J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Jun;19(3):321-326. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.3.321.
Effects of HMGB-1 Overexpression on Cell-Cycle Progression in MCF-7 Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Clinical Medicine & Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Korea.
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dschoi@smc.samsung.co.kr
- KMID: 1786806
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.3.321
Abstract
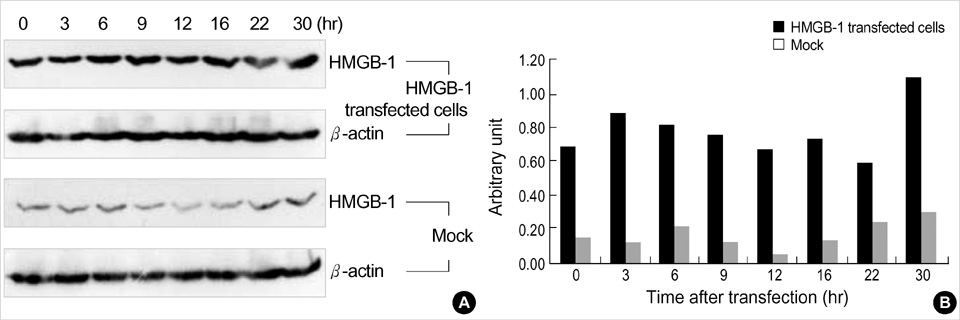
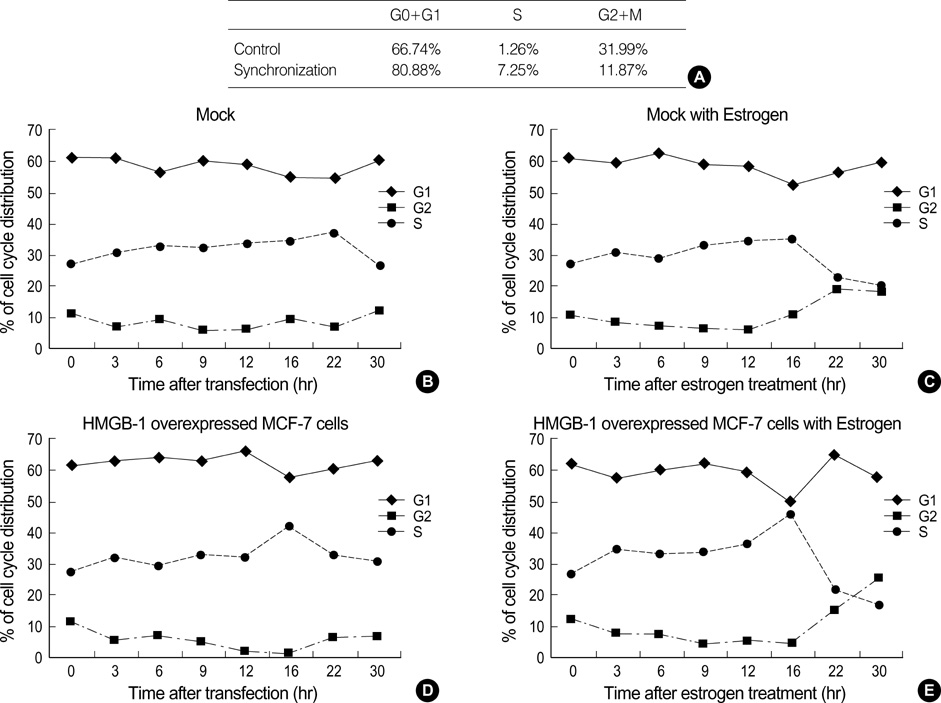
- High mobility group-1 (HMGB-1) enhances the DNA interactions and possesses a transcriptional activation potential for several families of sequence-specific transcriptional activators. In order to examine the effect of HMGB-1 on the cell cycle progression in MCF-7 cells, the HMGB-1 expression vector was transfected into synchronized MCF-7 cells, and the effect of HMGB-1 overexpression on the cell cycle was examined. The HMGB-1 protein level in the transfected cells increased 4.87-fold compared to the non-transfected cells. There were few changes in the cell cycle phase distribution after HMGB-1 overexpression in the MCF-7 cells. Following the estrogen treatment, the cell cycle progressed in both the HMGB-1 overexpressed MCF-7 and the mock-treated cells. However, a larger proportion of HMGB-1 overexpressing MCF-7 cells progressed to the either S or G2 phase than the mock-treated cells. The mRNA levels of the cell cycle regulators changed after being treated with estrogen in both the HMGB-1 overexpressing MCF-7 and the mock-treated cells, but the changes in the expression level of the cell cycle regulator genes were more prominent in the HMGB-1 overexpressing MCF-7 cells than in the mock-treated cells. In conclusion, HMGB-1 overexpression itself does not alter the MCF-7 cell cycle progression, but the addition of estrogen to the HMGB-1 overexpressing MCF-7 cells appears to accelerate the cell cycle progression.
