Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Jul;48(3):1141-1153. 10.4143/crt.2015.209.
Dexamethasone Inhibits TGF-β1-Induced Cell Migration by Regulating the ERK and AKT Pathways in Human Colon Cancer Cells Via CYR61
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 2Department of Biochemistry, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. moonjcho@jejunu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. dbs@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2344088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2015.209
Abstract
- PURPOSE
One of the features in cancer development is the migration of cancer cells to form metastatic lesions. CYR61 protein promotes migration and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in several cancer cell types. Evidence suggests that CYR61 and dexamethasone are relevant to colorectal cancer. However, relationships between them and colorectal cancer are still unclear. Understanding the molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer progression related with CYR61 and dexamethasone, which is widely used for combination chemotherapy, is necessary for improved therapy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
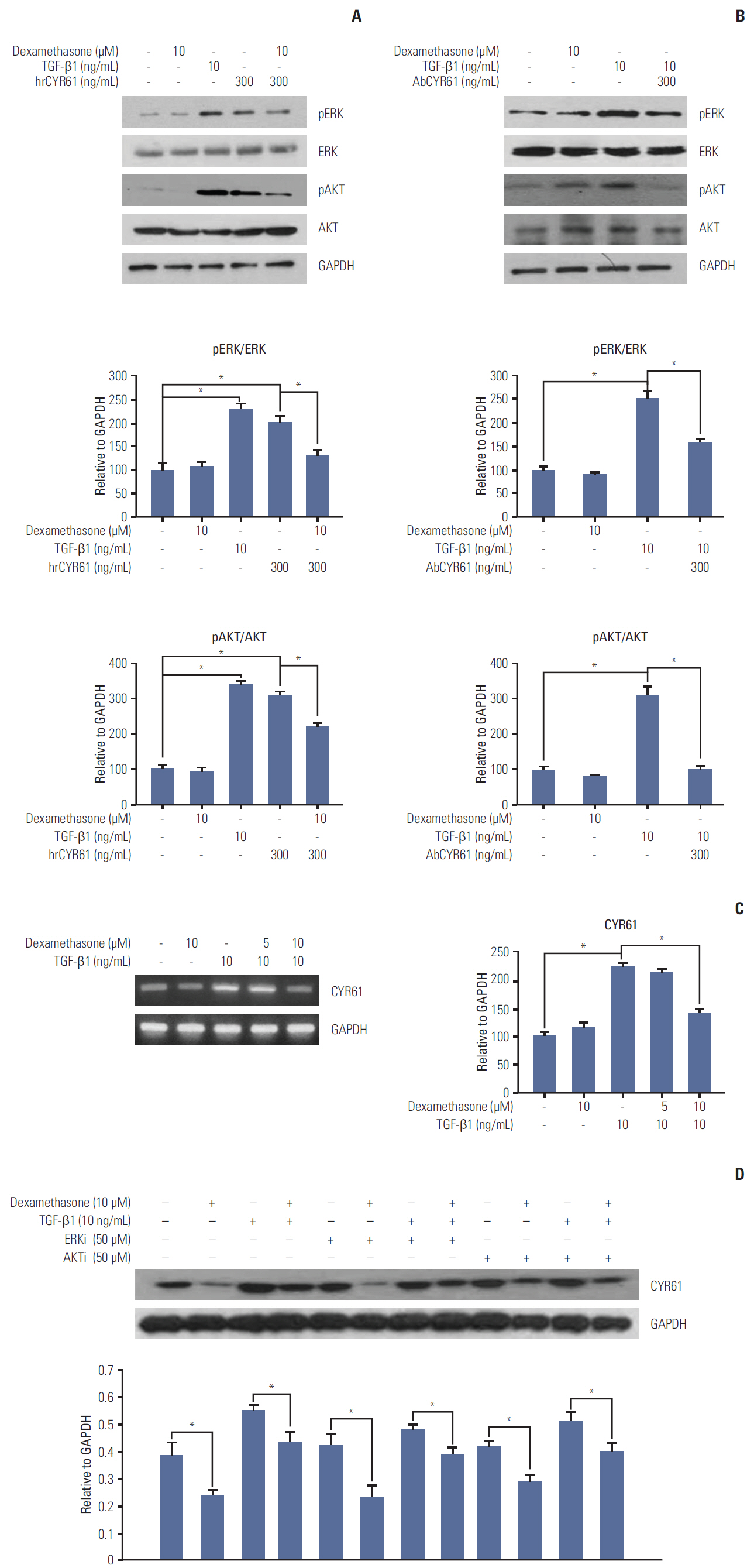
We used colorectal cancer cells, HCT116, co-treated with transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) and dexamethasone to examine the inhibitory migration effect of dexamethasone by migratory assay. Alternatively, both migratory pathways, expression of AKT and ERK, and the target factor CYR61 was also tested by co-treatment with TGF-β1 and dexamethasone.
