J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Sep;52(3):273-276.
Atypical Metronidazole-Induced Encephalopathy in Anaerobic Brain Abscess
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lessordi@naver.com
- 3Department of Neurology, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
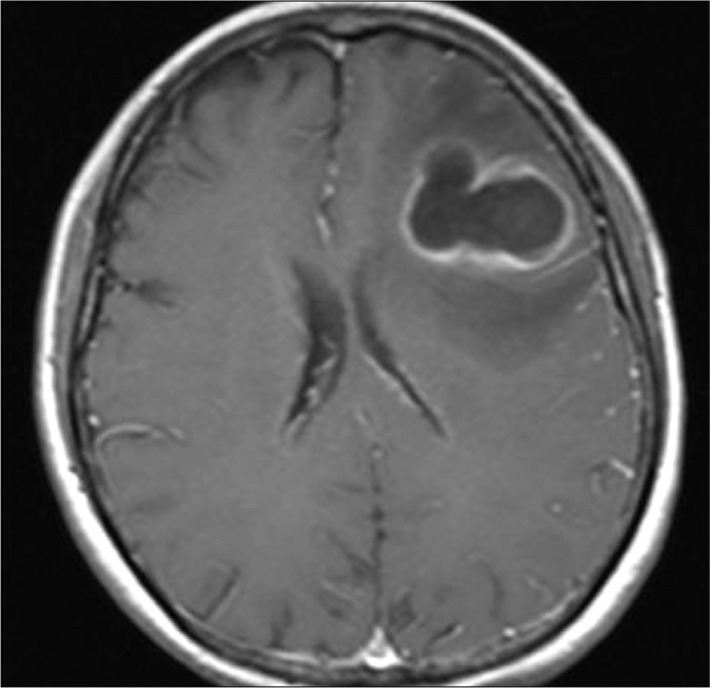
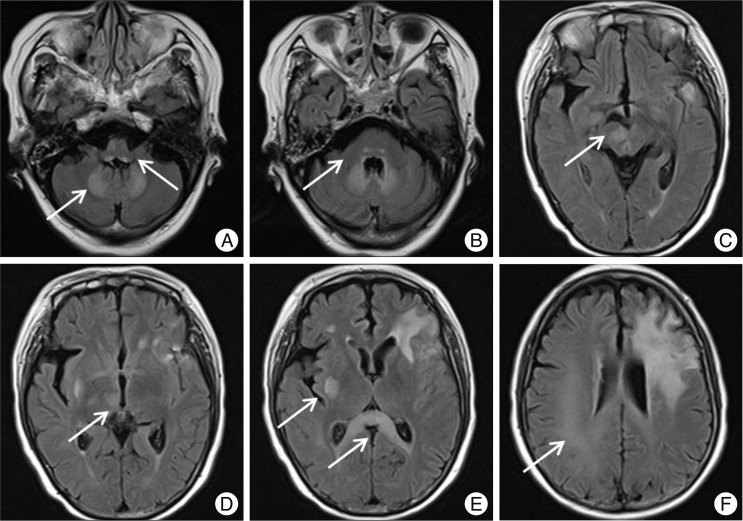
- Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy is a very rare complication of the long standing use of metronidazole. The encephalopathy is bilateral and symmetric in nature. We report on the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and clinical course of metronidazole-induced encephalopathy in a 60-year-old female with a persistent anaerobic brain abscess after draining of the abscess. After 3 months of metronidazole administration, the patient complained of dysarthria, tingling sense of all extremities, and left hemiparesis. MRI revealed symmetric hyperintensity lesions in medulla, pons, dentate nuclei of cerebellum, and splenium of corpus callosum, all of which represent typical findings of metronidazole-induced encephalopathy. In addition, asymmetric lesions in midbrain, thalamus, putamen and cerebral subcortical white matter were noted. The patient recovered after discontinuation of metronidazole and the remaining abscess was successfully treated with meropenem and levofloxacine.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahmed A, Loes DJ, Bressler EL. Reversible magnetic resonance imaging findings in metronidazole-induced encephalopathy. Neurology. 1995; 45:588–589. PMID: 7898724.
Article2. Bahn Y, Kim E, Park C, Park HC. Metronidazole induced encephalopathy in a patient with brain abscess. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 48:301–304. PMID: 21082066.
Article3. Bonkowsky JL, Sondrup C, Benedict SL. Acute reversible cerebellar lesions associated with metronidazole therapy. Neurology. 2007; 68:180. PMID: 17224569.
Article4. Cecil KM, Halsted MJ, Schapiro M, Dinopoulos A, Jones BV. Reversible MR imaging and MR spectroscopy abnormalities in association with metronidazole therapy. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2002; 26:948–951. PMID: 12488741.
Article5. Cottagnoud P, Cottagnoud M, Acosta F, Flatz L, Kuhn F, Stucki A, et al. Meropenem prevents levofloxacin-induced resistance in penicillin-resistant pneumococci and acts synergistically with levofloxacin in experimental meningitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2003; 22:656–662. PMID: 14557920.
Article6. De Bleecker JL, Leroy BP, Meire VI. Reversible visual deficit and Corpus callosum lesions due to metronidazole toxicity. Eur Neurol. 2005; 53:93–95. PMID: 15855780.
Article7. Glupczynski Y, Berhin C, Nizet H. Antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria in Belgium as determined by E-test methodology. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009; 28:261–267. PMID: 18797943.
Article8. Hammami N, Drissi C, Sebai R, Araar M, Maatallah Y, Belghith L, et al. Reversible metronidazole-induced encephalopathy. J Neuroradiol. 2007; 34:133–136. PMID: 17368540.
Article9. Heaney CJ, Campeau NG, Lindell EP. MR imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging changes in metronidazole (Flagyl)-induced cerebellar toxicity. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:1615–1617. PMID: 13679281.10. Horlen CK, Seifert CF, Malouf CS. Toxic metronidazole-induced MRI changes. Ann Pharmacother. 2000; 34:1273–1275. PMID: 11098341.
Article11. Kim DW, Park JM, Yoon BW, Baek MJ, Kim JE, Kim S. Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy. J Neurol Sci. 2004; 224:107–111. PMID: 15450780.
Article12. Kim E, Na DG, Kim EY, Kim JH, Son KR, Chang KH. MR imaging of metronidazole-induced encephalopathy : lesion distribution and diffusion-weighted imaging findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 28:1652–1658. PMID: 17885234.
Article13. Lamp KC, Freeman CD, Klutman NE, Lacy MK. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the nitroimidazole antimicrobials. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1999; 36:353–373. PMID: 10384859.
Article14. Lee SS, Cha SH, Lee SY, Song CJ. Reversible inferior colliculus lesion in metronidazole-induced encephalopathy : magnetic resonance findings on diffusion-weighted and fluid attenuated inversion recovery imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2009; 33:305–308. PMID: 19346865.
Article15. Rao DN, Mason RP. Generation of nitro radical anions of some 5-nitrofurans, 2- and 5-nitroimidazoles by norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin. A possible mechanism for neurotoxicity caused by nitroheterocyclic drugs. J Biol Chem. 1987; 262:11731–11736. PMID: 2887562.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Metronidazole Induced Encephalopathy in a Patient with Brain Abscess
- A Case of Metronidazole-Induced Encephalopathy: Atypical Involvement of the Brain on MRI
- Oculogyric Crisis Due to Metronidazole Toxic Encephalopathy
- A case of metronidazole induced encephalopathy in a cirrhotic patient
- Metronidazole-induced Reversible Cerebellopathy