J Breast Cancer.
2016 Dec;19(4):349-357. 10.4048/jbc.2016.19.4.349.
LncRNA Taurine-Upregulated Gene 1 Promotes Cell Proliferation by Inhibiting MicroRNA-9 in MCF-7 Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Chongqing Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology and Epigenetics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China.
- 2Department of Breast Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China.
- 3Department of Endocrine and Breast Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China. rengs016@163.com
- KMID: 2362921
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2016.19.4.349
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was designed to investigate the role of taurine-upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and the molecular mechanism involved in the regulation of microRNA-9 (miR-9).
METHODS
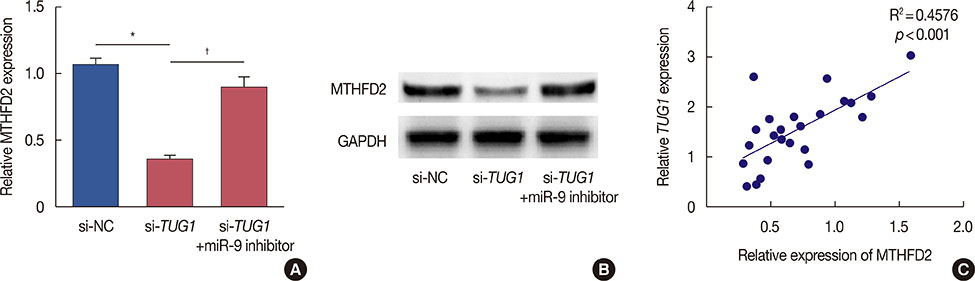
The expression of TUG1 in breast cancer tissues and cells was evaluated using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Cell viability was examined using a 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay; cell cycle progression and apoptosis were analyzed using flow cytometry. A dual luciferase reporter assay was used to detect the relationship between TUG1 and miR-9. The expression of methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 2 (MTHFD2) was measured by western blot.
RESULTS
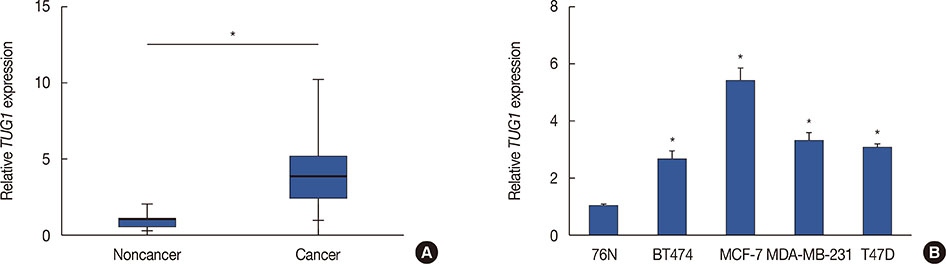
