J Korean Diabetes Assoc.
2006 Sep;30(5):336-346. 10.4093/jkda.2006.30.5.336.
Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) Expression in the Hypoxic Injury to Pancreatic Beta (MIN6) Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Korea.
- KMID: 2008263
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.5.336
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Islet transplantation is an alternative potential strategy to cure type 1 diabetes mellitus. However, two or more donors are usually needed for one recipient because a substantial part of the graft becomes nonfunctional due to several factors including hypoxia. Though hypoxic exposure of pancreatic beta cells has been reported to induce apoptotic cell death, the molecular processes involved in hypoxia-induced cell death are poorly understood. In type I diabetes, Nitric Oxide (NO) is known as an important cytokine, involved in the pathogenesis of beta cell dysfunction. Pancreatic beta cells are sensitive to the induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) when stimulated by TNF-a or IL-1beta. But contribution of iNOS in response to hypoxia is not yet fully understood.
METHODS
Mouse insulinoma cells (MIN6) were incubated in an anaerobic chamber (75% N2/15% CO2/5% H2) for up to 12 hours. Cell viability was measured after AO/PI staining. Caspase-3 activation was also determined using Western blot analysis. Nitric Oxide (NO) release into culture medium was measured using a Griess reagent. The expression of iNOS and PDX-1 mRNA and iNOS protein was examined using real time PCR and Western blot analysis.
RESULTS
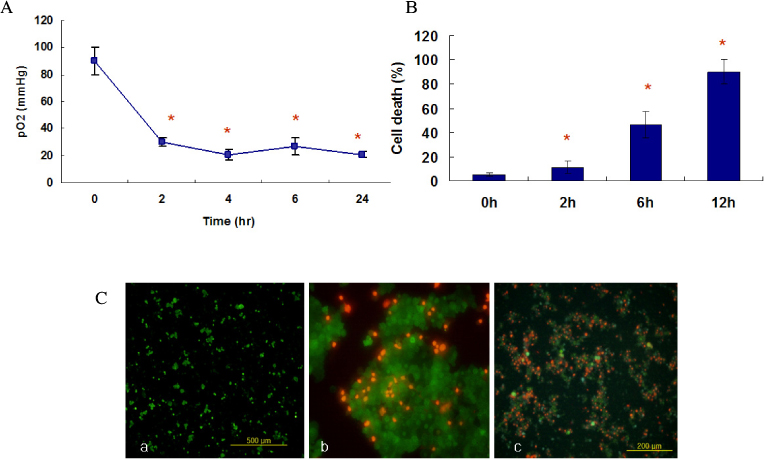
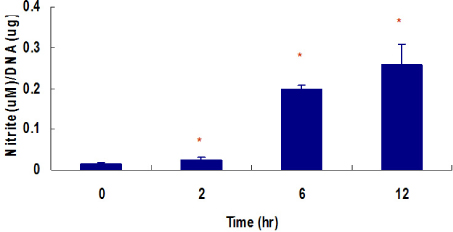
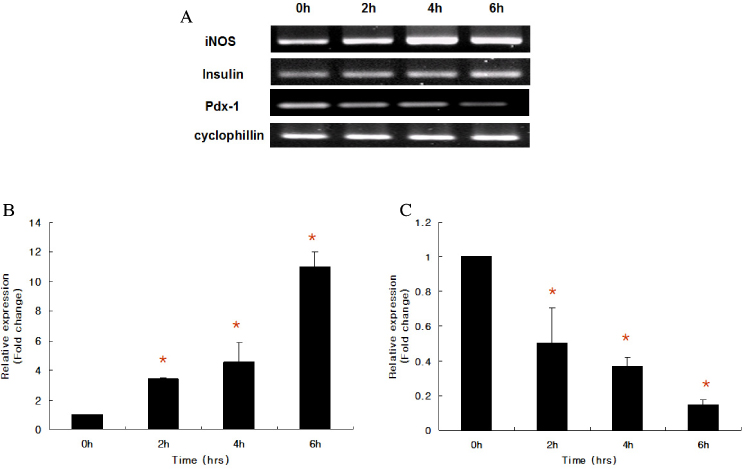
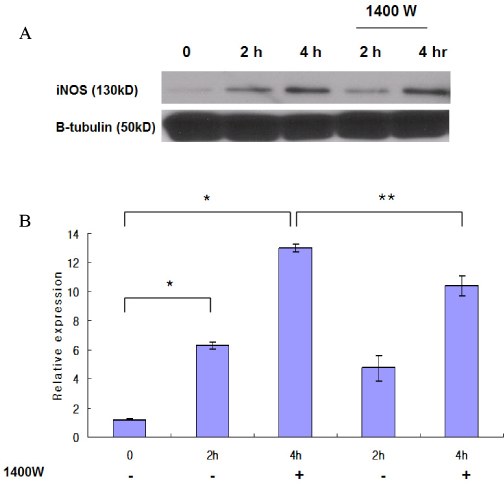
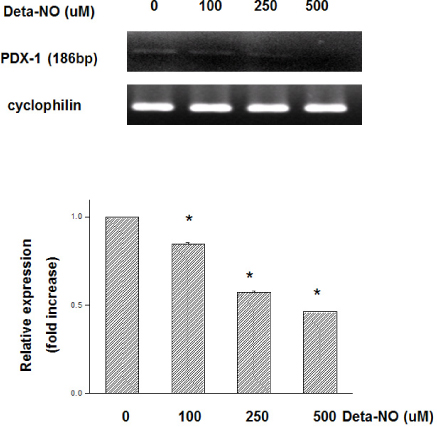
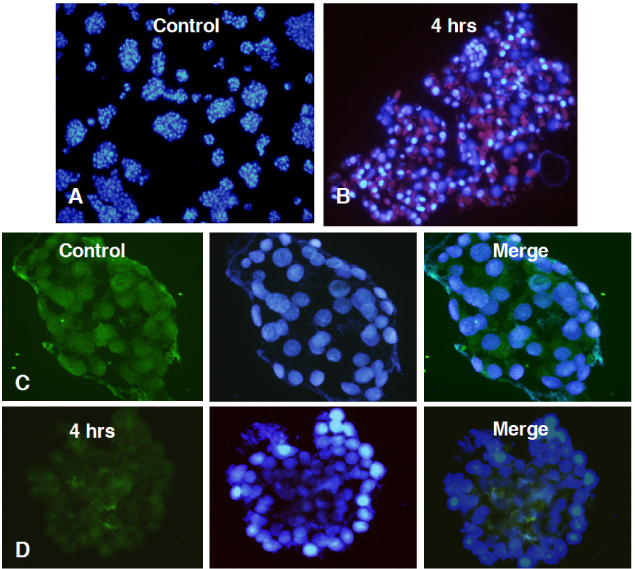
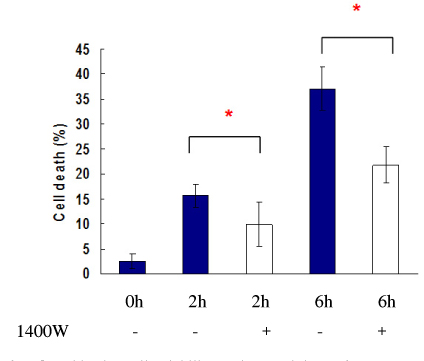
Marked cell death was observed within 6 hours after hypoxic exposure of MIN6 cells (control, < 5%; 2 hr, 11.0+/-7.6%; 6 hr, 46.2+/-12.8%, P < 0.05). Immunoreactivity to activated caspase-3 was observed at 2, 4 and 6 hrs. NO production was increased in a time dependent manner. Expression of iNOS mRNA and protein was significantly increased at 4 and 6 hour after hypoxia. iNOS expression was confirmed by immunostaining. Of note, Pdx-1 mRNA expression was markedly attenuated by hypoxic treatment. Pretreatment with a selective iNOS inhibitor, 1400 W, significantly prevented beta cell death induced by hypoxic injury.
CONCLUSION
Our data suggest that iNOS-NO play an important role in hypoxic injury to MIN6 cells. Therefore, iNOS-NO might be a potential therapeutic target for improving engraftment of the transplanted islets and suppression of iNOS would be helpful for prevention of beta cells damage to hypoxic injury.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Anoxia
Blotting, Western
Caspase 3
Cell Death
Cell Survival
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1
Humans
Insulin-Secreting Cells
Insulinoma
Islets of Langerhans Transplantation
Mice
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type II*
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Messenger
