J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Sep;29(Suppl 2):S146-S154. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.S2.S146.
Bilirubin Activates Transcription of HIF-1alpha in Human Proximal Tubular Cells Cultured in the Physiologic Oxygen Content
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Immunology, Seoul National University Postgraduate School, Seoul, Korea. mednep@snubh.org
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Renal Institute, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2069806
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.S2.S146
Abstract
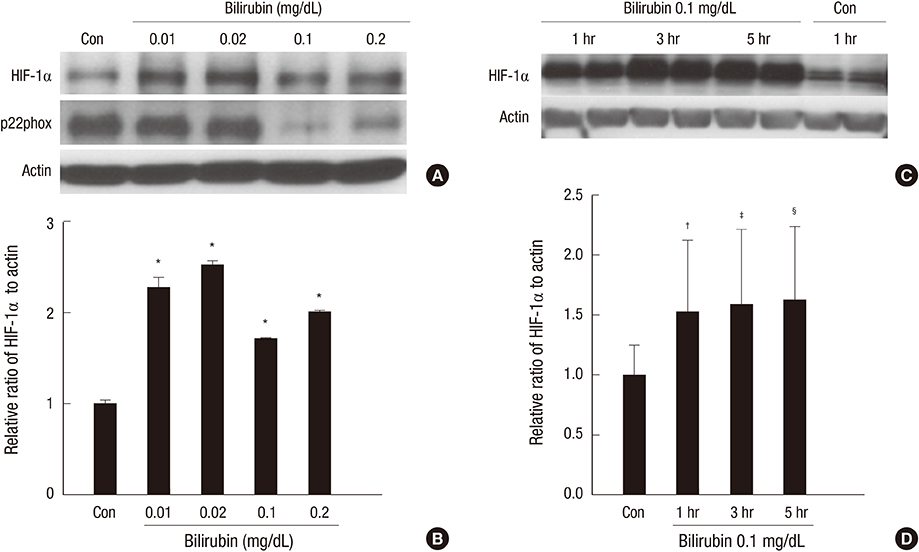
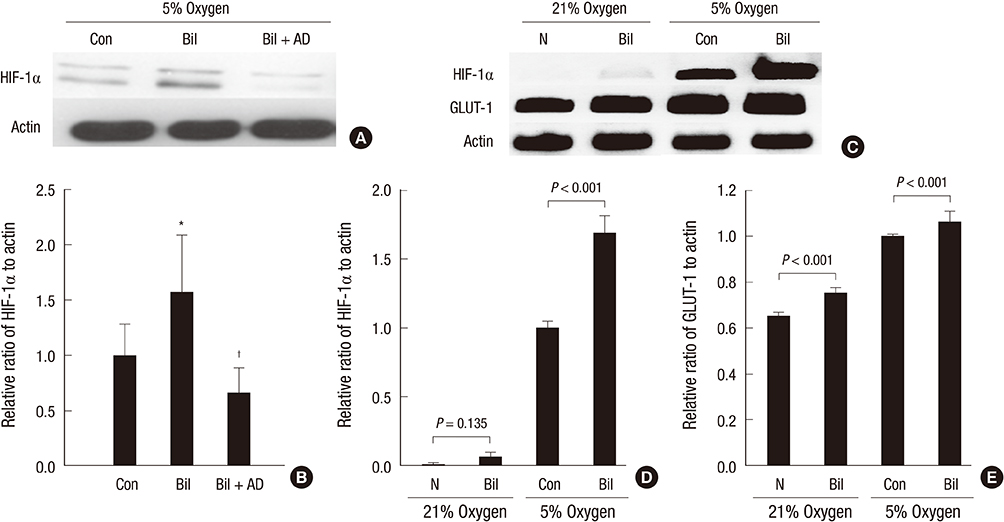
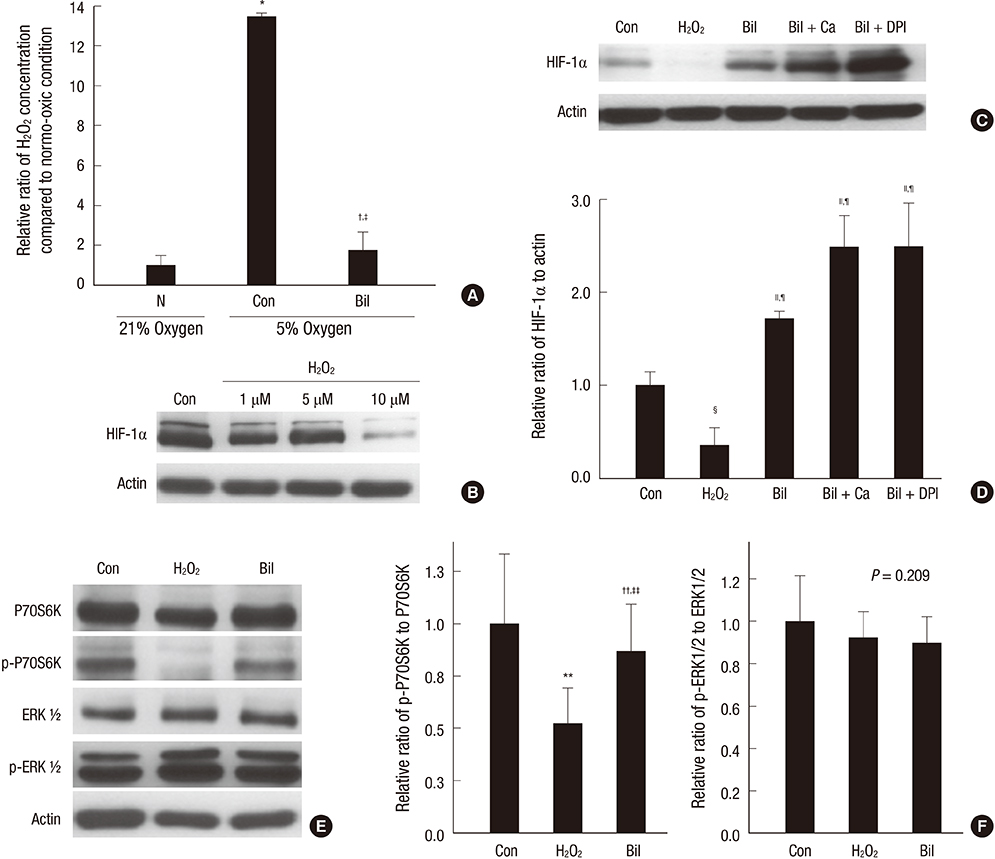
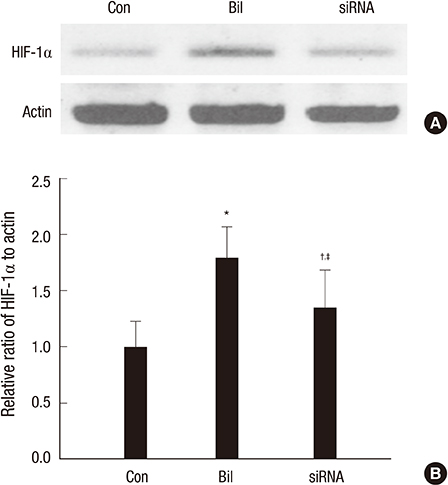
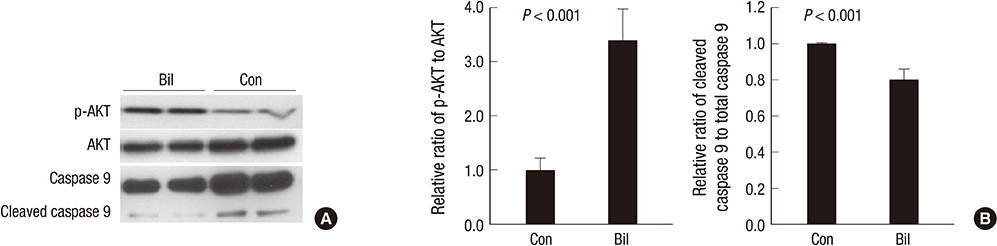
- The expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) is influenced by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Effect of bilirubin on HIF-1 expression in proximal tubular cells was investigated under physiological oxygen concentration, which is relative hypoxic condition mimicking oxygen content in the medulla of renal tissue. The human kidney (HK2) cells were cultured in 5% oxygen with or without bilirubin. HIF-1alpha protein expression was increased by bilirubin treatment at 0.01-0.2 mg/dL concentration. The messenger RNA expression of HIF-1alpha was increased by 1.69+/-0.05 folds in the cells cultured with 0.1 mg/dL bilirubin, compared to the control cells. The inhibitors of PI3K/mTOR, PI3K/AKT, and ERK 1/2 pathways did not attenuate increased HIF-1alpha expression by bilirubin. HIF-1alpha expression decreased by 10 microM exogenous hydrogen peroxide (H2O2); scavenger of ROS with or without bilirubin in the HK2 cells increased HIF-1alpha concentration more than that in the cells without bilirubin. Exogenous H2O2 decreased the phosphorylation of P70S6 kinase, which was completely reversed by bilirubin treatment. Knockdown of NOX4 gene by small interfering RNA (siRNA) increased HIF-1alpha mRNA expression. In coonclusion, bilirubin enhances HIF-1alpha transcription as well as the up-regulation of HIF-1alpha protein translation through the attenuation of ROS and subunits of NADPH oxidase.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Bilirubin/*pharmacology
Cell Line
Epithelial Cells/cytology/metabolism
Humans
Hydrogen Peroxide/toxicity
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1, alpha Subunit/genetics/*metabolism
Kidney Tubules, Proximal/cytology
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 1/metabolism
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 3/metabolism
