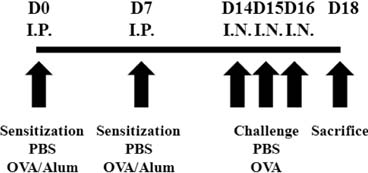
Immune Netw.
2014 Oct;14(5):249-254. 10.4110/in.2014.14.5.249.
TRIF Deficiency does not Affect Severity of Ovalbumin-induced Airway Inflammation in Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea. pjhak@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon 302-718, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 500-757, Korea. jonpark@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2391721
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2014.14.5.249
Abstract
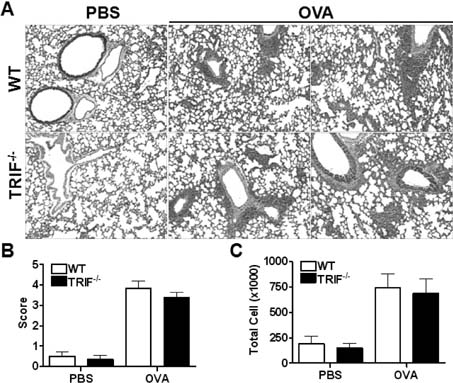
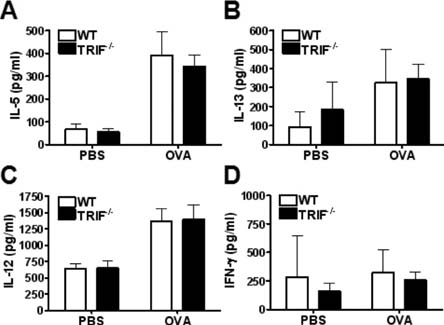
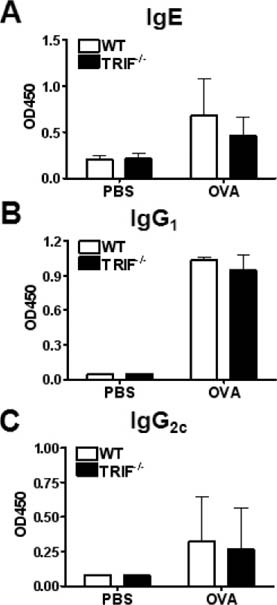
- Allergic asthma is a chronic pulmonary inflammatory disease characterized by reversible airway obstruction, hyperresponsiveness and eosinophils infiltration. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) signaling are closely associated with asthma and have emerged as a novel therapeutic target in allergic disease. The functions of TLR3 and TLR4 in allergic airway inflammation have been studied; however, the precise role of TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-beta (TRIF), the adaptor molecule for both TLR3 and TLR4, is not yet fully understood. To investigate this, we developed a mouse model of OVA-induced allergic airway inflammation and compared the severity of allergic airway inflammation in WT and TRIF-/- mice. Histopathological assessment revealed that the severity of inflammation in airway inflammation in TRIF-deficient mice was comparable to that in WT mice. The total number of cells recovered from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid did not differ between WT and TRIF-deficient mice. Moreover, TRIF deficiency did not affect Th1 and Th2 cytokine production in lung tissue nor the level of serum OVA-specific IgE, IgG1 and IgG2c. These findings suggest that TRIF-mediated signaling may not be critical for the development of allergic airway inflammation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. To T, Stanojevic S, Moores G, Gershon AS, Bateman ED, Cruz AA, Boulet LP. Global asthma prevalence in adults: findings from the cross-sectional world health survey. BMC Public Health. 2012; 12:204.
Article2. Shifren A, Witt C, Christie C, Castro M. Mechanisms of remodeling in asthmatic airways. J Allergy (Cairo). 2012; 2012:316049.
Article3. Holgate ST. Innate and adaptive immune responses in asthma. Nat Med. 2012; 18:673–683.
Article4. Agrawal DK, Shao Z. Pathogenesis of allergic airway inflammation. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2010; 10:39–48.
Article5. Kuhl K, Hanania NA. Targeting IgE in asthma. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2012; 18:1–5.
