrophages via Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase-derived Reactive Oxygen Species Production
- 6-hydroxydopamine Induces Neuronal Apoptosis in Mouse Cortical Cell Cultures