Cancer Res Treat.
2023 Oct;55(4):1190-1197. 10.4143/crt.2023.320.
Should We Perform Repeated Re-biopsy for the Detection of T790M Mutation?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Biostatistics, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2547793
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2023.320
Abstract
- Purpose
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutations have been detected in the second or third rebiopsy, even if the T790M mutation was not identified in the first rebiopsy. This meta-analysis investigated the EGFR T790M mutation detection rates and its additional advantages with repeated rebiopsies.
Materials and Methods
We searched through the PubMed and EMBASE databases up to June 2022. Studies reporting rebiopsy to identify the EGFR T790M mutation in case of disease progression among patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and multiple rebiopsies were included. The quality of the included studies was checked using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 (QUADAS-2) tool.
Results
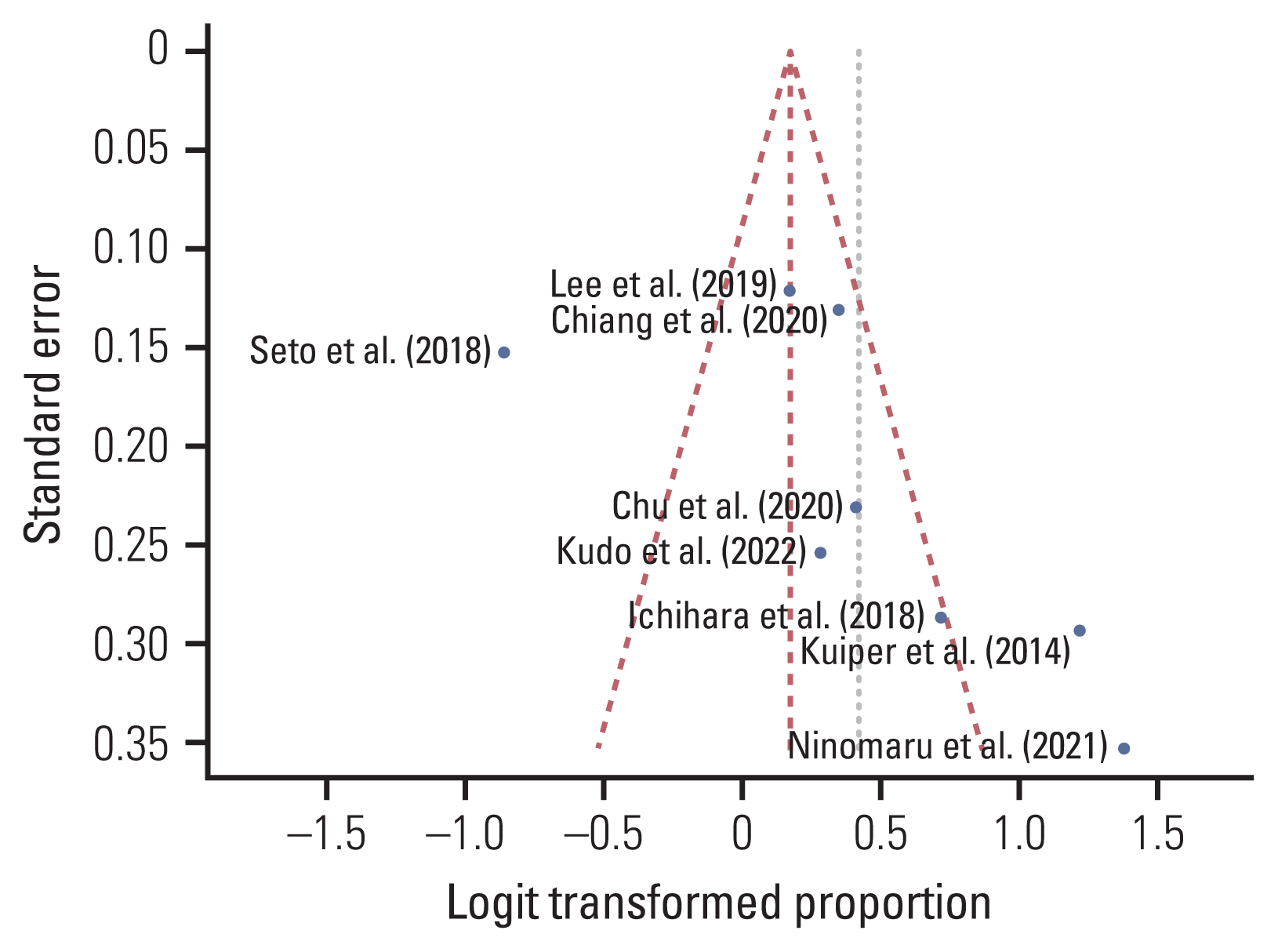
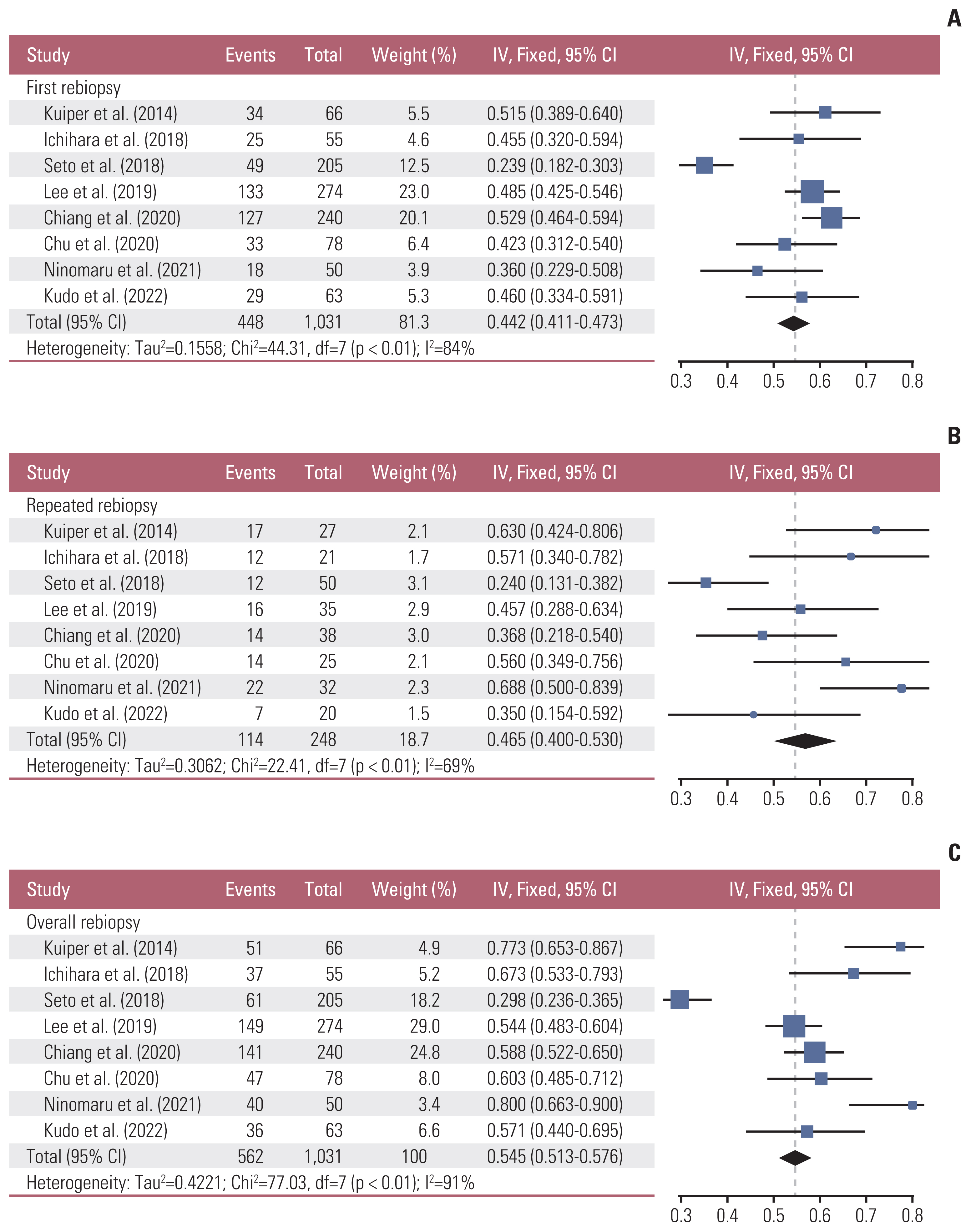
Eight studies meeting the eligibility criteria, reporting 1,031 EGFR mutation–positive patients were selected. The pooled EGFR T790M mutation detection rate of the first and repeated rebiopsies were 0.442 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.411 to 0.473; I2=84%; p < 0.01) and 0.465 (95% CI, 0.400 to 0.530; I2=69%; p < 0.01), respectively. Overall, the pooled detection rate of EGFR T790M mutation was 0.545 (95% CI, 0.513 to 0.576), which increased by 10.3% with repeated rebiopsies.
Conclusion
This meta-analysis identified that repeated rebiopsy increases the detection rate of EGFR T790M mutation by 10.3%, even if EGFR T790M mutation is not detected in the first rebiopsy. Our results indicate that the spatiotemporal T790M heterogeneity can be overcome with repeated rebiopsy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021; 71:209–49.2. Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:113–25.3. Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D, Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med. 2011; 3:75ra26.4. Camidge DR, Pao W, Sequist LV. Acquired resistance to TKIs in solid tumours: learning from lung cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014; 11:473–81.5. Ahn MJ, Han JY, Lee KH, Kim SW, Kim DW, Lee YG, et al. Lazertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from the dose escalation and dose expansion parts of a first-in-human, open-label, multicentre, phase 1–2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019; 20:1681–90.6. Chabon JJ, Simmons AD, Lovejoy AF, Esfahani MS, Newman AM, Haringsma HJ, et al. Circulating tumour DNA profiling reveals heterogeneity of EGFR inhibitor resistance mechanisms in lung cancer patients. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:11815.7. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NSCLC (version 2. 2023) [Internet]. Plymouth Meeting, PA: National Comprehensive Cancer Network; 2023 [cited 2023 Jan 10]. Available from: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf .8. Seto T, Nogami N, Yamamoto N, Atagi S, Tashiro N, Yoshimura Y, et al. Real-world EGFR T790M testing in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a prospective observational study in Japan. Oncol Ther. 2018; 6:203–15.9. Kim I, Seol HY, Kim SH, Kim MH, Lee MK, Eom JS. Favorable conditions for the detection of EGFR T790M mutation using plasma sample in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2023; 15:1445.10. Ichihara E, Hotta K, Kubo T, Higashionna T, Ninomiya K, Ohashi K, et al. Clinical significance of repeat rebiopsy in detecting the EGFR T790M secondary mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2018; 9:29525–31.11. Ninomaru T, Hata A, Kokan C, Okada H, Tomimatsu H, Ishida J. Higher osimertinib introduction rate achieved by multiple repeated rebiopsy after acquired resistance to first/second generation EGFR-TKIs. Thorac Cancer. 