Korean J Nutr.
2011 Jun;44(3):196-202. 10.4163/kjn.2011.44.3.196.
Effect of EGCG on Expression of Neurogenin 3 via the MAP Kinase Signaling Pathway in AR42J Cells, a Rat Pancreatic Tumor Cell Line
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery and the Sealy Center for Cancer Cell biology, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, Texas 77555, USA.
- 2Department of Food Nutrition, Gimcheon University, Gimcheon 740-704, Korea. wkchoe@gmail.com
- KMID: 2268508
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/kjn.2011.44.3.196
Abstract
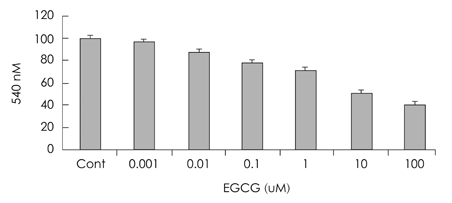
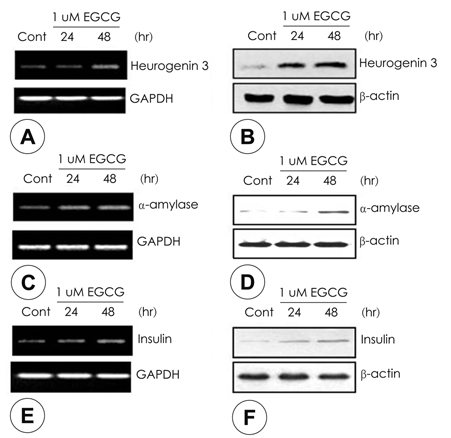
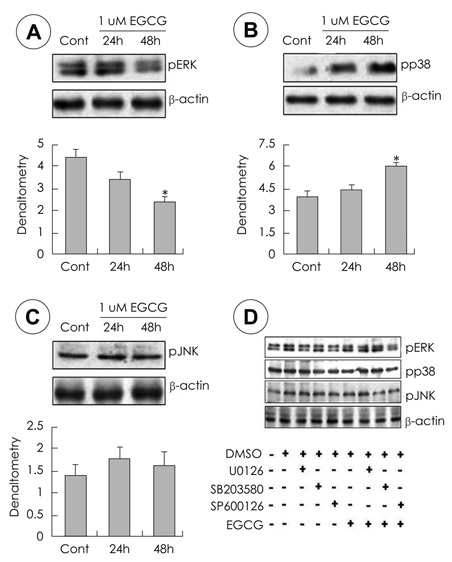
- Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), or epigallocatechin 3-gallate, is the ester of epigallocatechin and gallic acid, and is a type of catechin. EGCG may be therapeutic for many disorders including diabetics and some types of cancer. However it is unknown whether EGCG can induce transdifferentiation of pancreatic cells in pancreatitis. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of EGCG on the expression of pancreatic regenerating related markers in pancreatic AR42J cells, a model of pancreatic progenitor cells. AR42J cells, differentiated with betacellulin and activin A, were cultured with/without EGCG in a time-dependent manner. Cell growth rate, levels of mRNA, and protein expression were examined with the MTT assay, quantitative PCR, and Western blots, respectively. The results showed that AR42J cell growth rates were inhibited by EGCG in a dose-dependent manner. mRNA and protein expression of amylase, insulin and neurogenin 3 (ngn 3) increased in AR42J cells treated with EGCG. Additionally, we demonstrated that the signal transduction pathway of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase is active in EGCG-treated AR42J cells. ERK and JNK phosphorylation decreased in cells treated with EGCG but not p38 phosphorylation. Activation of the p38 MAP kinase pathway was confirmed by specific MAP kinase pathways inhibitors: U0126 for ERK, SP600126 for JNK, and SB203580 for p38. Activated p38 phosphorylation was inhibited by the specific p38 inhibitor SB203580 but p38 phosphorylation was inhibited with increased EGCG treatment. The ERK and JNK MAP kinase pathways were not affected by EGCG treatment. Although further studies are needed, these results suggest that EGCG affects the induction of pancreatic cell regeneration by increasing the ngn 3 protein and mRNA expression and activating the p38 MAP kinase pathway.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Activins
Amylases
Animals
Blotting, Western
Butadienes
Catechin
Cell Line, Tumor
Gallic Acid
Imidazoles
Insulin
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Nitriles
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Pancreatitis
Phosphorylation
Phosphotransferases
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Pyridines
Rats
Regeneration
RNA, Messenger
Signal Transduction
Stem Cells
Activins
Amylases
Butadienes
Catechin
Gallic Acid
Imidazoles
Insulin
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Nitriles
Phosphotransferases
Pyridines
RNA, Messenger
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Figure
Reference
-
1. Suzuki K, Kori S, Morikawa M, Takagi A, Namiki H. Oxidative stress-mediated bimodal regulation of polymorphonuclear leukocyte spreading by polyphenolic compounds. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010. 10(11):1448–1455.
