Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2014 Sep;7(3):175-180. 10.3342/ceo.2014.7.3.175.
Dexamethasone Inhibits Interleukin-1beta-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Expression in Cochlear Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. entnamsi@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Immunology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. kwontk@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 1973466
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.3.175
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
To investigate the effect of interleukin (IL)-1beta on matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 expression in cochlea and regulation of IL-1beta-mediated MMP-9 expression by dexamethasone and the molecular and signaling mechanisms involved.
METHODS
House ear institute-organ of Corti 1 (HEI-OC1) cells were used and exposed to IL-1beta with/without dexamethasone. Glucocorticoid receptor antagonist, RU486, was used to see the role of dexamethasone. PD98059 (an extracellular signal-regulated kinases [ERKs] inhibitor), SB203580 (a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases [MAPK] inhibitor), SP600125 (a c-Jun N-terminal kinase [JNK] inhibitor) were also used to see the role of MAPKs signaling pathway(s) in IL-1beta-induced MMP-9 expression in HEI-OC1 cells. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and gelatin zymography were used to measure mRNA expression level of MMP-9 and activity of MMP-9, respectively.
RESULTS
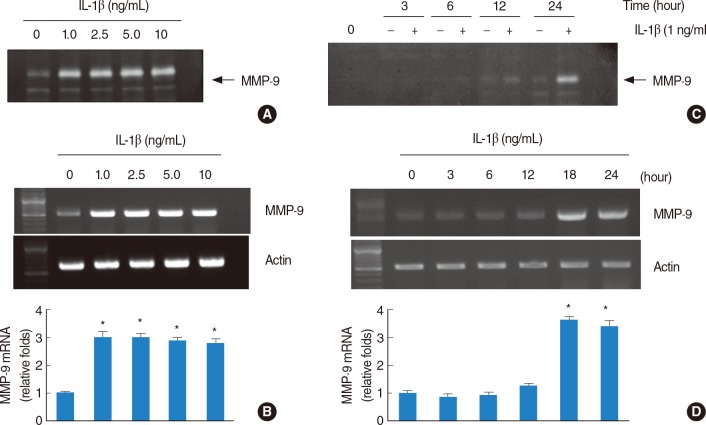
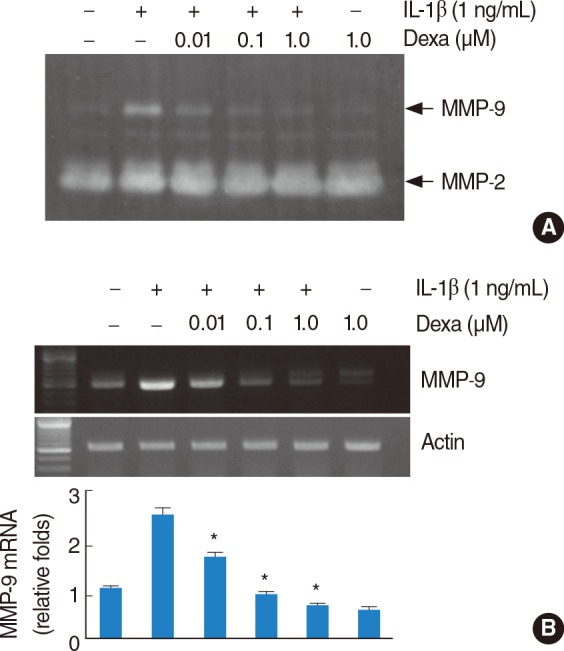
Treatment with IL-1beta-induced the expression of MMP-9 in a dose- and time-dependent manner. IL-1beta (1 ng/mL)-induced MMP-9 expression was inhibited by dexamethasone. Interestingly, p38 MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, significantly inhibited IL-1beta-induced MMP-9 mRNA and MMP-9 activity. However, inhibition of JNKs and ERKs had no effect on the IL-1beta-induced MMP-9 expression.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1beta strongly induces MMP-9 expression via activation of p38 MAPK signaling pathway in HEI-OC1 cells and the induction was inhibited by dexamethasone.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cochlea
Dexamethasone*
Ear
Extracellular Signal-Regulated MAP Kinases
Gelatin
Interleukin-1beta
Interleukins
JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9*
Mifepristone
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Receptors, Glucocorticoid
RNA, Messenger
Dexamethasone
Extracellular Signal-Regulated MAP Kinases
Gelatin
Interleukin-1beta
Interleukins
JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9
Mifepristone
RNA, Messenger
Receptors, Glucocorticoid
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Figure
Reference
-
1. Satoh H, Firestein GS, Billings PB, Harris JP, Keithley EM. Proinflammatory cytokine expression in the endolymphatic sac during inner ear inflammation. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2003; 6. 4(2):139–147. PMID: 12943369.