RESULTS
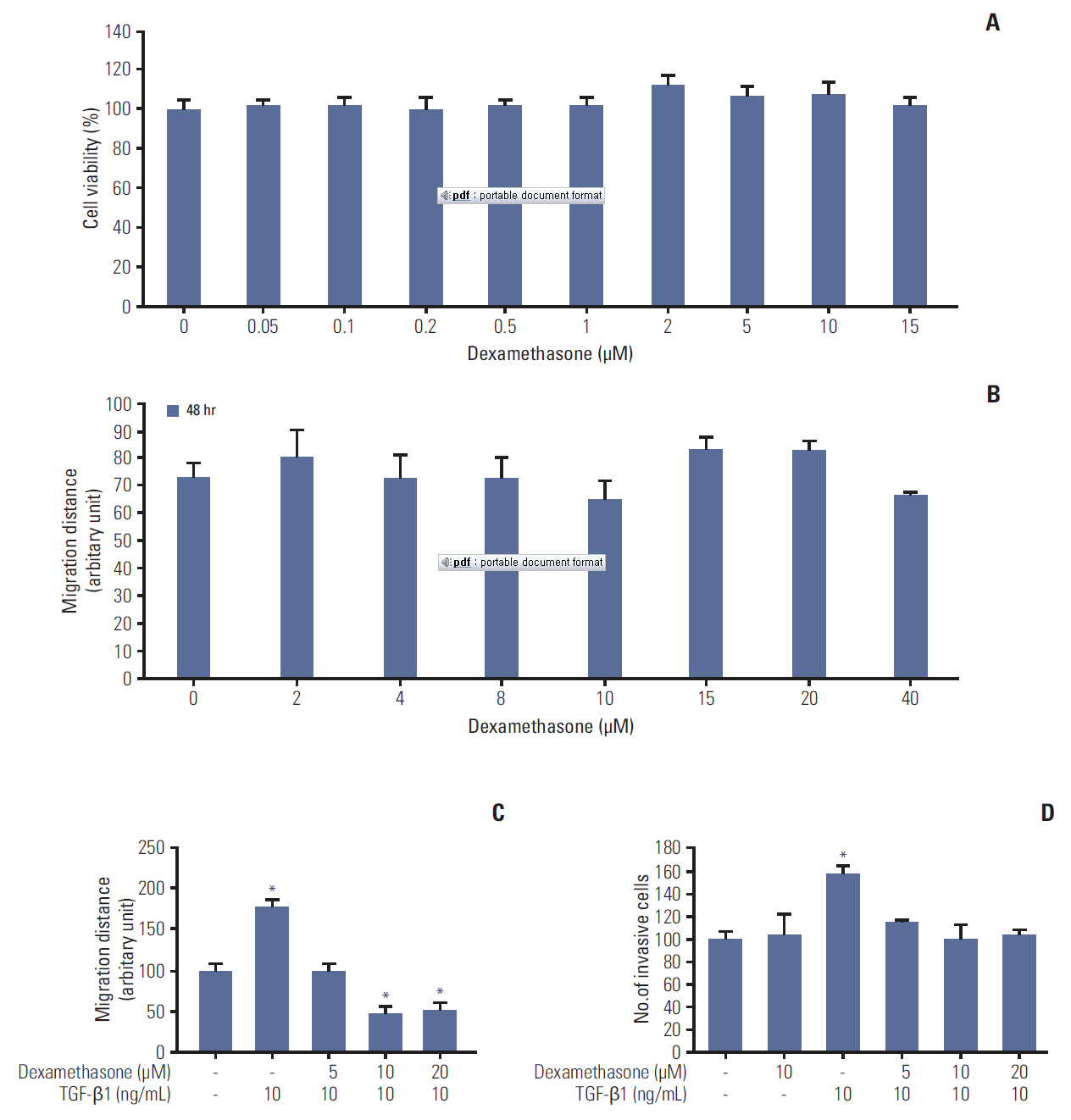
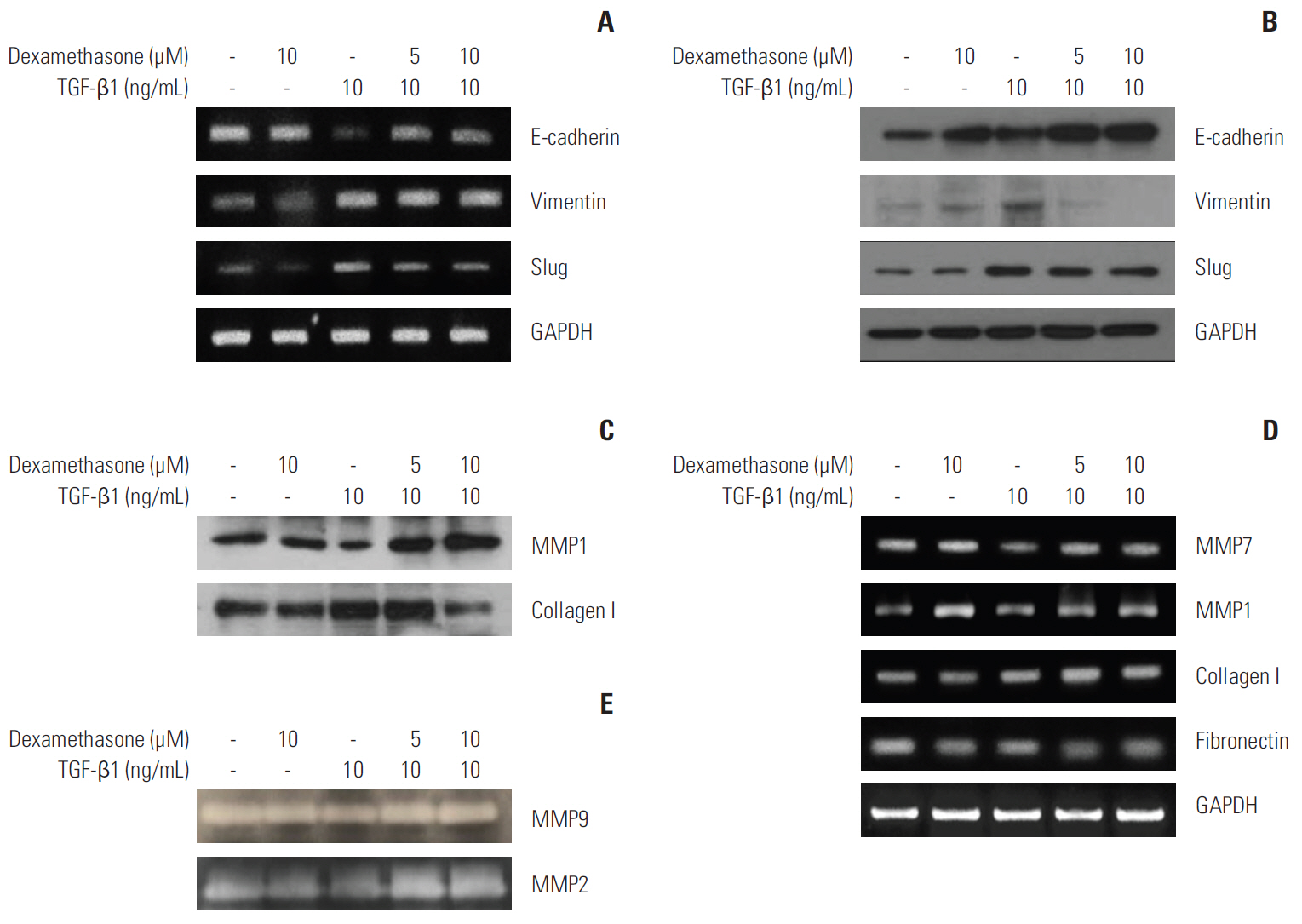
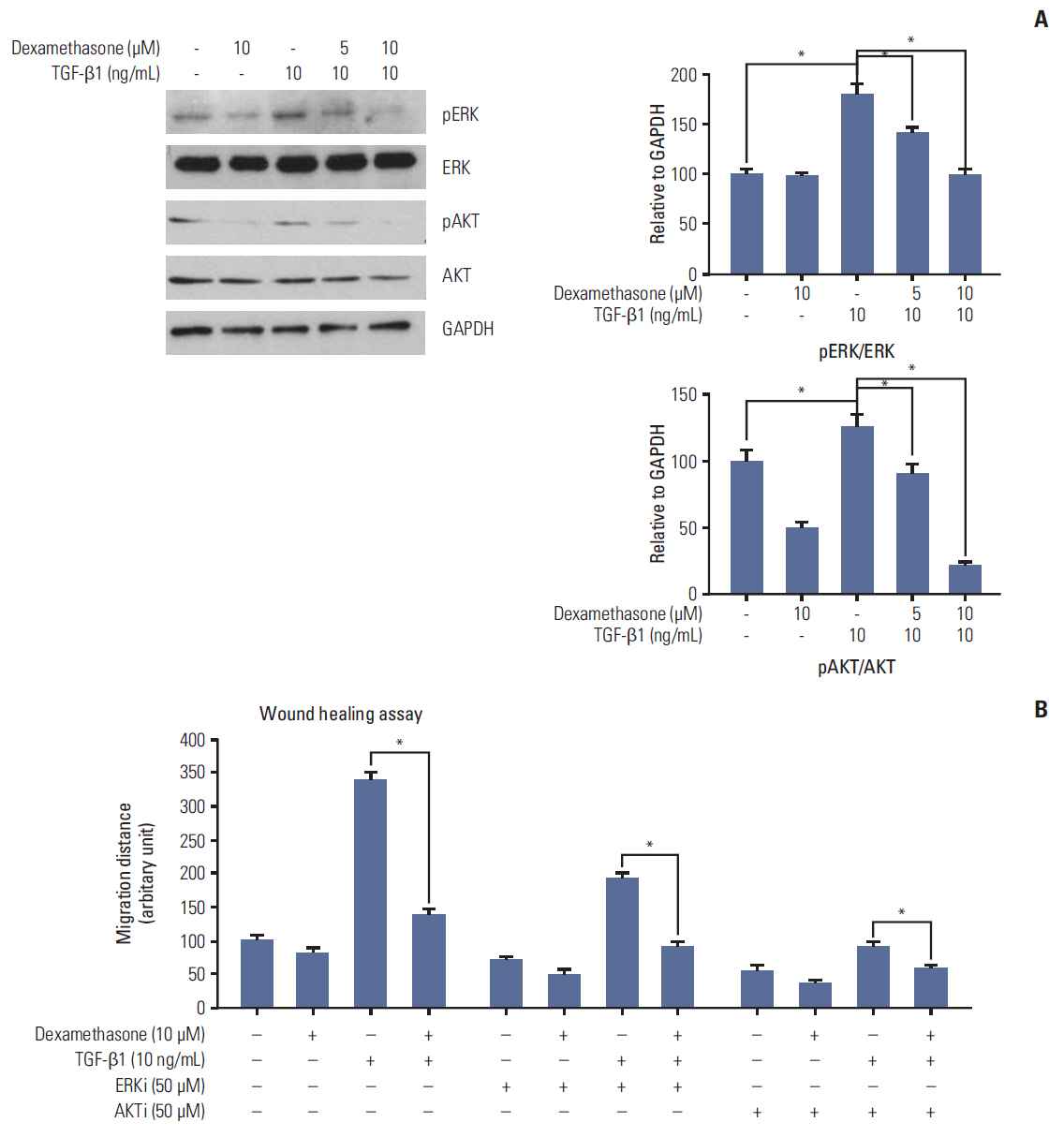
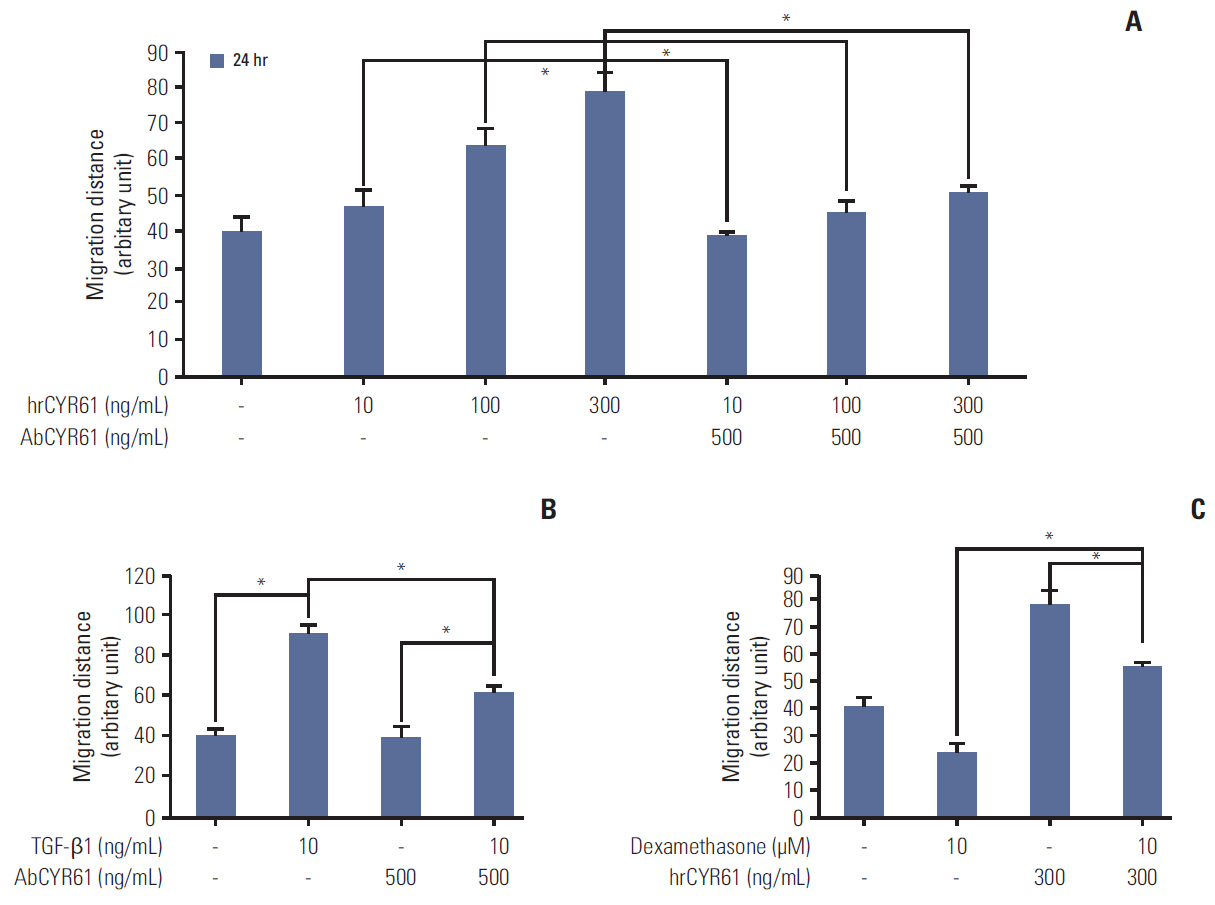
We report that dexamethasone significantly inhibited TGF-β1-induced cell migration, without affecting cell proliferation. Importantly, we observed that TGF-β1 promoted the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process and that dexamethasone co-treatment abolished this effect. ERK and AKT signaling pathways were found to mediate TGF-β1-induced migration, which was inhibited by dexamethasone. In addition, TGF-β1 treatment induced CYR61 expression whereas dexamethasone reduced it. These observations were compatible with the modulation of migration observed following treatment of HCT116 cells with human recombinant CYR61 and anti-CYR61 antibody. Our results also indicated that TGF-β1 enhanced collagen I and reduced matrix metalloproteinase 1 expression, which was reversed by dexamethasone treatment.
