Yonsei Med J.
2018 Jan;59(1):43-50. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.43.
TRIM56 Suppresses Multiple Myeloma Progression by Activating TLR3/TRIF Signaling
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hematology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiao Tong University, Xi'an 710061, China. zhangmeizmst@163.com
- KMID: 2418847
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.43
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Tripartite-motif-containing protein 56 (TRIM56) has been found to exhibit a broad antiviral activity, depending upon E3 ligase activity. Here, we attempted to evaluate the function of TRIM56 in multiple myeloma (MM) and its underlying molecular basis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
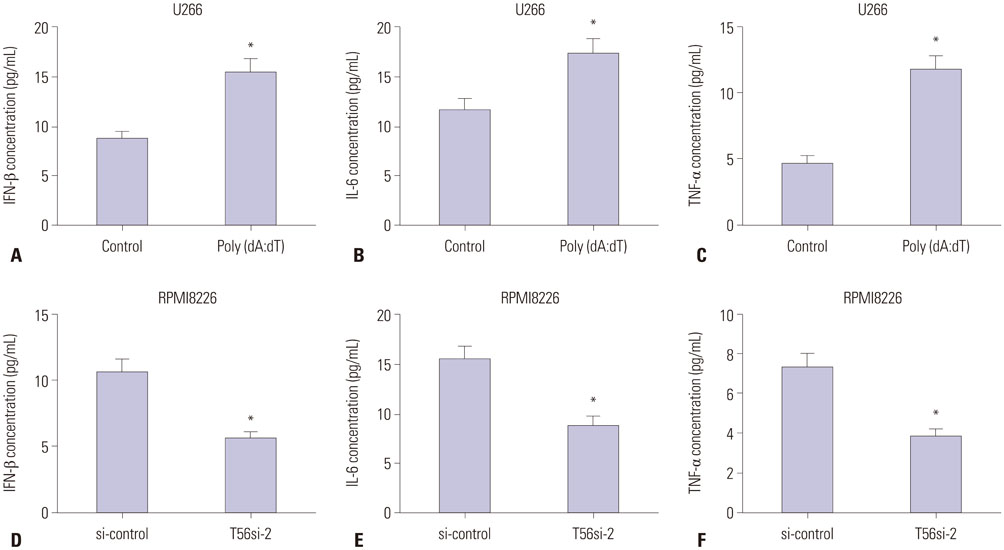
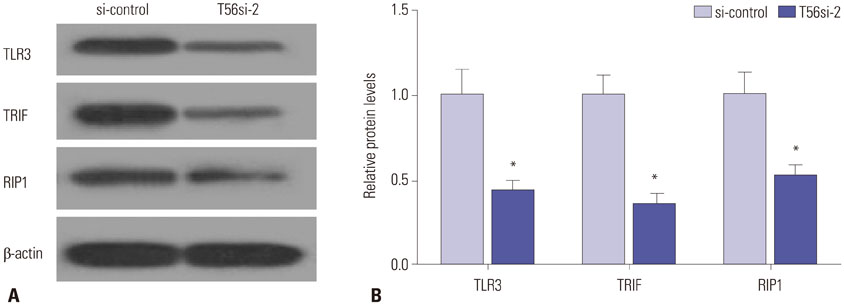
TRIM56 expression at the mRNA and protein level was measured by qRT PCR and western blot analysis. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) and flow cytometry analysis was performed to investigate the effect of TRIM56 on MM cell proliferation and apoptosis. The concentrations of interferon (IFN)-β, interleukin (IL)-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α in MM cell culture supernatants were detected with respective commercial ELISA kits. Western blot was employed to determine the effect of TRIM56 on toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3)/toll-IL-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-β (TRIF) signaling pathway.
