J Lung Cancer.
2009 Dec;8(2):92-98. 10.6058/jlc.2009.8.2.92.
Combining Erlotinib with Cytotoxic Chemotherapy May Overcome Resistance Caused by T790M Mutation of EGFR Gene in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Lung and Esophageal Cancer Clinic, Division of Pulmonology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea. Kyc0923@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2The Brain Korea 21 Project, Center for Biomedical Human Resources, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2199968
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6058/jlc.2009.8.2.92
Abstract
- PURPOSE
T790M is a mechanism underlying acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs). We hypothesized that a synergistic combination of cytotoxic drugs and EGFR-TKIs may overcome resistance.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
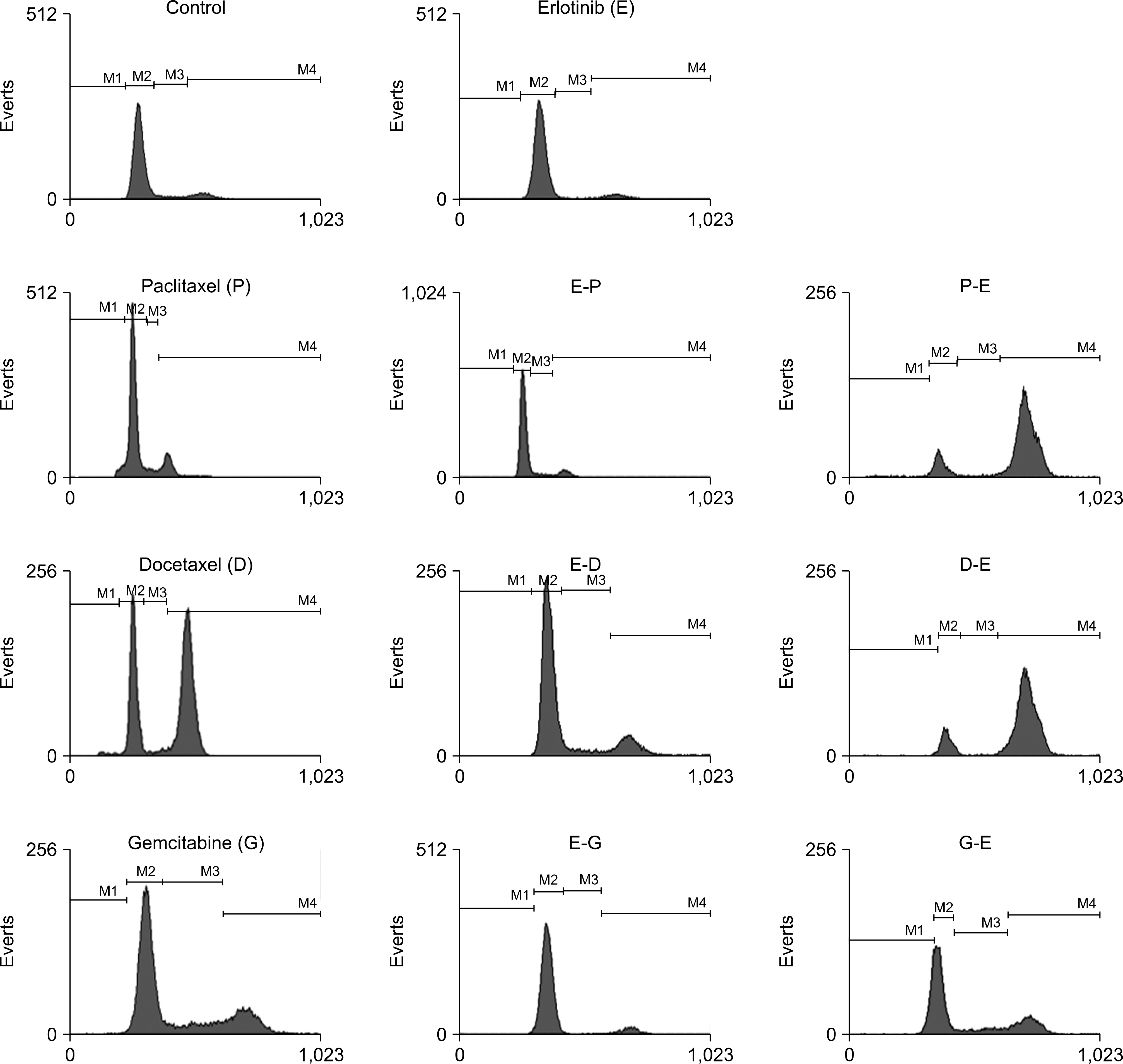
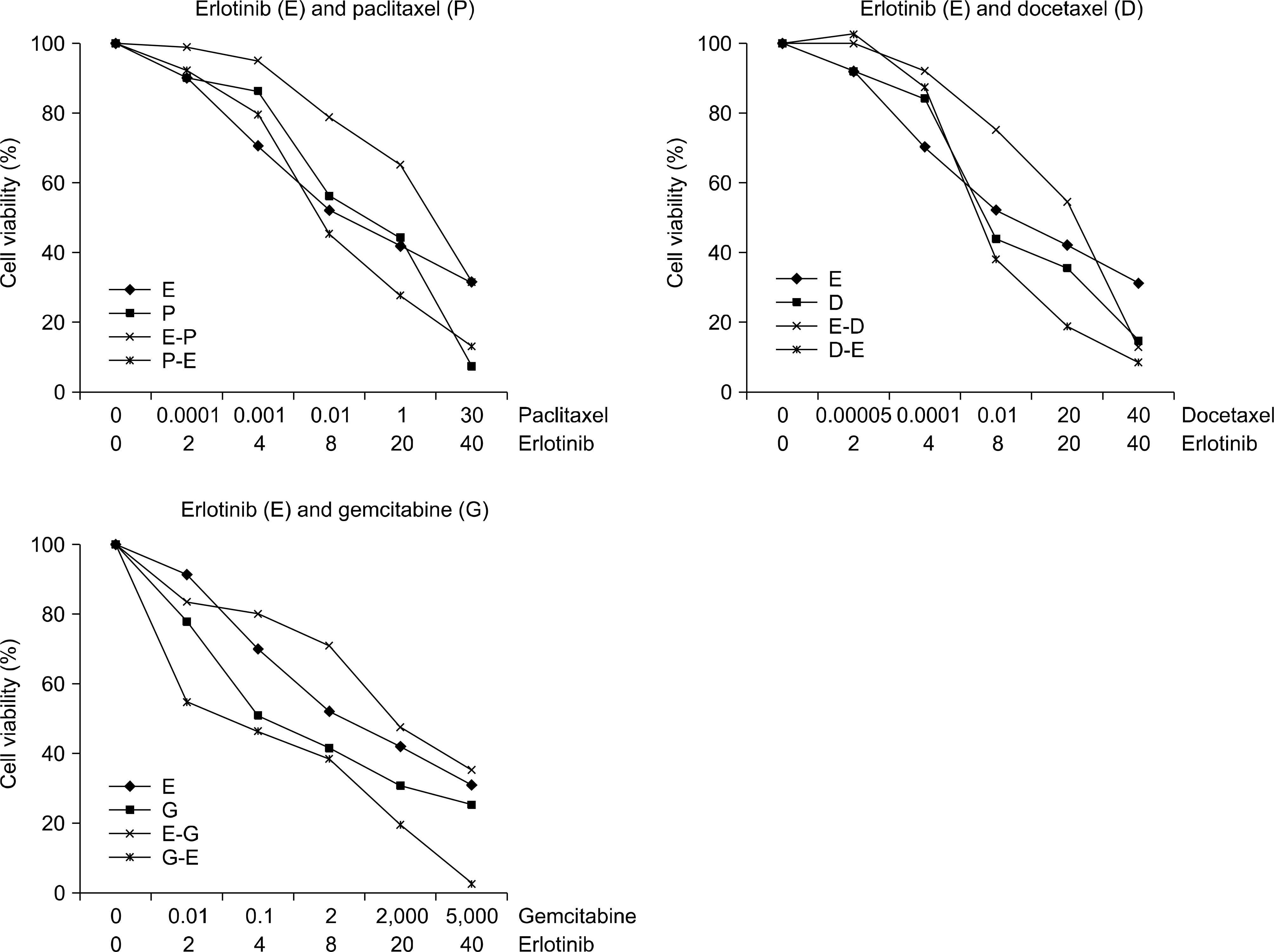
The antiproliferative effects and cell cycle distributions following treatments with Erlotinib (E) and cytotoxic drugs (C) were studied using a lung cancer cell line (NCI-H1975) harboring two mutations (L858R and T790M) in the EGFR gene. The cell viability assay and cell cycle analysis were conducted via an MTT assay and flow cytometry. The results of the treatments in different sequences were assessed using the combination index.