MeSH Terms
-
Blotting, Western
Cell Cycle
Cell Line, Tumor
Densitometry
Estrogens/metabolism
G2 Phase
Genetic Vectors
HMGB1 Protein/*biosynthesis
Human
Kinetics
Oligonucleotides/chemistry
Plasmids/metabolism
Protein Structure, Tertiary
RNA, Messenger/metabolism
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
S Phase
Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
Time Factors
Trans-Activation (Genetics)
Transfection
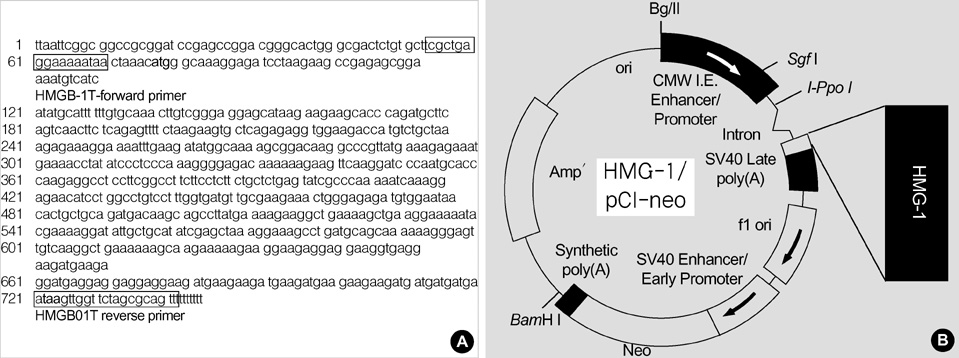
Figure
Reference
-
1. Melvin VS, Edwards DP. Coregulatory proteins in steroid hormone receptor action: The role of chromatin high mobility group proteins HMG-1 and -2. Steroids. 1999. 64:576–586.2. Bustin M, Reeves R. High-mobility-group chromosomal proteins: architectural components that facilitate chromatin function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1996. 54:35–100.
Article3. Tremethick DJ, Molloy PL. High mobility group proteins 1 and 2 stimulate transcription in vitro by RNA polymerases II and III. J Biol Chem. 1986. 261:6986–6992.
Article4. Wen L, Huang JK, Johnson BH, Reeck GR. A human placental cDNA clone that encodes nonhistone chromosomal protein HMG-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989. 17:1197–1214.
Article5. Spada F, Brunet A, Mercier Y, Renard JP, Bianchi ME, Thompson EM. High mobility group 1 (HMG1) protein in mouse preimplantation embryos. Mech Dev. 1998. 76:57–66.
Article6. Lum HK, Lee KL. The human HMGB1 promoter is modulated by a silencer and an enhancer-containing intron. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2001. 1520:79–84.
Article7. Chau KY, Lam HY, Lee KL. Estrogen treatment induces elevated expression of HMG-1 in MCF-7 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1998. 241:269–272.
Article8. Lee KL, Pentecost BT, D'Anna JA, Tobey RA, Gurley LR, Dixon GH. Characterization of cDNA sequences corresponding to three distinct HMG-1 mRNA species in line CHO Chinese hamster cells and cell cycle expression of the HMG-1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987. 15:5051–5068.
Article9. Kato Y, Iwai K. An approach to searching for specific proteins associated with active genes in hen oviduct. Endocrinol Jpn. 1984. 31:509–522.
Article10. Onate SA, Prendergast P, Wagner JP, Nissen M, Reeves R, Pettijohn DE, Edwarrds DP. The DNA-bending protein HMG-1 enhances progesterone receptor binding to its target DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1994. 14:3376–3391.11. Borrmann L, Kim I, Schultheiss D, Rogalla P, Bullerdiek J. Regulation of the expression of HMG-1, a co-activator of the estrogen receptor. Anticancer Res. 2001. 21:301–306.12. Prall OW, Sarcevic B, Musgrove EA, Watts CK, Sutherland RL. Estrogen-induced activation of Cdk4 and Cdk2 during G1-S phase progression is accompanied by increased cyclin D1 expression and decreased cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor association with cyclin E-Cdk2. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:10882–10894.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inductoin of Radioresistance by Overexpression of Glutathione S-Transferase K1 (hGSTK1) in MCF-7 Cells
- Effect of bFGF on the MCF-7 Cell Cycle with CD44+/CD24-: Promoting the G0/G1-->G2/S Transition
- The Changes of Cell Cycle Phase Fractions and Expression of p53 by the Treatment of Staurosporine in MCF-7 Cell Line
- LncRNA Taurine-Upregulated Gene 1 Promotes Cell Proliferation by Inhibiting MicroRNA-9 in MCF-7 Cells
- In Vitro and In Vivo Study on the Effect of Lysosome-associated Protein Transmembrane 4 Beta on the Progression of Breast Cancer