RESULTS
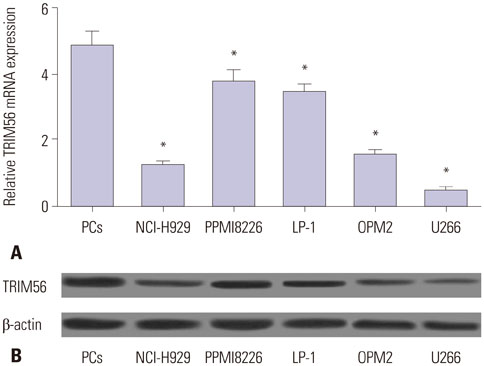
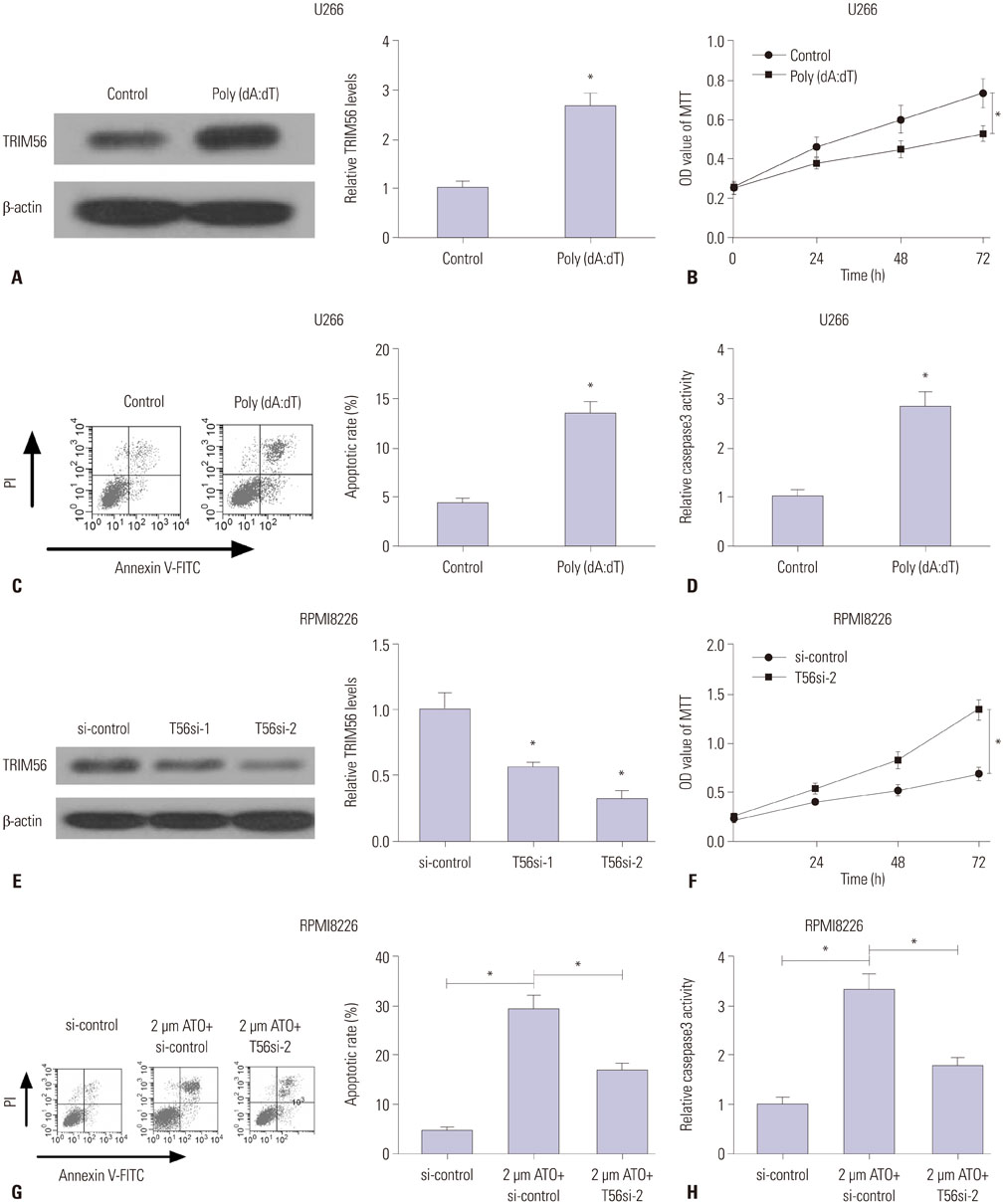
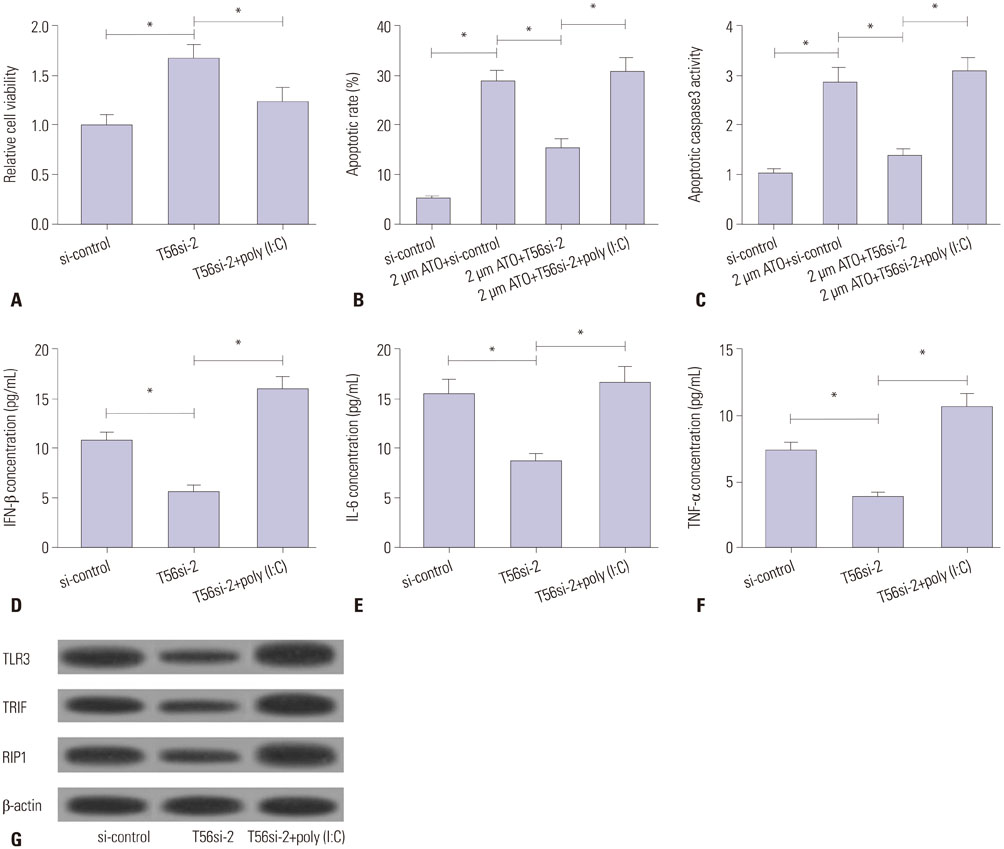
TRIM56 expression was prominently decreased in MM cells. Poly (dA:dT)-induced TRIM56 overexpression in U266 cells suppressed proliferation, induced apoptosis, and enhanced inflammatory cytokine production, while TRIM56 knockdown improved growth, diminished apoptosis, and inhibited inflammatory cytokine secretion in RPMI8226 cells. Moreover, TRIM56 knockdown blocked TLR3 signaling pathway. Furthermore, poly (I:C), a TLR3 agonist, markedly abolished TRIM56 depletion-induced increase of proliferation, decrease of apoptosis, and reduction of inflammatory factor in MM cells.
CONCLUSION
TRIM56 may act as a tumor suppressor in MM through activation of TLR3/TRIF signaling pathway, contributing to a better understanding of the molecular mechanism of TRIM56 involvement in MM pathogenesis and providing a promising therapy strategy for patients with MM.