NADPH Oxidase/antagonists & inhibitors/genetics/metabolism
Oxygen/*pharmacology
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinases/metabolism
Phosphorylation/drug effects
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-akt/metabolism
RNA Interference
Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinases, 70-kDa/metabolism
Signal Transduction/drug effects
TOR Serine-Threonine Kinases/metabolism
Transcriptional Activation/*drug effects
Up-Regulation/drug effects
Bilirubin
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1, alpha Subunit
Hydrogen Peroxide
NADPH Oxidase
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinases
TOR Serine-Threonine Kinases
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-akt
Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinases, 70-kDa
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 1
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 3
Oxygen
Figure
Reference
-
1. Palm F, Nordquist L. Renal tubulointerstitial hypoxia: cause and consequence of kidney dysfunction. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011; 38:474–480.2. Palm F, Cederberg J, Hansell P, Liss P, Carlsson PO. Reactive oxygen species cause diabetes-induced decrease in renal oxygen tension. Diabetologia. 2003; 46:1153–1160.3. Manotham K, Tanaka T, Matsumoto M, Ohse T, Miyata T, Inagi R, Kurokawa K, Fujita T, Nangaku M. Evidence of tubular hypoxia in the early phase in the remnant kidney model. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004; 15:1277–1288.4. Oh SW, Ahn JM, Lee YM, Kim S, Chin HJ, Chae DW, Na KY. Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor by cobalt is associated with the attenuation of tissue injury and apoptosis in cyclosporine-induced nephropathy. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2012; 226:197–206.5. Song YR, You SJ, Lee YM, Chin HJ, Chae DW, Oh YK, Joo KW, Han JS, Na KY. Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor attenuates renal injury in rat remnant kidney. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010; 25:77–85.6. Rosenberger C, Mandriota S, Jürgensen JS, Wiesener MS, Hörstrup JH, Frei U, Ratcliffe PJ, Maxwell PH, Bachmann S, Eckardt KU. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha in hypoxic and ischemic rat kidneys. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002; 13:1721–1732.7. Basile DP, Donohoe D, Roethe K, Osborn JL. Renal ischemic injury results in permanent damage to peritubular capillaries and influences long-term function. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001; 281:F887–F899.8. Wilcox CS, Palm F, Welch WJ. Renal oxygenation and function of the rat kidney: effects of inspired oxygen and preglomerular oxygen shunting. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013; 765:329–334.9. Rama I, Bruene B, Torras J, Koehl R, Cruzado JM, Bestard O, Franquesa M, Lloberas N, Weigert A, Herrero-Fresneda I, et al. Hypoxia stimulus: An adaptive immune response during dendritic cell maturation. Kidney Int. 2008; 73:816–825.10. Gunaratnam L, Bonventre JV. HIF in kidney disease and development. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009; 20:1877–1887.11. Welch WJ, Baumgärtl H, Lübbers D, Wilcox CS. Nephron pO2 and renal oxygen usage in the hypertensive rat kidney. Kidney Int. 2001; 59:230–237.12. Fu YY, Kang KJ, Ahn JM, Kim HR, Na KY, Chae DW, Kim S, Chin HJ. Hyperbilirubinemia reduces the streptozotocin-induced pancreatic damage through attenuating the oxidative stress in the Gunn rat. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010; 222:265–273.13. Nangaku M, Rosenberger C, Heyman SN, Eckardt KU. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor in kidney disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013; 40:148–157.14. Chun YS, Kim MS, Park JW. Oxygen-dependent and -independent regulation of HIF-1alpha. J Korean Med Sci. 2002; 17:581–588.15. Déry MA, Michaud MD, Richard DE. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: regulation by hypoxic and non-hypoxic activators. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005; 37:535–540.16. Pagé EL, Robitaille GA, Pouysségur J, Richard DE. Induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by transcriptional and translational mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:48403–48409.17. Blouin CC, Pagé EL, Soucy GM, Richard DE. Hypoxic gene activation by lipopolysaccharide in macrophages: implication of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Blood. 2004; 103:1124–1130.18. Richard DE, Berra E, Gothié E, Roux D, Pouysségur J. p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and enhance the transcriptional activity of HIF-1. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:32631–32637.19. Yang ZZ, Zhang AY, Yi FX, Li PL, Zou AP. Redox regulation of HIF-1alpha levels and HO-1 expression in renal medullary interstitial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003; 284:F1207–F1215.20. Katavetin P, Miyata T, Inagi R, Tanaka T, Sassa R, Ingelfinger JR, Fujita T, Nangaku M. High glucose blunts vascular endothelial growth factor response to hypoxia via the oxidative stress-regulated hypoxia-inducible factor/hypoxia-responsible element pathway. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 17:1405–1413.21. Goyal P, Weissmann N, Grimminger F, Hegel C, Bader L, Rose F, Fink L, Ghofrani HA, Schermuly RT, Schmidt HH, et al. Upregulation of NAD(P)H oxidase 1 in hypoxia activates hypoxia-inducible factor 1 via increase in reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004; 36:1279–1288.22. Vítek L, Jirsa M, Brodanová M, Kalab M, Marecek Z, Danzig V, Novotný L, Kotal P. Gilbert syndrome and ischemic heart disease: a protective effect of elevated bilirubin levels. Atherosclerosis. 2002; 160:449–456.23. Mashitani T, Hayashino Y, Okamura S, Tsujii S, Ishii H. Correlations between serum bilirubin levels and diabetic nephropathy progression among Japanese type 2 diabetic patients: a prospective cohort study (Diabetes Distress and Care Registry at Tenri [DDCRT 5]). Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:252–258.24. Cheriyath P, Gorrepati VS, Peters I, Nookala V, Murphy ME, Srouji N, Fischman D. High total bilirubin as a protective factor for diabetes mellitus: an analysis of NHANES data from 1999 - 2006. J Clin Med Res. 2010; 2:201–206.25. Jung CH, Lee MJ, Kang YM, Hwang JY, Jang JE, Leem J, Park JY, Kim HK, Lee WJ. Higher serum bilirubin level as a protective factor for the development of diabetes in healthy Korean men: a 4 year retrospective longitudinal study. Metabolism. 2014; 63:87–93.26. Han SS, Na KY, Chae DW, Kim YS, Kim S, Chin HJ. High serum bilirubin is associated with the reduced risk of diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010; 221:133–140.27. Fukui M, Tanaka M, Shiraishi E, Harusato I, Hosoda H, Asano M, Hasegawa G, Nakamura N. Relationship between serum bilirubin and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int. 2008; 74:1197–1201.28. Chin HJ, Song YR, Kim HS, Park M, Yoon HJ, Na KY, Kim Y, Chae DW, Kim S. The bilirubin level is negatively correlated with the incidence of hypertension in normotensive Korean population. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:S50–S56.29. Chin HJ, Cho HJ, Lee TW, Na KY, Oh KH, Joo KW, Yoon HJ, Kim YS, Ahn C, Han JS, et al. The mildly elevated serum bilirubin level is negatively associated with the incidence of end stage renal disease in patients with IgA nephropathy. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:S22–S29.30. Oh SW, Lee ES, Kim S, Na KY, Chae DW, Kim S, Chin HJ. Bilirubin attenuates the renal tubular injury by inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis. BMC Nephrol. 