Article6. Yazdanbakhsh M, Kremsner PG, van Ree R. Allergy, parasites, and the hygiene hypothesis. Science. 2002; 296:490–494.
Article7. Strachan DP. Hay fever, hygiene, and household size. BMJ. 1989; 299:1259–1260.
Article8. Matricardi PM, Rosmini F, Riondino S, Fortini M, Ferrigno L, Rapicetta M, Bonini S. Exposure to foodborne and orofecal microbes versus airborne viruses in relation to atopy and allergic asthma: epidemiological study. BMJ. 2000; 320:412–417.
Article9. Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2004; 5:987–995.
Article10. Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004; 4:499–511.
Article11. Sato S, Sugiyama M, Yamamoto M, Watanabe Y, Kawai T, Takeda K, Akira S. Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-beta (TRIF) associates with TNF receptor-associated factor 6 and TANK-binding kinase 1, and activates two distinct transcription factors, NF-kappa B and IFN-regulatory factor-3, in the Toll-like receptor signaling. J Immunol. 2003; 171:4304–4310.
Article12. Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006; 13:816–825.
Article13. Kumar H, Kawai T, Akira S. Pathogen recognition in the innate immune response. Biochem J. 2009; 420:1–16.
Article14. Eisenbarth SC, Piggott DA, Huleatt JW, Visintin I, Herrick CA, Bottomly K. Lipopolysaccharide-enhanced, toll-like receptor 4-dependent T helper cell type 2 responses to inhaled antigen. J Exp Med. 2002; 196:1645–1651.
Article15. Torres D, Dieudonne A, Ryffel B, Vilain E, Si-Tahar M, Pichavant M, Lassalle P, Trottein F, Gosset P. Double-stranded RNA exacerbates pulmonary allergic reaction through TLR3: implication of airway epithelium and dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2010; 185:451–459.
Article16. Stowell NC, Seideman J, Raymond HA, Smalley KA, Lamb RJ, Egenolf DD, Bugelski PJ, Murray LA, Marsters PA, Bunting RA, Flavell RA, Alexopoulou L, San Mateo LR, Griswold DE, Sarisky RT, Mbow ML, Das AM. Long-term activation of TLR3 by poly(I:C) induces inflammation and impairs lung function in mice. Respir Res. 2009; 10:43.
Article17. Hollingsworth JW 2nd, Cook DN, Brass DM, Walker JK, Morgan DL, Foster WM, Schwartz DA. The role of Toll-like receptor 4 in environmental airway injury in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004; 170:126–132.
Article18. Bortolatto J, Borducchi E, Rodriguez D, Keller AC, Faquim-Mauro E, Bortoluci KR, Mucida D, Gomes E, Christ A, Schnyder-Candrian S, Schnyder B, Ryffel B, Russo M. Toll-like receptor 4 agonists adsorbed to aluminium hydroxide adjuvant attenuate ovalbumin-specific allergic airway disease: role of MyD88 adaptor molecule and interleukin-12/interferon-gamma axis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:1668–1679.
Article19. Hammad H, Chieppa M, Perros F, Willart MA, Germain RN, Lambrecht BN. House dust mite allergen induces asthma via Toll-like receptor 4 triggering of airway structural cells. Nat Med. 2009; 15:410–416.
Article20. Abston ED, Coronado MJ, Bucek A, Bedja D, Shin J, Kim JB, Kim E, Gabrielson KL, Georgakopoulos D, Mitzner W, Fairweather D. Th2 regulation of viral myocarditis in mice: different roles for TLR3 versus TRIF in progression to chronic disease. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012; 2012:129486.
Article21. Kaisho T, Hoshino K, Iwabe T, Takeuchi O, Yasui T, Akira S. Endotoxin can induce MyD88-deficient dendritic cells to support T(h)2 cell differentiation. Int Immunol. 2002; 14:695–700.
Article22. Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996; 383:787–793.
Article23. Takatsu K, Takaki S, Hitoshi Y. Interleukin-5 and its receptor system: implications in the immune system and inflammation. Adv Immunol. 1994; 57:145–190.