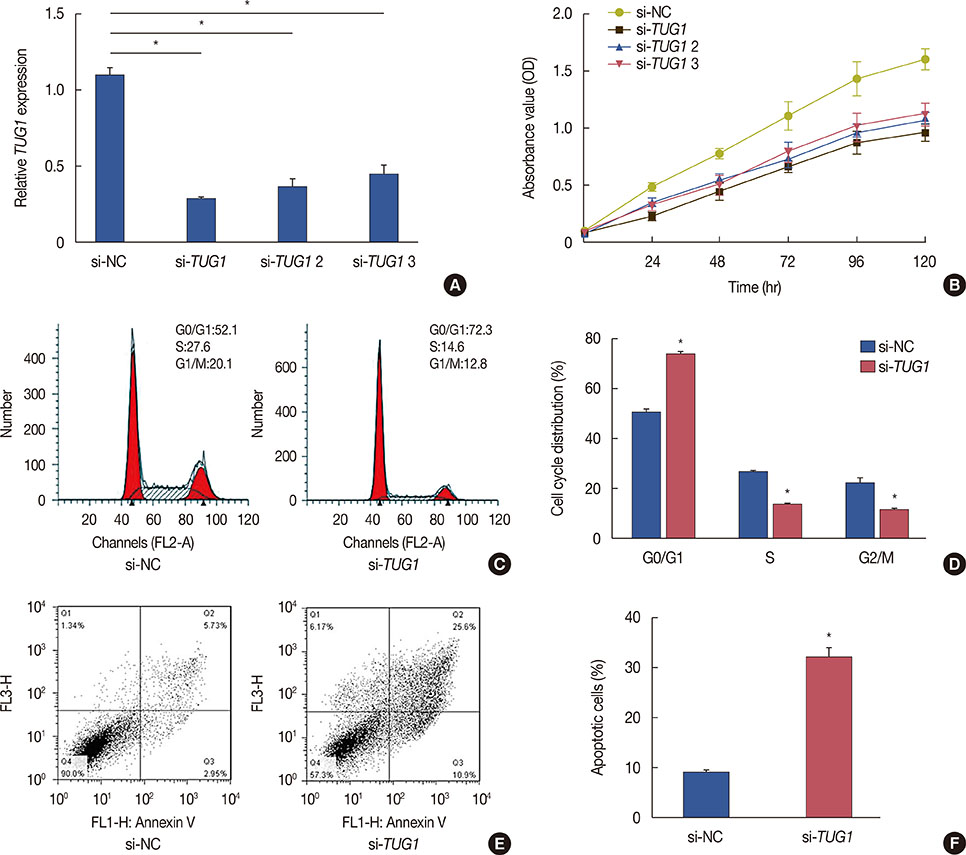
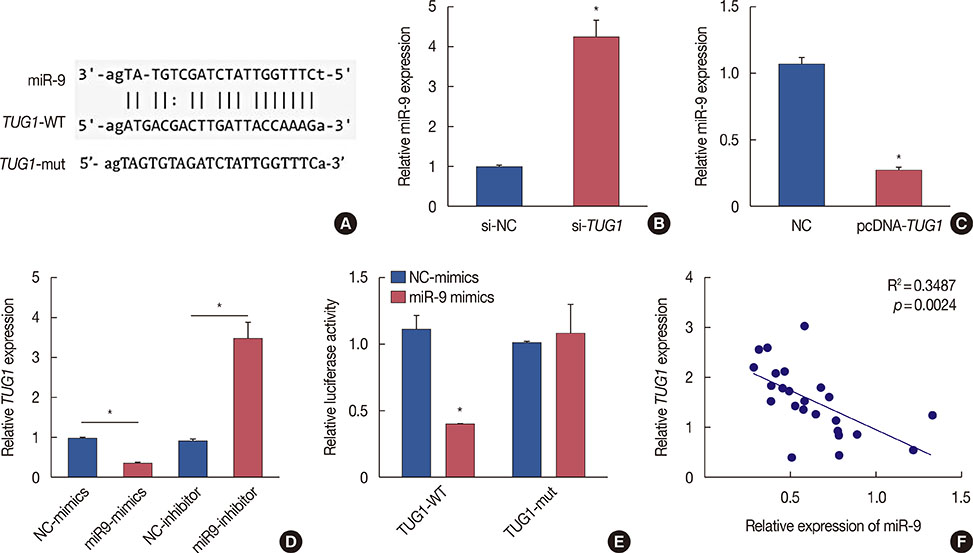
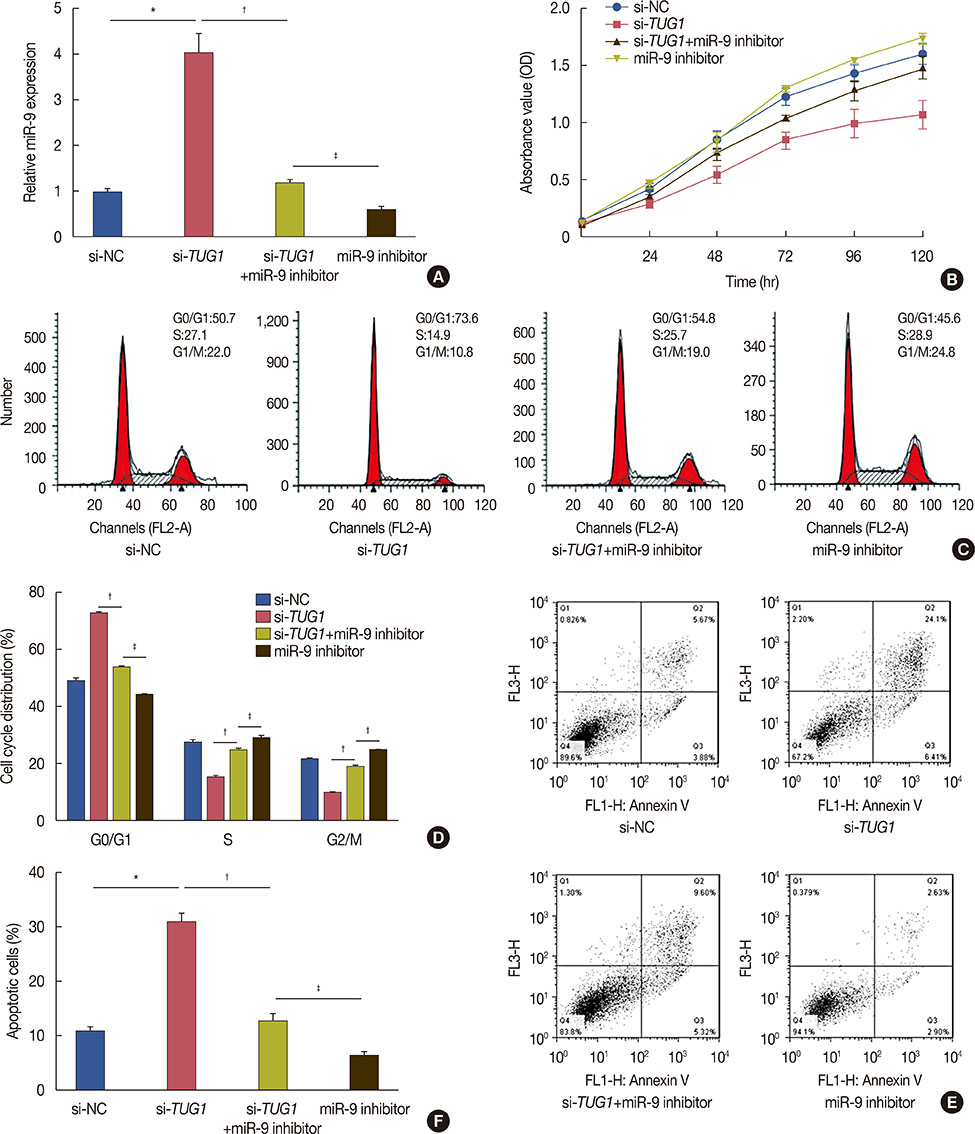
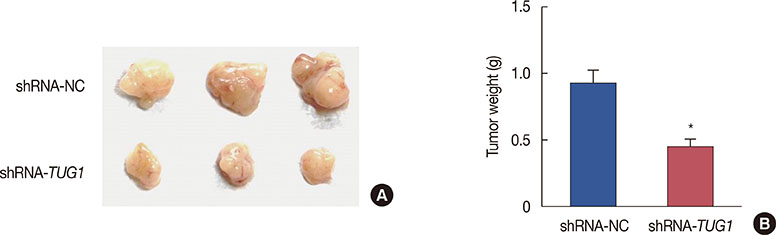
Higher expression of TUG1 was observed in breast cancer tissues and cell lines than in the corresponding controls. TUG1 knockdown reduced proliferation, suppressed cell cycle progression, and promoted apoptosis of MCF-7 cells. The dual luciferase reporter assay showed that TUG1 could negatively regulate the expression of miR-9. MiR-9 inhibition abrogated the effect of TUG1 knockdown on the proliferation, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis of MCF-7 cells. TUG1 positively regulated the expression of MTHFD2 in breast cancer cells.
CONCLUSION
TUG1 knockdown was significantly associated with decreased cell proliferation and it promoted apoptosis of breast cancer cells through the regulation of miR-9.
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis
Blotting, Western
Breast Neoplasms
Cell Cycle
Cell Line
Cell Proliferation*
Cell Survival
Flow Cytometry
Luciferases
MCF-7 Cells*
Methylenetetrahydrofolate Dehydrogenase (NADP)
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Reverse Transcription
RNA, Long Noncoding*
Luciferases
Methylenetetrahydrofolate Dehydrogenase (NADP)
RNA, Long Noncoding
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yan S, Jiao X, Zou H, Li K. Prognostic significance of c-Met in breast cancer: a meta-analysis of 6010 cases. Diagn Pathol. 2015; 10:62.