2013; 14:105.31. Adin CA, Croker BP, Agarwal A. Protective effects of exogenous bilirubin on ischemia-reperfusion injury in the isolated, perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005; 288:F778–F784.32. Demirogullari B, Ekingen G, Guz G, Bukan N, Erdem O, Ozen IO, Memis L, Sert S. A comparative study of the effects of hemin and bilirubin on bilateral renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2006; 103:e1–e5.33. Fujii M, Inoguchi T, Sasaki S, Maeda Y, Zheng J, Kobayashi K, Takayanagi R. Bilirubin and biliverdin protect rodents against diabetic nephropathy by downregulating NAD(P)H oxidase. Kidney Int. 2010; 78:905–919.34. Kietzmann T, Görlach A. Reactive oxygen species in the control of hypoxia-inducible factor-mediated gene expression. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2005; 16:474–486.35. Wang GL, Jiang BH, Semenza GL. Effect of altered redox states on expression and DNA-binding activity of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995; 212:550–556.36. Liu Q, Berchner-Pfannschmidt U, Möller U, Brecht M, Wotzlaw C, Acker H, Jungermann K, Kietzmann T. A Fenton reaction at the endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the redox control of hypoxia-inducible gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:4302–4307.37. Huang LE, Arany Z, Livingston DM, Bunn HF. Activation of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor depends primarily upon redox-sensitive stabilization of its alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:32253–32259.38. Goyal P, Weissmann N, Grimminger F, Hegel C, Bader L, Rose F, Fink L, Ghofrani HA, Schermuly RT, Schmidt HH, et al. Upregulation of NAD-(P)H oxidase 1 in hypoxia activates hypoxia-inducible factor 1 via increase in reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004; 36:1279–1288.39. Higgins DF, Kimura K, Bernhardt WM, Shrimanker N, Akai Y, Hohenstein B, Saito Y, Johnson RS, Kretzler M, Cohen CD, et al. Hypoxia promotes fibrogenesis in vivo via HIF-1 stimulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 2007; 117:3810–3820.40. Sun S, Ning X, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Nie Y, Han S, Liu L, Du R, Xia L, He L, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha induces Twist expression in tubular epithelial cells subjected to hypoxia, leading to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Kidney Int. 2009; 75:1278–1287.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Oxygen-Dependent and -Independent Regulation of HIF-1alpha
- HIF-1alpha: a Valid Therapeutic Target for Tumor Therapy
- CaMKII Inhibitor KN-62 Blunts Tumor Response to Hypoxia by Inhibiting HIF-1alpha in Hepatoma Cells
- Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: its protein stability and biological functions
- The Effect of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on HIF-1alpha and VEGF in Human Lung Cancer Cell Line