Tissue Donors
Transplants
Caspase 3
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type II
RNA, Messenger
Figure
Reference
-
1. Saaddine JB, Cadwell B, Gregg EW, Engelgau MM, Vinicor F, Imperatore G, Narayan KM. Improvements in diabetes processes of care and intermediate outcomes: United States, 1988-2002. Ann Intern Med. 2006. 144:525–527.2. Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS, Toth E, Warnock GL, Kneteman NM, Rajotte RV. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000. 343:230–238.3. Weir GC. Can we make surrogate beta-cells better than the original? Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004. 15:347–357.4. Yoon KH, Ko SH, Cho JH, Lee JM, Ahn YB, Song KH, Yoo SJ, Kang MI, Cha BY, LeeKW , Son HY, Kang SK, Kim HS, Lee IK, Bonner-Weir S. Selective beta-cell loss and alpha-cell expansion in patients with type 2diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 88:2300–2308.5. Robertson RP. Islet transplantation as a treatment for diabetes - a work in progress. N Engl J Med. 2005. 350:694–705.6. Barshes NR, Wyllie S, Goss JA. Inflammation-mediated dysfunction and apoptosis in pancreatic islet transplantation: implications for intrahepatic grafts. J Leukoc Biol. 2005. 77:587–597.7. Linn T, Schmitz J, Hauck-Schmalenberger I, Lai Y, Bretzel RG, Brandhorst H, randhorst D. Ischaemia is linked to inflammation and induction of angiogenesis in pancreatic islets. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. 144:179–187.8. Kroncke KD, Fehsel K, Suschek C, Kolb-Bachofen V. Inducible nitric oxide synthase-derived nitric oxide in gene regulation, cell death and cell survival. Int Immunopharmacol. 2001. 1:1407–1420.9. Beck KF, Eberhardt W, Frank S, Huwiler A, Messmer UK, Muhl H, Pfeilschifter J. Inducible NO synthase: role in cellular signalling. J Exp Biol. 1999. 202:645–653.10. Corbett JA, Sweetland MA, Wang JL, Lancaster JR Jr, McDaniel ML. Nitric oxide mediates cytokine-induced inhibition of insulin secretion by human islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. 90:1731–1735.11. Eizirik DL, Pavlovic D. Is there a role for nitric oxide in beta-cell dysfunction and damage in IDDM? Diabetes Metab Rev. 1997. 13:293–307.12. Welsh N, Eizirik DL, Bendtzen K, Sandler S. Interleukin-1 beta-induced nitric oxide production in isolated rat pancreatic islets requires gene transcription and may lead to inhibition of the Krebs cycle enzyme aconitase. Endocrinology. 1991. 126:3167–3173.13. Steller H. Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science. 1995. 267:1445–1449.14. Henningsson R, Salehi A, Lundquist I. Role of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in glucose-stimulated insulin release. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002. 283:C296–C304.15. Postovit LM, Sullivan R, Adams MA, Graham CH. Nitric oxide signalling and cellular adaptations to changes in oxygenation. Toxicology. 2005. 208:235–248.16. Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: oxygen homeostasis and disease pathophysiology. Trends Mol Med. 2001. 7:345–350.17. Moritz W, Meier F, Stroka DM, Giuliani M, Kugelmeier P, Nett PC, Lehmann R, Candinas D, Gassmann M, Weber M. Apoptosis in hypoxic human pancreatic islets correlates with HIF-1alpha expression. FASEB J. 2002. 