CONCLUSION
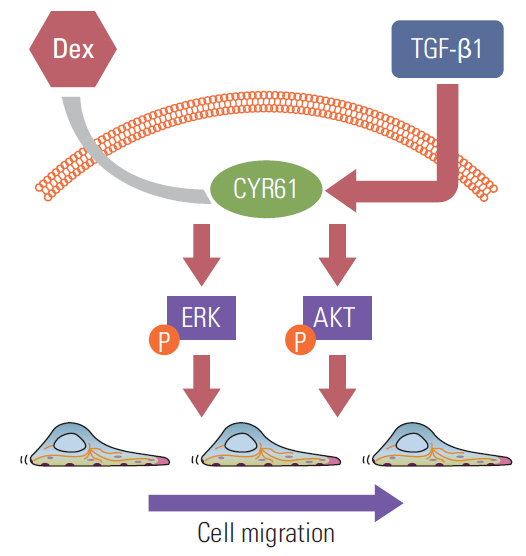
These findings suggested that dexamethasone inhibits AKT and ERK phosphorylation, leading to decreased CYR61 expression, which in turn blocks TGF-β1-induced migration.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cell Movement*
Cell Proliferation
Collagen
Colon*
Colonic Neoplasms*
Colorectal Neoplasms
Cysteine-Rich Protein 61
Dexamethasone*
Drug Therapy, Combination
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
HCT116 Cells
Humans*
Matrix Metalloproteinase 1
Phosphorylation
Transforming Growth Factors
Collagen
Cysteine-Rich Protein 61
Dexamethasone
Matrix Metalloproteinase 1
Transforming Growth Factors
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cunningham D, Atkin W, Lenz HJ, Lynch HT, Minsky B, Nordlinger B, et al. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2010; 375:1030–47.
Article2. Kalluri R, Weinberg RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 2009; 119:1420–8.
Article3. Wells A, Yates C, Shepard CR. E-cadherin as an indicator of mesenchymal to epithelial reverting transitions during the metastatic seeding of disseminated carcinomas. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2008; 25:621–8.
Article4. Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, Ishi H, Beppu T, Nakamori S, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer development and its clinical significance. Cancer Sci. 2010; 101:293–9.
Article5. Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Kempf RC, Long J, Laidler P, et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathways in controlling growth and sensitivity to therapy-implications for cancer and aging. Aging (Albany NY). 2011; 3:192–222.
Article6. Holbourn KP, Acharya KR, Perbal B. The CCN family of proteins: structure-function relationships. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008; 33:461–73.
Article7. Sun ZJ, Wang Y, Cai Z, Chen PP, Tong XJ, Xie D. Involvement of Cyr61 in growth, migration, and metastasis of prostate cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2008; 99:1656–67.
Article8. Terada N, Kulkarni P, Getzenberg RH. Cyr61 is a potential prognostic marker for prostate cancer. Asian J Androl. 2012; 14:405–8.
Article9. Jeong D, Heo S, Ahn TS, Lee S, Park S, Kim H, et al. Cyr61 expression is associated with prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:164.
Article10. Auphan N, DiDonato JA, Rosette C, Helmberg A, Karin M. Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of NF-kappa B activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis. Science. 1995; 270:286–90.11. Rinehart J, Keville L, Measel J, Spiekerman AM, Burke K. Corticosteroid alteration of carboplatin-induced hematopoietic toxicity in a murine model. Blood. 1995; 86:4493–9.