2021; 12:746–51.12. Kudo K, Nishii K, Makimoto G, Ishikawa N, Tsubata Y, Kodani M, et al. First and repeat rebiopsy for detecting EGFR T790M mutation in non-small-cell lung cancer: CS-Lung-003 prospective observational registry study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022; 148:1869–77.13. McInnes MD, Moher D, Thombs BD, McGrath TA, Bossuyt PM, et al. PRISMA-DTA Group. Preferred reporting items for a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies: The PRISMA-DTA Statement. JAMA. 2018; 319:388–96.14. Kuiper JL, Heideman DA, Thunnissen E, Paul MA, van Wijk AW, Postmus PE, et al. Incidence of T790M mutation in (sequential) rebiopsies in EGFR-mutated NSCLC-patients. Lung Cancer. 2014; 85:19–24.15. Lee K, Kim Y, Jung HA, Lee SH, Ahn JS, Ahn MJ, et al. Repeat biopsy procedures and T790M rates after afatinib, gefitinib, or erlotinib therapy in patients with lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2019; 130:87–92.16. Chiang CL, Huang HC, Shen CI, Luo YH, Chen YM, Chiu CH. Post-progression survival in secondary EGFR T790M-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer patients with and without osimertinib after failure of a previous EGFR TKI. Target Oncol. 2020; 15:503–12.17. Chu Q, Agha A, Devost N, Walton RN, Ghosh S, Ho C. Biopsy on progression in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a Canadian experience. Curr Oncol. 2020; 27:27–33.18. Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011; 155:529–36.19. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327:557–60.20. Hunter JP, Saratzis A, Sutton AJ, Boucher RH, Sayers RD, Bown MJ. In meta-analyses of proportion studies, funnel plots were found to be an inaccurate method of assessing publication bias. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014; 67:897–903.21. Hata A, Katakami N, Yoshioka H, Kaji R, Masago K, Fujita S, et al. Spatiotemporal T790M heterogeneity in individual patients with EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer after acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI. J Thorac Oncol. 2015; 10:1553–9.22. Gregorc V, Lazzari C, Mandala M, Ippati S, Bulotta A, Cangi MG, et al. Intratumoral cellular heterogeneity: implications for drug resistance in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021; 13:2023.23. Kim H, Chae KJ, Yoon SH, Kim M, Keam B, Kim TM, et al. Repeat biopsy of patients with acquired resistance to EGFR TKIs: implications of biopsy-related factors on T790M mutation detection. Eur Radiol. 