Immune Netw.
2011 Jun;11(3):155-162. 10.4110/in.2011.11.3.155.
Ribosomal Protein L19 and L22 Modulate TLR3 Signaling
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Instititute for Immunology and Immunological Diseases, and Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea. inhong@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2150702
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2011.11.3.155
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
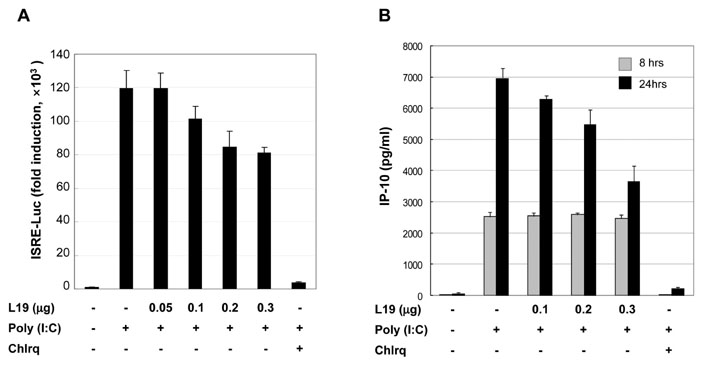
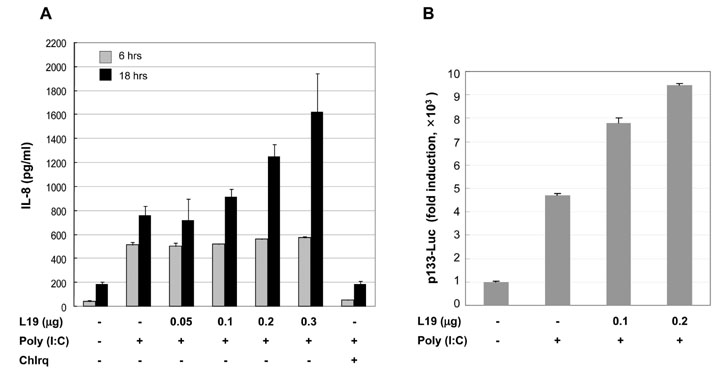
Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) recognizes double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and induces inflammation. In this study we attempted to ascertain if there are endogenous host molecules controlling the production of cytokines and chemokines. Two candidates, ribosomal protein L19 and L22, were analyzed to determine if they influence cytokine production followed by TLR3 activation. In this study we report that L19 acts upon production of IP-10 or IL-8 differently in glioblastoma cells.
METHODS
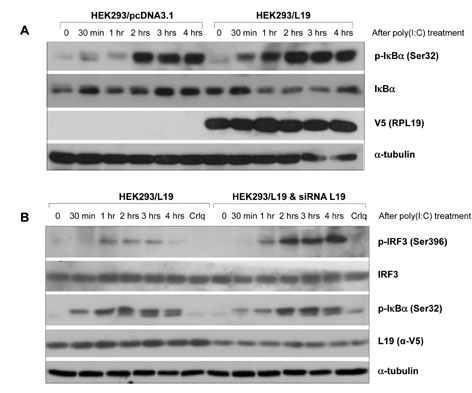
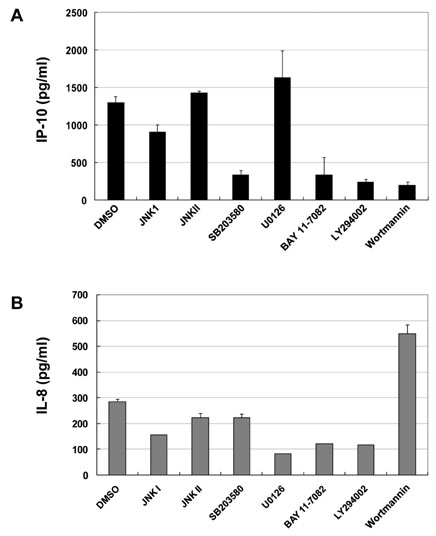
L19 or L22 was transfected into HEK293-TLR3, A549 or A172 cells. After treatment with several inhibitors of NF-kB, PI3K, p38 or ERK, production of IL-8 or IP-10 was measured by ELISA. siRNA was introduced to suppress expression of L19. After Vesicular stomatitis virus infection, viral multiplication was measured by western blot.
RESULTS
L19 increased ERK activation to produce IL-8. In A172 cells, in which TLR3 is expressed at endosomes, L19 inhibited interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) activation and IP-10 production to facilitate viral multiplication, whereas L19 inhibited viral multiplication in A549 cells bearing TLR3 on their cell membrane.
CONCLUSION
Our results suggest that L19 regulates TLR3 signaling, which is cell type specific and may be involved in pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammatory diseases.
MeSH Terms
-
Autoimmune Diseases
Chemokines
Cytokines
Endosomes
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Glioblastoma
Inflammation
Interferon Regulatory Factor-3
Interleukin-8
NF-kappa B
Ribosomal Proteins
RNA, Double-Stranded
RNA, Small Interfering
Toll-Like Receptor 3
Ursidae
Vesicular Stomatitis
Viruses
Chemokines
Cytokines
Interferon Regulatory Factor-3
Interleukin-8
NF-kappa B
RNA, Double-Stranded
RNA, Small Interfering
Ribosomal Proteins
Toll-Like Receptor 3
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wang T, Town T, Alexopoulou L, Anderson JF, Fikrig E, Flavell RA. Toll-like receptor 3 mediates West Nile virus entry into the brain causing lethal encephalitis. Nat Med. 2004. 10:1366–1373.