RESULTS
Antagonisms were noted when erlotinib was administered before cytotoxic drugs (EC sequence), whereas synergisms were observed when pre-treatment with cytotoxic drugs was administered before erlotinib (CE sequence). Treatment in the EC sequence arrested the cells in G0/G1 phase and reduced the apoptotic fraction. However, treatment in the CE sequence arrested the cells in the G2/M and S phase and a trend toward higher fractions of apoptotic cell death was observed.
CONCLUSION
Our studies demonstrated a schedule-dependent effect of cytotoxic drugs and erlotinib in an NSCLC cell line with the T790M mutation. Sequential treatment may overcome EGFR-TKI resistance.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:92–98.
Article2. Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of nonsmall-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2129–2139.
Article3. Tsao MS, Sakurada A, Cutz JC, et al. Erlotinib in lung cancer – molecular and clinical predictors of outcome. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:133–144.
Article4. Gatzemeier U, Pluzanska A, Szczesna A, et al. Phase III study of erlotinib in combination with cisplatin and gemcitabine in advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer: the Tarceva Lung Cancer Investigation Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:1545–1552.
Article5. Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C, et al. Gefitinib in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial–INTACT 1. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:777–784.6. Herbst RS, Giaccone G, Schiller JH, et al. Gefitinib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial–INTACT 2. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:785–794.7. Herbst RS, Prager D, Hermann R, et al. TRIBUTE: a phase III trial of erlotinib hydrochloride (OSI-774) combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:5892–5899.
Article8. Schiff PB, Horwitz SB. Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980; 77:1561–1565.
Article9. Rosell R, Danenberg KD, Alberola V, et al. Ribonucleotide reductase messenger RNA expression and survival in gem-citabine/cisplatin-treated advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2004; 10:1318–1325.
Article10. Tracy S, Mukohara T, Hansen M, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Janne PA. Gefitinib induces apoptosis in the EGFRL858R nonsmall-cell lung cancer cell line H3255. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:7241–7244.
Article11. Mahaffey CM, Davies AM, Lara PN Jr, et al. Schedule-dependent apoptosis in K-ras mutant nonsmall-cell lung cancer cell lines treated with docetaxel and erlotinib: rationale for pharmacodynamic separation. Clin Lung Cancer. 2007; 8:548–553.
Article12. Morelli MP, Cascone T, Troiani T, et al. Sequence-dependent antiproliferative effects of cytotoxic drugs and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Ann Oncol. 2005; 16(Suppl 4):iv61–68.
Article13. Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of nonsmall-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:786–792.14. Chou TC, Talalay P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984; 22:27–55.
Article15. Tortora G, Caputo R, Damiano V, et al. Cooperative antitumor effect of mixed backbone oligonucleotides targeting protein kinase A in combination with cytotoxic drugs or biologic agents. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1998; 8:141–145.
Article16. Li T, Ling YH, Goldman ID, Perez-Soler R. Schedule-dependent cytotoxic synergism of pemetrexed and erlotinib in human nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:3413–3422.
Article17. Solit DB, She Y, Lobo J, et al. Pulsatile administration of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib is significantly more effective than continuous dosing for sensitizing tumors to paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:1983–1989.
Article18. Davies AM, Lara PN, Lau DH, Mack PC, Gumerlock PH, Gandara DR. Intermittent erlotinib in combination with docetaxel (DOC): phase I schedules designed to achieve pharmacodynamic separation. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:A7038.
Article19. Davies AM, Ho C, Lara PN Jr, Mack P, Gumerlock PH, Gandara DR. Pharmacodynamic separation of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and chemotherapy in nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2006; 7:385–388.
Article20. Riely GJ, Rizvi NA, Kris MG, et al. Randomized phase II study of pulse erlotinib before or after carboplatin and paclitaxel in current or former smokers with advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:264–270.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acquired Resistance Mechanism of EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication to EGFR TKIs in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Chronicles of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Targeting EGFR C797S Containing Triple Mutations
- EGFR C797S as a Resistance Mechanism of Lazertinib in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR T790M Mutation
- Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors and Overcoming Strategies in Lung Cancer
- Should We Perform Repeated Re-biopsy for the Detection of T790M Mutation?