MeSH Terms
-
Adaptor Proteins, Vesicular Transport/*metabolism
Apoptosis/drug effects
Cell Line, Tumor
Cell Proliferation/drug effects
Cytokines/secretion
*Disease Progression
Down-Regulation/drug effects
Gene Knockdown Techniques
Humans
Multiple Myeloma/*metabolism/*pathology
Poly I-C/pharmacology
*Signal Transduction/drug effects
Toll-Like Receptor 3/*metabolism
Tripartite Motif Proteins/deficiency/*metabolism
Ubiquitin-Protein Ligases/deficiency/*metabolism
Adaptor Proteins, Vesicular Transport
Cytokines
Toll-Like Receptor 3
Tripartite Motif Proteins
Ubiquitin-Protein Ligases
Figure
Reference
-
1. Munshi NC, Anderson KC, Bergsagel PL, Shaughnessy J, Palumbo A, Durie B, et al. Consensus recommendations for risk stratification in multiple myeloma: report of the International Myeloma Workshop Consensus Panel 2. Blood. 2011; 117:4696–4700.
Article2. Palumbo A, Anderson K. Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1046–1060.
Article3. Manier S, Sacco A, Leleu X, Ghobrial IM, Roccaro AM. Bone marrow microenvironment in multiple myeloma progression. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012; 2012:157496.
Article4. Wang F, Zhang W, Guo L, Bao W, Jin N, Liu R, et al. Gambogic acid suppresses hypoxia-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/vascular endothelial growth factor expression via inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target protein of rapamycin pathway in multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Sci. 2014; 105:1063–1070.
Article5. Pratt G, Goodyear O, Moss P. Immunodeficiency and immunotherapy in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2007; 138:563–579.
Article6. Chiron D, Jego G, Pellat-Deuceunynck C. Toll-like receptors: expression and involvement in multiple myeloma. Leuk Res. 2010; 34:1545–1550.
Article7. Kawai T, Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 2010; 11:373–384.
Article8. Lester SN, Li K. Toll-like receptors in antiviral innate immunity. J Mol Biol. 2014; 426:1246–1264.
Article9. Matsumoto M, Seya T. TLR3: interferon induction by double-stranded RNA including poly(I:C). Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008; 60:805–812.
Article10. Chiron D, Pellat-Deceunynck C, Amiot M, Bataille R, Jego G. TLR3 ligand induces NF-κB activation and various fates of multiple myeloma cells depending on IFN-α production. J Immunol. 2009; 182:4471–4478.
Article11. Abdi J, Engels F, Garssen J, Redegeld F. The role of toll-like receptor mediated signalling in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011; 80:225–240.
Article12. Munir M. TRIM proteins: another class of viral victims. Sci Signal. 2010; 3:jc2.
Article13. Ozato K, Shin DM, Chang TH, Morse HC 3rd. TRIM family proteins and their emerging roles in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008; 8:849–860.
Article14. Meroni G, Diez-Roux G. TRIM/RBCC, a novel class of ‘single protein RING finger’ E3 ubiquitin ligases. Bioessays. 2005; 27:1147–1157.
Article15. Hatakeyama S. TRIM family proteins: roles in autophagy, immunity, and carcinogenesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017; 42:297–311.
Article16. Wang J, Liu B, Wang N, Lee YM, Liu C, Li K. TRIM56 is a virus- and interferon-inducible E3 ubiquitin ligase that restricts pestivirus infection. J Virol. 2011; 85:3733–3745.
Article17. Shen Y, Li NL, Wang J, Liu B, Lester S, Li K. TRIM56 is an essential component of the TLR3 antiviral signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:36404–36413.
Article18. Saha MN, Jiang H, Yang Y, Reece D, Chang H. PRIMA-1Met/APR-246 displays high antitumor activity in multiple myeloma by induction of p73 and Noxa. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013; 12:2331–2341.