Article2. Diamond MS, Klein RS. West Nile virus: crossing the blood-brain barrier. Nat Med. 2004. 10:1294–1295.
Article3. Le Goffic R, Balloy V, Lagranderie M, Alexopoulou L, Escriou N, Flavell R, Chignard M, Si-Tahar M. Detrimental contribution of the Toll-like receptor (TLR)3 to influenza A virus-induced acute pneumonia. PLoS Pathog. 2006. 2:e53.
Article4. Guillot L, Le Goffic R, Bloch S, Escriou N, Akira S, Chignard M, Si-Tahar M. Involvement of toll-like receptor 3 in the immune response of lung epithelial cells to double-stranded RNA and influenza A virus. J Biol Chem. 2005. 280:5571–5580.
Article5. Rudd BD, Smit JJ, Flavell RA, Alexopoulou L, Schaller MA, Gruber A, Berlin AA, Lukacs NW. Deletion of TLR3 alters the pulmonary immune environment and mucus production during respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Immunol. 2006. 176:1937–1942.
Article6. Thomas KW, Monick MM, Staber JM, Yarovinsky T, Carter AB, Hunninghake GW. Respiratory syncytial virus inhibits apoptosis and induces NF-kappa B activity through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:492–501.
Article7. Basu D, Walkiewicz MP, Frieman M, Baric RS, Auble DT, Engel DA. Novel influenza virus NS1 antagonists block replication and restore innate immune function. J Virol. 2009. 83:1881–1891.
Article8. Deng L, Dai P, Parikh T, Cao H, Bhoj V, Sun Q, Chen Z, Merghoub T, Houghton A, Shuman S. Vaccinia virus subverts a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein-dependent innate immune response in keratinocytes through its double-stranded RNA binding protein, E3. J Virol. 2008. 82:10735–10746.
Article9. Leung DW, Ginder ND, Fulton DB, Nix J, Basler CF, Honzatko RB, Amarasinghe GK. Structure of the Ebola VP35 interferon inhibitory domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. 106:411–416.
Article10. Maisnier-Patin S, Paulander W, Pennhag A, Andersson DI. Compensatory evolution reveals functional interactions between ribosomal proteins S12, L14 and L19. J Mol Biol. 2007. 366:207–215.
Article11. Bee A, Ke Y, Forootan S, Lin K, Beesley C, Forrest SE, Foster CS. Ribosomal protein l19 is a prognostic marker for human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. 12(7 Pt 1):2061–2065.
Article12. Fok V, Mitton-Fry RM, Grech A, Steitz JA. Multiple domains of EBER 1, an Epstein-Barr virus noncoding RNA, recruit human ribosomal protein L22. RNA. 2006. 12:872–882.
Article13. Elia A, Vyas J, Laing KG, Clemens MJ. Ribosomal protein L22 inhibits regulation of cellular activities by the Epstein-Barr virus small RNA EBER-1. Eur J Biochem. 2004. 271:1895–1905.
Article14. Baril M, Racine ME, Penin F, Lamarre D. MAVS dimer is a crucial signaling component of innate immunity and the target of hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease. J Virol. 2009. 83:1299–1311.
Article15. Finberg RW, Kurt-Jones EA. Viruses and Toll-like receptors. Microbes Infect. 2004. 6:1356–1360.
Article16. Bowie AG, Haga IR. The role of Toll-like receptors in the host response to viruses. Mol Immunol. 2005. 42:859–867.
Article17. Schröder NW, Schumann RR. Single nucleotide polymorphisms of Toll-like receptors and susceptibility to infectious disease. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005. 5:156–164.
Article18. Olson JK, Miller SD. Microglia initiate central nervous system innate and adaptive immune responses through multiple TLRs. J Immunol. 2004. 173:3916–3924.
Article19. Matsushima H, Yamada N, Matsue H, Shimada S. TLR3-, TLR7-, and TLR9-mediated production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines from murine connective tissue type skin-derived mast cells but not from bone marrow-derived mast cells. J Immunol. 2004. 173:531–541.
Article20. Rudd BD, Burstein E, Duckett CS, Li X, Lukacs NW. Differential role for TLR3 in respiratory syncytial virus-induced chemokine expression. J Virol. 2005. 79:3350–3357.
Article21. Park C, Lee S, Cho IH, Lee HK, Kim D, Choi SY, Oh SB, Park K, Kim JS, Lee SJ. TLR3-mediated signal induces proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine gene expression in astrocytes: differential signaling mechanisms of TLR3-induced IP-10 and IL-8 gene expression. Glia. 2006. 53:248–256.
Article22. Kutsch O, Oh J, Nath A, Benveniste EN. Induction of the chemokines interleukin-8 and IP-10 by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tat in astrocytes. J Virol. 2000. 74:9214–9221.
Article23. Guha M, Mackman N. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway limits lipopolysaccharide activation of signaling pathways and expression of inflammatory mediators in human monocytic cells. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:32124–32132.
Article24. Hazeki K, Nigorikawa K, Hazeki O. Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in innate immunity. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007. 30:1617–1623.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Novel PA-X Protein Translated from Influenza A Virus Segment 3
- Linezolid Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Korea: High Rate of False Resistance to Linezolid by the VITEK 2 System
- TRIM56 Suppresses Multiple Myeloma Progression by Activating TLR3/TRIF Signaling
- Diagnosis of canine brucellosis using recombinant ribosomal protein L7/L12
- Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and its regulation during differentiation of human leukemic cells