Article12. Gundisch S, Boeckeler E, Behrends U, Amtmann E, Ehrhardt H, Jeremias I. Glucocorticoids augment survival and proliferation of tumor cells. Anticancer Res. 2012; 32:4251–61.13. Rinehart J, Arnold S, Kloecker G, Lim A, Zaydan MA, Baeker T, et al. Phase II randomized trial of carboplatin and gemcitabine with or without dexamethasone pre-treatment in patients with Stage IV non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013; 71:1375–83.
Article14. Singh PP, Lemanu DP, Taylor MH, Hill AG. Association between preoperative glucocorticoids and long-term survival and cancer recurrence after colectomy: follow-up analysis of a previous randomized controlled trial. Br J Anaesth. 2014; 113 Suppl 1:i68–73.
Article15. Seo GY, Park S, Huh JS, Cho M. The protective effect of glycitin on UV-induced skin photoaging in human primary dermal fibroblast. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem. 2014; 57:463–8.
Article16. Nicolas FJ, Lehmann K, Warne PH, Hill CS, Downward J. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells is accompanied by down-regulation of Smad3 expression, leading to resistance to transforming growth factor-beta-induced growth arrest. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:3251–6.17. Suman S, Kurisetty V, Das TP, Vadodkar A, Ramos G, Lakshmanaswamy R, et al. Activation of AKT signaling promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor growth in colorectal cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 2014; 53 Suppl 1:E151–60.
Article18. Lau LF. CCN1/CYR61: the very model of a modern matricellular protein. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011; 68:3149–63.
Article19. Haque I, Mehta S, Majumder M, Dhar K, De A, McGregor D, et al. Cyr61/CCN1 signaling is critical for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness and promotes pancreatic carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer. 2011; 10:8.
Article20. Chen J, Song Y, Yang J, Gong L, Zhao P, Zhang Y, et al. The up-regulation of cysteine-rich protein 61 induced by transforming growth factor beta enhances osteosarcoma cell migration. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013; 384:269–77.
Article21. Lee YJ, Lee DM, Lee SH. Production of Cyr61 protein is modulated by extracellular acidification and PI3K/Akt signaling in prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013; 58:169–76.
Article22. Shim SH, Hah JH, Hwang SY, Heo DS, Sung MW. Dexamethasone treatment inhibits VEGF production via suppression of STAT3 in a head and neck cancer cell line. Oncol Rep. 2010; 23:1139–43.
Article23. Bernardi RJ, Trump DL, Yu WD, McGuire TF, Hershberger PA, Johnson CS. Combination of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) with dexamethasone enhances cell cycle arrest and apoptosis: role of nuclear receptor cross-talk and Erk/Akt signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 2001; 7:4164–73.24. Jang YH, Shin HS, Choi HS, Ryu ES, Kim MJ, Min SK, et al. Effects of dexamethasone on the TGF-β1-induced epithelialto-mesenchymal transition in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Lab Invest. 2013; 93:194–206.
Article25. Sabile AA, Arlt MJ, Muff R, Husmann K, Hess D, Bertz J, et al. Caprin-1, a novel Cyr61-interacting protein, promotes osteosarcoma tumor growth and lung metastasis in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013; 1832:1173–82.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 4-O-Methylhonokiol Protects HaCaT Cells from TGF-β1-Induced Cell Cycle Arrest by Regulating Canonical and Non-Canonical Pathways of TGF-β Signaling
- Parthenolide inhibits transforming growth factor β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells
- Synergistic effect of ERK inhibition on tetrandrine-induced apoptosis in A549 human lung carcinoma cells
- Effects of Curcumin on Apoptosis in SW480 Human Colon Cancer Cell Line
- Aspirin-Triggered Resolvin D1 Inhibits TGF-β1-Induced EndMT through Increasing the Expression of Smad7 and Is Closely Related to Oxidative Stress