16:745–747.18. Keinanen R, Vartiainen N, Koistinaho J. Molecular cloning and characterization of the rat inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) gene. Gene. 1999. 234:297–305.19. Dionne KE, Colton CK, Yarmush ML. Effect of hypoxia on insulin secretion by isolated rat and canine islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1993. 42:12–21.20. Davalli AM, Scaglia L, Zangen DH, Hollister J, Bonner-Weir S, Weir GC. Vulnerability of islets in the immediate posttransplantation period. Dynamic changes in structure and function. Diabetes. 1996. 45:1161–1167.21. Biarnes M, Montolio M, Nacher V, Raurell M, Soler J, Montanya E. Beta-cell death and mass in syngeneically transplanted islets exposed to short-and long-term hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 2002. 51:66–72.22. Carlsson PO, Palm F, Andersson A, Liss P. Markedly decreased oxygen tension in transplanted rat pancreatic islets irrespective of the implantation site. Diabetes. 2001. 50:489–495.23. Zagorska A, Jozef Dulak. HIF-1: the knowns and unknowns of hypoxia sensing. Acta Biochimica Polonica. 2004. 51:563–585.24. McCabe C, Samali A, O'brien T. Beta cell cytoprotective strategies: establishing the relative roles for iNOS and ROS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. 342:1240–1248.25. Stoorling J, Binzer J, Andersson AK, Zullig RA, Tonnesen M, Lehmann R, Spinas GA, Sandler S, Billestrup N, Mandrup-Poulsen T. Nitric oxide contributes to cytokine-induced apoptosis in pancreatic beta cells via potentiation of JNK activity and inhibition of Akt. Diabetologia. 2005. 48:2039–2050.26. Brune B, von Knethen A, Sandau KB. Nitric oxide and its role in apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998. 351:261–272.27. Beeharry N, Chambers JA, Faragher RG, Garnett KE, Green IC. Analysis of cytokine-induced NO-dependent apoptosis using RNA interference or inhibition by 1400W. Nitric Oxide. 2004. 10:112–118.28. Rydgren T, Sandler S. Efficacy of 1400 W, a novel inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase, inpreventing interleukin-1beta-induced suppression of pancreatic islet function invitro and multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes in vivo. Eur J Endocrinol. 2002. 147:543–551.29. Kato Y, Miura Y, Yamamoto N, Ozaki N, Oiso Y. Suppressive effects of a selective inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) inhibitor on pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Diabetologia. 2003. 46:1228–1233.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nitric oxide in liver fibrosis: The role of inducible nitric oxide synthase
- Inhibitory Effect of Esculetin on the Inducuble Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in TNF-stimulated 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
- Expression of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Human Colorectal
- Change of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression by Ultraviolet B Irradiation on the Skin of a Rat
- The roles of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in pancreatic cancer