2018; 28:861–8.24. Hong KS, Cho J, Jang JG, Jang MH, Ahn JH. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided re-biopsy of non-small cell lung cancer with acquired resistance after EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. Thorac Cancer. 2023; 14:363–70.25. Oxnard GR, Arcila ME, Sima CS, Riely GJ, Chmielecki J, Kris MG, et al. Acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant lung cancer: distinct natural history of patients with tumors harboring the T790M mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:1616–22.26. Lin MW, Yu SL, Hsu YC, Chen YM, Lee YH, Hsiao YJ, et al. Salvage surgery for advanced lung adenocarcinoma after epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. Ann Thorac Surg. 2023; 116:111–9.27. Uozu S, Imaizumi K, Yamaguchi T, Goto Y, Kawada K, Minezawa T, et al. Feasibility of tissue re-biopsy in non-small cell lung cancers resistant to previous epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapies. BMC Pulm Med. 2017; 17:175.28. Chan DL, Toh GL, Goh LL. Clinical implementation of plasma EGFR T790M testing using droplet digital PCR in TKI-resistant NSCLC patients. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020; 116:104515.29. Li X, Zhou C. Comparison of cross-platform technologies for EGFR T790M testing in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:100801–18.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of tissue-based and plasma-based testing for EGFR mutation in non–small cell lung cancer patients
- Assessment of Anti-tumor Efficacy of Osimertinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients by Liquid Biopsy Using Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid, Plasma, or Pleural Effusion
- Provisional Guideline Recommendation for EGFR Gene Mutation Testing in Liquid Samples of Lung Cancer Patients: A Proposal by the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group
- Acquired Resistance Mechanism of EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication to EGFR TKIs in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Chronicles of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Targeting EGFR C797S Containing Triple Mutations