Article2. Kürbitz C, Heise D, Redmer T, Goumas F, Arlt A, Lemke J, Rimbach G, Kalthoff H, Trauzold A. Epicatechin gallate and catechin gallate are superior to epigallocatechin gallate in growth suppression and anti-inflammatory activities in pancreatic tumor cells. Cancer Sci. 2011. 102(4):728–734.
Article3. Larsen CA, Dashwood RH, Bisson WH. Tea catechins as inhibitors of receptor tyrosine kinases: mechanistic insights and human relevance. Pharmacol Res. 2010. 62(6):457–464.
Article4. Singh R, Akhtar N, Haqqi TM. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate: inflammation and arthritis. Life Sci. 2010. 86(25-26):907–918.
Article5. Yadav D, Whitcomb DC. The role of alcohol and smoking in pancreatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. 7(3):131–145.
Article6. Yadav D. Recent advances in the epidemiology of alcoholic pancreatitis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011. 13(2):157–165.
Article7. Etemad B, Whitcomb DC. Chronic pancreatitis: diagnosis, classification, and new genetic developments. Gastroenterology. 2001. 120(3):682–707.
Article8. Lankisch PG, Assmus C, Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB. Epidemiology of pancreatic diseases in Lüneburg County. A study in a defined German population. Pancreatology. 2002. 2(5):469–477.
Article9. Lankisch PG, Lowenfels AB, Maisonneuve P. What is the risk of alcoholic pancreatitis in heavy drinkers? Pancreas. 2002. 25(4):411–412.
Article10. Yadav D, Eigenbrodt ML, Briggs MJ, Williams DK, Wiseman EJ. Pancreatitis: prevalence and risk factors among male veterans in a detoxification program. Pancreas. 2007. 34(4):390–398.11. Choudhuri G, Lakshmi CP, Goel A. Pancreatic diabetes. Trop Gastroenterol. 2009. 30(2):71–75.12. Joglekar MV, Parekh VS, Hardikar AA. New pancreas from old: microregulators of pancreas regeneration. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2007. 18(10):393–400.
Article13. Docherty K. Growth and development of the islets of Langerhans: implications for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2001. 1(6):641–650.
Article14. Schwitzgebel VM. Programming of the pancreas. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001. 185(1-2):99–108.
Article15. Zhang YQ, Mashima H, Kojima I. Changes in the expression of transcription factors in pancreatic AR42J cells during differentiation into insulin-producing cells. Diabetes. 2001. 50:Suppl 1. S10–S14.
Article16. Ogihara T, Watada H, Kanno R, Ikeda F, Nomiyama T, Tanaka Y, Nakao A, German MS, Kojima I, Kawamori R. p38 MAPK is involved in activin A- and hepatocyte growth factor-mediated expression of pro-endocrine gene neurogenin 3 in AR42J-B13 cells. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278(24):21693–21700.
Article17. Gradwohl G, Dierich A, LeMeur M, Guillemot F. Neurogenin3 is required for the development of the four endocrine cell lineages of the pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97(4):1607–1611.
Article18. Edlund H. Transcribing pancreas. Diabetes. 1998. 47(12):1817–1823.
Article19. Wilson ME, Scheel D, German MS. Gene expression cascades in pancreatic development. Mech Dev. 2003. 120(1):65–80.
Article20. Schwitzgebel VM, Scheel DW, Conners JR, Kalamaras J, Lee JE, Anderson DJ, Sussel L, Johnson JD, German MS. Expression of neurogenin3 reveals an islet cell precursor population in the pancreas. Development. 2000. 127(16):3533–3542.
Article21. Apelqvist A, Li H, Sommer L, Beatus P, Anderson DJ, Honjo T, Hrabe de Angelis M, Lendahl U, Edlund H. Notch signalling controls pancreatic cell differentiation. Nature. 1999. 400(6747):877–881.
Article22. Jensen J, Heller RS, Funder-Nielsen T, Pedersen EE, Lindsell C, Weinmaster G, Madsen OD, Serup P. Independent development of pancreatic alpha- and beta-cells from neurogenin3-expressing precursors: a role for the notch pathway in repression of premature differentiation. Diabetes. 2000. 49(2):163–176.
Article23. Trevisanato SI, Kim YI. Tea and health. Nutr Rev. 2000. 58(1):1–10.
Article24. Rice-Evans C. Implications of the mechanisms of action of tea polyphenols as antioxidants in vitro for chemoprevention in humans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1999. 220(4):262–266.