Article24. Wills-Karp M. Interleukin-13 in asthma pathogenesis. Immunol Rev. 2004; 202:175–190.
Article25. Chung F. Anti-inflammatory cytokines in asthma and allergy: interleukin-10, interleukin-12, interferon-gamma. Mediators Inflamm. 2001; 10:51–59.
Article26. Coffman RL, Lebman DA, Rothman P. Mechanism and regulation of immunoglobulin isotype switching. Adv Immunol. 1993; 54:229–270.
Article27. Matsumoto K, Inoue H. Viral infections in asthma and COPD. Respir Investig. 2014; 52:92–100.
Article28. Nicholson KG, Kent J, Ireland DC. Respiratory viruses and exacerbations of asthma in adults. BMJ. 1993; 307:982–986.
Article29. Atmar RL, Guy E, Guntupalli KK, Zimmerman JL, Bandi VD, Baxter BD, Greenberg SB. Respiratory tract viral infections in inner-city asthmatic adults. Arch Intern Med. 1998; 158:2453–2459.
Article30. Joshi P, Shaw A, Kakakios A, Isaacs D. Interferon-gamma levels in nasopharyngeal secretions of infants with respiratory syncytial virus and other respiratory viral infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 2003; 131:143–147.
Article31. Armann J, von Mutius E. Do bacteria have a role in asthma development? Eur Respir J. 2010; 36:469–471.
Article32. Korppi M. Management of bacterial infections in children with asthma. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2009; 7:869–877.
Article33. Johnston SL, Blasi F, Black PN, Martin RJ, Farrell DJ, Nieman RB. The effect of telithromycin in acute exacerbations of asthma. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:1589–1600.
Article34. Kim YK, Oh SY, Jeon SG, Park HW, Lee SY, Chun EY, Bang B, Lee HS, Oh MH, Kim YS, Kim JH, Gho YS, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY, Zhu Z. Airway exposure levels of lipopolysaccharide determine type 1 versus type 2 experimental asthma. J Immunol. 2007; 178:5375–5382.
Article35. Delayre-Orthez C, de Blay F, Frossard N, Pons F. Dose-dependent effects of endotoxins on allergen sensitization and challenge in the mouse. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:1789–1795.
Article36. Reed CE, Milton DK. Endotoxin-stimulated innate immunity: A contributing factor for asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:157–166.
Article37. O'Neill LA. Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for inflammatory and infectious diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003; 3:396–403.38. Shalaby KH, Allard-Coutu A, O'Sullivan MJ, Nakada E, Qureshi ST, Day BJ, Martin JG. Inhaled birch pollen extract induces airway hyperresponsiveness via oxidative stress but independently of pollen-intrinsic NADPH oxidase activity, or the TLR4-TRIF pathway. J Immunol. 2013; 191:922–933.
Article39. Sahiner UM, Semic-Jusufagic A, Curtin JA, Birben E, Belgrave D, Sackesen C, Simpson A, Yavuz TS, Akdis CA, Custovic A, Kalayci O. Polymorphisms of endotoxin pathway and endotoxin exposure: in vitro IgE synthesis and replication in a birth cohort. Allergy. 2014; doi: 10.1111/all.12504.40. Hsia BJ, Whitehead GS, Thomas SY, Nakano K, Gowdy KM, Aloor JJ, Nakano H, Cook DN. Trif-dependent induction of Th17 immunity by lung dendritic cells. Mucosal Immunol. 2014; doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.56.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Enhancement of Allergen-induced Airway Inflammation by NOX2 Deficiency
- Changes in airway eosinophils and bone marrow eosinophil progenitors following allergen-challenge in mouse model of asthma
- Receptor Interacting Protein 2 (RIP2) Is Dispensable for OVA-Induced Airway Inflammation in Mice
- An Intratracheal Challenge Murine Model of Asthma: Can Bronchial Inflammation Affect the Nose?
- Effects of CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides in Chronic Inflammation and Remodeling of Airway in a Murine Model of Bronchial Asthma