Article19. Park WH, Seol JG, Kim ES, Hyun JM, Jung CW, Lee CC, et al. Arsenic trioxide-mediated growth inhibition in MC/CAR myeloma cells via cell cycle arrest in association with induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p21, and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2000; 60:3065–3071.20. Tsuchida T, Zou J, Saitoh T, Kumar H, Abe T, Matsuura Y, et al. The ubiquitin ligase TRIM56 regulates innate immune responses to intracellular double-stranded DNA. Immunity. 2010; 33:765–776.
Article21. Watanabe M, Hatakeyama S. TRIM proteins and diseases. J Biochem. 2017; 161:135–144.
Article22. Qin Y, Cui H, Zhang H. Overexpression of TRIM25 in lung cancer regulates tumor cell progression. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2016; 15:707–715.
Article23. Yamada Y, Takayama KI, Fujimura T, Ashikari D, Obinata D, Takahashi S, et al. A novel prognostic factor TRIM44 promotes cell proliferation and migration, and inhibits apoptosis in testicular germ cell tumor. Cancer Sci. 2017; 108:32–41.
Article24. Chen Y, Guo Y, Yang H, Shi G, Xu G, Shi J, et al. TRIM66 overexpresssion contributes to osteosarcoma carcinogenesis and indicates poor survival outcome. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:23708–23719.
Article25. Yi J, Huang D, Li X, Jiang G, Dong J, Liu Y. TRIM26 acts as a tumor suppressor in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2016; 9:6385–6390.26. Sutton SK, Koach J, Tan O, Liu B, Carter DR, Wilmott JS, et al. TRIM16 inhibits proliferation and migration through regulation of interferon beta 1 in melanoma cells. Oncotarget. 2014; 5:10127–10139.
Article27. Lee OH, Lee J, Lee KH, Woo YM, Kang JH, Yoon HG, et al. Role of the focal adhesion protein TRIM15 in colon cancer development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015; 1853:409–421.
Article28. Ai L, Kim WJ, Alpay M, Tang M, Pardo CE, Hatakeyama S, et al. TRIM29 suppresses TWIST1 and invasive breast cancer behavior. Cancer Res. 2014; 74:4875–4887.
Article29. Harashima N, Inao T, Imamura R, Okano S, Suda T, Harada M. Roles of the PI3K/Akt pathway and autophagy in TLR3 signalinginduced apoptosis and growth arrest of human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012; 61:667–676.
Article30. Salaun B, Coste I, Rissoan MC, Lebecque SJ, Renno T. TLR3 can directly trigger apoptosis in human cancer cells. J Immunol. 2006; 176:4894–4901.
Article31. Khvalevsky E, Rivkin L, Rachmilewitz J, Galun E, Giladi H. TLR3 signaling in a hepatoma cell line is skewed towards apoptosis. J Cell Biochem. 2007; 100:1301–1312.
Article32. Morikawa T, Sugiyama A, Kume H, Ota S, Kashima T, Tomita K, et al. Identification of Toll-like receptor 3 as a potential therapeutic target in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:5703–5709.
Article33. Jiang Q, Wei H, Tian Z. Poly I:C enhances cycloheximide-induced apoptosis of tumor cells through TLR3 pathway. BMC Cancer. 2008; 8:12.
Article34. Bohnhorst J, Rasmussen T, Moen SH, Fløttum M, Knudsen L, Børset M, et al. Toll-like receptors mediate proliferation and survival of multiple myeloma cells. Leukemia. 2006; 20:1138–1144.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- TRIF Deficiency does not Affect Severity of Ovalbumin-induced Airway Inflammation in Mice
- Rapid Progression of Solitary Plasmacytoma to Multiple Myeloma in Lumbar Vertebra
- Multiple myeloma
- Studying the Effect of Downregulating Autophagy-Related Gene LC3 on TLR3 Apoptotic Pathway Mediated by dsRNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
- Four Cases of Multiple Myeloma