Article2. Gratton MA, Rao VH, Meehan DT, Askew C, Cosgrove D. Matrix metalloproteinase dysregulation in the stria vascularis of mice with Alport syndrome: implications for capillary basement membrane pathology. Am J Pathol. 2005; 5. 166(5):1465–1474. PMID: 15855646.3. Okada Y, Morodomi T, Enghild JJ, Suzuki K, Yasui A, Nakanishi I, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts: purification and activation of the precursor and enzymic properties. Eur J Biochem. 1990; 12. 194(3):721–730. PMID: 2269296.
Article4. Jang CH, Shin SH, Cho HH, Moon SJ, Cho YB. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and -2 in pediatric chronic otitis media with effusion. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; 7. 70(7):1155–1158. PMID: 16413616.
Article5. Dinh CT, Haake S, Chen S, Hoang K, Nong E, Eshraghi AA, et al. Dexamethasone protects organ of corti explants against tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced loss of auditory hair cells and alters the expression levels of apoptosis-related genes. Neuroscience. 2008; 11. 157(2):405–413. PMID: 18838114.
Article6. Kalinec GM, Webster P, Lim DJ, Kalinec F. A cochlear cell line as an in vitro system for drug ototoxicity screening. Audiol Neurootol. 2003; Jul-Aug. 8(4):177–189. PMID: 12811000.
Article7. Overall CM, Wrana JL, Sodek J. Independent regulation of collagenase, 72-kDa progelatinase, and metalloendoproteinase inhibitor expression in human fibroblasts by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1989; 1. 264(3):1860–1869. PMID: 2536374.8. Ishii K, Schröter-Kermani C, Xu D, Merker HJ, Jahnke V. Extracellular matrix in the rat spiral limbus. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1992; 249(4):224–230. PMID: 1642880.
Article9. Cosgrove D, Samuelson G, Pinnt J. Immunohistochemical localization of basement membrane collagens and associated proteins in the murine cochlea. Hear Res. 1996; 8. 97(1-2):54–65. PMID: 8844186.
Article10. Cosgrove D, Rodgers KD. Expression of the major basement membrane-associated proteins during postnatal development in the murine cochlea. Hear Res. 1997; 3. 105(1-2):159–170. PMID: 9083813.
Article11. Rao VH, Lees GE, Kashtan CE, Nemori R, Singh RK, Meehan DT, et al. Increased expression of MMP-2, MMP-9 (type IV collagenases/gelatinases), and MT1-MMP in canine X-linked Alport syndrome (XLAS). Kidney Int. 2003; 5. 63(5):1736–1748. PMID: 12675849.
Article12. Chandrasekhar SS. Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: clinical and laboratory evaluation. Otol Neurotol. 2001; 1. 22(1):18–23. PMID: 11314710.
Article13. Pitovski DZ, Drescher MJ, Drescher DG. Glucocorticoid receptors in the mammalian inner ear: RU 28362 binding sites. Hear Res. 1994; 6. 77(1-2):216–220. PMID: 7928734.
Article14. Rarey KE, Curtis LM. Receptors for glucocorticoids in the human inner ear. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996; 7. 115(1):38–41. PMID: 8758627.
Article15. Liang KC, Lee CW, Lin WN, Lin CC, Wu CB, Luo SF, et al. Interleukin-1beta induces MMP-9 expression via p42/p44 MAPK, p38 MAPK, JNK, and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathways in human tracheal smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 2007; 6. 211(3):759–770. PMID: 17311279.16. Eberhardt W, Huwiler A, Beck KF, Walpen S, Pfeilschifter J. Amplification of IL-1 beta-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by superoxide in rat glomerular mesangial cells is mediated by increased activities of NF-kappa B and activating protein-1 and involves activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Immunol. 2000; 11. 165(10):5788–5797. PMID: 11067938.17. Wu CY, Hsieh HL, Jou MJ, Yang CM. Involvement of p42/p44 MAPK, p38 MAPK, JNK and nuclear factor-kappa B in interleukin-1beta-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in rat brain astrocytes. J Neurochem. 2004; 9. 90(6):1477–1488. PMID: 15341531.
Article18. McCawley LJ, Li S, Wattenberg EV, Hudson LG. Sustained activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway: a mechanism underlying receptor tyrosine kinase specificity for matrix metalloproteinase-9 induction and cell migration. J Biol Chem. 1999; 2. 274(7):4347–4353. PMID: 9933637.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Vitamin D Inhibits Expression and Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase in Human Lung Fibroblasts (HFL-1) Cells
- Signal transduction of cytokines in inducing matrix metalloproteinas-9 in myometrial smooth muscle cells from term pregnant women
- EGCC inhibits tumor growth by inbibiting Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 induction in UM-SCC-1 cells
- Effects of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on the Interleukin-1 beta-Induced Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Dexamethasone Inhibits TGF-β1-Induced Cell Migration by Regulating the ERK and AKT Pathways in Human Colon Cancer Cells Via CYR61