Article25. Kao YH, Hiipakka RA, Liao S. Modulation of endocrine systems and food intake by green tea epigallocatechin gallate. Endocrinology. 2000. 141(3):980–987.
Article26. Asaumi H, Watanabe S, Taguchi M, Tashiro M, Nagashio Y, Nomiyama Y, Nakamura H, Otsuki M. Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits ethanol-induced activation of pancreatic stellate cells. Eur J Clin Invest. 2006. 36(2):113–122.
Article27. Sakurai N, Mochizuki K, Kameji H, Shimada M, Goda T. (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate enhances the expression of genes related to insulin sensitivity and adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes at an early stage of differentiation. Nutrition. 2009. 25(10):1047–1056.
Article28. Bursill CA, Abbey M, Roach PD. A green tea extract lowers plasma cholesterol by inhibiting cholesterol synthesis and up-regulating the LDL receptor in the cholesterol-fed rabbit. Atherosclerosis. 2007. 193(1):86–93.
Article29. Ryu OH, Lee J, Lee KW, Kim HY, Seo JA, Kim SG, Kim NH, Baik SH, Choi DS, Choi KM. Effects of green tea consumption on inflammation, insulin resistance and pulse wave velocity in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006. 71(3):356–358.
Article30. Nagao T, Komine Y, Soga S, Meguro S, Hase T, Tanaka Y, Tokimitsu I. Ingestion of a tea rich in catechins leads to a reduction in body fat and malondialdehyde-modified LDL in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005. 81(1):122–129.
Article31. Imai K, Nakachi K. Cross sectional study of effects of drinking green tea on cardiovascular and liver diseases. BMJ. 1995. 310(6981):693–696.
Article32. Hamamoto K, Yamada S, Hara A, Kodera T, Seno M, Kojima I. Extracellular matrix modulates insulin production during differentiation of AR42J cells: functional role of Pax6 transcription factor. J Cell Biochem. 2011. 112(1):318–329.
Article33. Fukazawa T, Matsuoka J, Naomoto Y, Nakai T, Durbin ML, Kojima I, Lakey JR, Tanaka N. Development of a novel beta-cell specific promoter system for the identification of insulin-producing cells in in vitro cell cultures. Exp Cell Res. 2006. 312(17):3404–3412.
Article34. Kojima I, Umezawa K. Conophylline: a novel differentiation inducer for pancreatic beta cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. 38(5-6):923–930.35. Joglekar MV, Parekh VS, Hardikar AA. New pancreas from old: microregulators of pancreas regeneration. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2007. 18(10):393–400.
Article36. Docherty K. Growth and development of the islets of Langerhans: implications for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2001. 1(6):641–650.
Article37. Schwitzgebel VM. Programming of the pancreas. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001. 185(1-2):99–108.
Article38. Carvalho KM, Morais TC, de Melo TS, de Castro Brito GA, de Andrade GM, Rao VS, Santos FA. The natural flavonoid quercetin ameliorates cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010. 33(9):1534–1539.
Article39. Thrower EC, Yuan J, Usmani A, Liu Y, Jones C, Minervini SN, Alexandre M, Pandol SJ, Guha S. A novel protein kinase D inhibitor attenuates early events of experimental pancreatitis in isolated rat acini. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. 300(1):G120–G129.
Article40. Umezawa K, Hiroki A, Kawakami M, Naka H, Takei I, Ogata T, Kojima I, Koyano T, Kowithayakorn T, Pang HS, Kam TS. Induction of insulin production in rat pancreatic acinar carcinoma cells by conophylline. Biomed Pharmacother. 2003. 57(8):341–350.
Article41. Chen LA, Li J, Silva SR, Jackson LN, Zhou Y, Watanabe H, Ives KL, Hellmich MR, Evers BM. PKD3 is the predominant protein kinase D isoform in mouse exocrine pancreas and promotes hormone-induced amylase secretion. J Biol Chem. 2009. 284(4):2459–2471.
Article42. Takabayashi F, Harada N. Effects of green tea catechins (Polyphenon 100) on cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. Pancreas. 1997. 14(3):276–279.
Article43. Kao YH, Chang HH, Lee MJ, Chen CL. Tea, obesity, and diabetes. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2006. 50(2):188–210.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dexamethasone-induced differentiation of pancreatic AR42J cell involves p21(waf1/cip1)and MAP kinase pathway
- Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor-gamma Inhibits the Activation of STAT3 in Cerulein-stimulated Pancreatic Acinar Cells
- IL-1beta Induces Lysozyme Overexpression through a Mechanism Involving ERK/p38 Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Activation in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Involvement of MAPK pathway in hypoxia-induced up-regulation of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in a human prostatic cancer cell line, PC3MLN4
- The Protective Effect of EGCG on INS-1 Cell in the Oxidative Stress and Mechanism