Article2. O'Brien KM, Fei C, Sandler DP, Nichols HB, DeRoo LA, Weinberg CR. Hormone therapy and young-onset breast cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 2015; 181:799–807.3. Shuvalov O, Petukhov A, Daks A, Fedorova O, Ermakov A, Melino G, et al. Current genome editing tools in gene therapy: new approaches to treat cancer. Curr Gene Ther. 2015; 15:511–529.
Article4. Gibb EA, Brown CJ, Lam WL. The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol Cancer. 2011; 10:38.
Article5. Xing Z, Park PK, Lin C, Yang L. LncRNA BCAR4 wires up signaling transduction in breast cancer. RNA Biol. 2015; 12:681–689.
Article6. Jadaliha M, Zong X, Malakar P, Ray T, Singh DK, Freier SM, et al. Functional and prognostic significance of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 as a metastasis driver in ER negative lymph node negative breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:40418–40436.
Article7. Ke H, Zhao L, Feng X, Xu H, Zou L, Yang Q, et al. NEAT1 is required for survival of breast cancer cells through FUS and miR-548. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2016; 10:Suppl 1. 11–17.
Article8. Young TL, Matsuda T, Cepko CL. The noncoding RNA taurine upregulated gene 1 is required for differentiation of the murine retina. Curr Biol. 2005; 15:501–512.
Article9. Zhang Q, Geng PL, Yin P, Wang XL, Jia JP, Yao J. Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA TUG1 inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013; 14:2311–2315.
Article10. Li J, Zhang M, An G, Ma Q. LncRNA TUG1 acts as a tumor suppressor in human glioma by promoting cell apoptosis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016; 241:644–649.
Article11. Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004; 116:281–297.12. Krichevsky AM, King KS, Donahue CP, Khrapko K, Kosik KS. A microRNA array reveals extensive regulation of microRNAs during brain development. RNA. 2003; 9:1274–1281.
Article13. Lu J, Luo H, Liu X, Peng Y, Zhang B, Wang L, et al. miR-9 targets CXCR4 and functions as a potential tumor suppressor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2014; 35:554–563.
Article14. Wang H, Zhang W, Zuo Y, Ding M, Ke C, Yan R, et al. miR-9 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by targeting LASS2 in bladder cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015; 36:9631–9640.
Article15. Gwak JM, Kim HJ, Kim EJ, Chung YR, Yun S, Seo AN, et al. MicroRNA-9 is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition, breast cancer stem cell phenotype, and tumor progression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014; 147:39–49.
Article16. Im JH, Muschel RJ. New evidence of lncRNA role in tumor progression and metastasis. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2012; 1:55–56.17. Tuo YL, Li XM, Luo J. Long noncoding RNA UCA1 modulates breast cancer cell growth and apoptosis through decreasing tumor suppressive miR-143. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015; 19:3403–3411.18. Xu S, Sui S, Zhang J, Bai N, Shi Q, Zhang G, et al. Downregulation of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the PI3K-AKT pathway in breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8:4881–4891.19. Han L, Ma P, Liu SM, Zhou X. Circulating long noncoding RNA GAS5 as a potential biomarker in breast cancer for assessing the surgical effects. Tumour Biol. 2016; 37:6847–6854.
Article20. Sun J, Ding C, Yang Z, Liu T, Zhang X, Zhao C, et al. The long non-coding RNA TUG1 indicates a poor prognosis for colorectal cancer and promotes metastasis by affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Transl Med. 2016; 14:42.
Article21. Zhang E, He X, Yin D, Han L, Qiu M, Xu T, et al. Increased expression of long noncoding RNA TUG1 predicts a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and regulates cell proliferation by epigenetically silencing of p57. Cell Death Dis. 2016; 7:e2109.
Article22. Ma B, Li M, Zhang L, Huang M, Lei JB, Fu GH, et al. Upregulation of long non-coding RNA TUG1 correlates with poor prognosis and disease status in osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol. 2016; 37:4445–4455.
Article23. Kallen AN, Zhou XB, Xu J, Qiao C, Ma J, Yan L, et al. The imprinted H19 lncRNA antagonizes let-7 microRNAs. Mol Cell. 2013; 52:101–112.
Article24. Wang J, Zhao H, Tang D, Wu J, Yao G, Zhang Q. Overexpressions of microRNA-9 and microRNA-200c in human breast cancers are associated with lymph node metastasis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2013; 28:283–288.
Article25. Zhou X, Marian C, Makambi KH, Kosti O, Kallakury BV, Loffredo CA, et al. MicroRNA-9 as potential biomarker for breast cancer local recurrence and tumor estrogen receptor status. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e39011.
Article26. Selcuklu SD, Donoghue MT, Rehmet K, de Souza Gomes M, Fort A, Kovvuru P, et al. MicroRNA-9 inhibition of cell proliferation and identification of novel miR-9 targets by transcriptome profiling in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:29516–29528.
Article27. Liu F, Liu Y, He C, Tao L, He X, Song H, et al. Increased MTHFD2 expression is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35:8685–8690.
Article28. Mandal CC, Ghosh-Choudhury N, Yoneda T, Choudhury GG, Ghosh-Choudhury N. Simvastatin prevents skeletal metastasis of breast cancer by an antagonistic interplay between p53 and CD44. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286:11314–11327.
Article29. Zhang EB, Yin DD, Sun M, Kong R, Liu XH, You LH, et al. P53-regulated long non-coding RNA TUG1 affects cell proliferation in human non-small cell lung cancer, partly through epigenetically regulating HOXB7 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2014; 5:e1243.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- c-Myc-Induced Long Non-Coding RNA Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 7 Regulates Glycolysis in Breast Cancer
- LncRNA STARD7-AS1 suppresses cervical cancer cell proliferation while promoting autophagy by regulating miR-31-5p/TXNIP axis to inactivate the mTOR signaling
- LncRNA linc01194 promotes the progress of endometrial carcinoma by up-regulating SOX2 through binding to IGF2BP1
- LncRNA DLG1-AS1 Promotes Cancer Cell Proliferation in Triple Negative Breast Cancer by Downregulating miR-203
- Upregulation of long non-coding RNA XIST has anticancer effects on epithelial ovarian cancer cells through inverse downregulation of hsa-miR-214-3p