Blood Res.
2019 Jun;54(2):102-107. 10.5045/br.2019.54.2.102.
Enhanced polo-like kinase 1 expression in myelodysplastic syndromes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hematology Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Hematology, Yeoido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Laboratory of Hematological Disease and Immunology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yoojink@catholic.ac.kr
- 4Leukemia Research Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2451009
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2019.54.2.102
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Cancer is characterized by uncontrolled cellular proliferation, and Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1), a key regulator of the cell cycle, is overexpressed in many cancers, including acute leukemia and lymphoma. However, the dynamics of PLK1 transcription in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are unknown. This study aimed to investigate the transcript dynamics of PLK1 and determine its role in the pathophysiology of MDS.
METHODS
PLK1 mRNA obtained from the bone marrow samples of 67 patients with MDS, 16 patients with secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML), and 10 healthy controls were analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR and compared according to various clinical parameters.
RESULTS
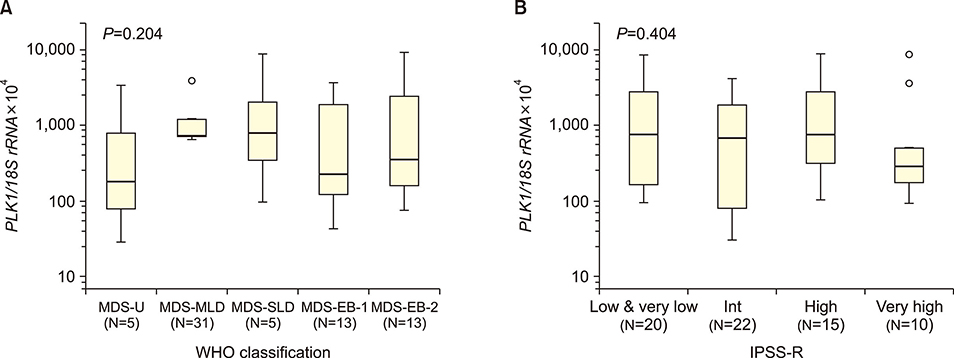
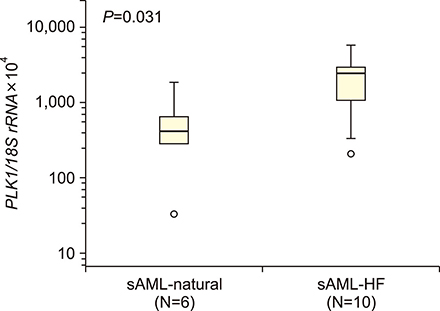
The median PLK1 expression levels differed slightly, but not significantly, between MDS and sAML patients [661.21 (range, 29.38-8,987.31) vs. 1,462.05 (32.22-5,734.09), respectively], but were significantly higher (P<0.001) than the levels in the healthy controls [19.0 (1.60-49.90)]. Further analyses of PLK1 levels according to the WHO classification of MDS, prognostic risk groups, karyotype risk groups, marrow blast percentage, and depth of cytopenia did not reveal any significant associations. In patients progressing to sAML, PLK1 expression levels differed significantly according to the presence or absence of resistance to hypomethylation treatment (2,470.58 vs. 415.98, P=0.03).
CONCLUSION
PLK1 is upregulated in MDS patients; however, its role in the pathophysiology of MDS is unclear. Gene upregulation in cases with pharmacotherapeutic resistance warrants further investigation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Bone Marrow
Cell Cycle
Cell Proliferation
Classification
DNA Methylation
Gene Expression
Humans
Karyotype
Leukemia
Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute
Lymphoma
Myelodysplastic Syndromes*
Phosphotransferases*
Protein-Serine-Threonine Kinases
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Messenger
Up-Regulation
Phosphotransferases
Protein-Serine-Threonine Kinases
RNA, Messenger
Figure
Reference
-
1. Adès L, Itzykson R, Fenaux P. Myelodysplastic syndromes. Lancet. 2014; 383:2239–2252.
Article2. Gangat N, Patnaik MM, Tefferi A. Myelodysplastic syndromes: contemporary review and how we treat. Am J Hematol. 2016; 91:76–89.
Article3. Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 1997; 89:2079–2088.
Article4. Greenberg PL, Tuechler H, Schanz J, et al. Revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2012; 120:2454–2465.
Article5. Malcovati L, Germing U, Kuendgen A, et al. Time-dependent prognostic scoring system for predicting survival and leukemic evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:3503–3510.
Article6. Fenaux P, Adès L. How we treat lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2013; 121:4280–4286.
Article7. Steensma DP, Bejar R, Jaiswal S, et al. Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential and its distinction from myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2015; 126:9–16.
Article8. Sperling AS, Gibson CJ, Ebert BL. The genetics of myelodysplastic syndrome: from clonal haematopoiesis to secondary leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017; 17:5–19.
Article9. Bejar R, Stevenson K, Abdel-Wahab O, et al. Clinical effect of point mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:2496–2506.
Article10. Galimberti S, Ghio F, Guerrini F, et al. WT1 expression levels at diagnosis could predict long-term time-to-progression in adult patients affected by acute myeloid leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 2010; 149:451–454.
Article11. Cilloni D, Gottardi E, Messa F, et al. Significant correlation between the degree of WT1 expression and the International Prognostic Scoring System Score in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:1988–1995.
Article12. Yoon JH, Jeon YW, Yahng SA, et al. Wilms tumor gene 1 expression as a predictive marker for relapse and survival after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myelodysplastic syndromes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015; 21:460–467.
Article13. Barr FA, Silljé HH, Nigg EA. Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004; 5:429–440.
Article14. Eckerdt F, Yuan J, Strebhardt K. Polo-like kinases and oncogenesis. Oncogene. 2005; 24:267–276.
Article15. Takahashi T, Sano B, Nagata T, et al. Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is overexpressed in primary colorectal cancers. Cancer Sci. 2003; 94:148–152.
Article16. Wolf G, Elez R, Doermer A, et al. Prognostic significance of polo-like kinase (PLK) expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 1997; 14:543–549.
Article17. Renner AG, Dos Santos C, Recher C, et al. Polo-like kinase 1 is overexpressed in acute myeloid leukemia and its inhibition preferentially targets the proliferation of leukemic cells. Blood. 2009; 114:659–662.
Article18. Talati C, Griffiths EA, Wetzler M, Wang ES. Polo-like kinase inhibitors in hematologic malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016; 98:200–210.
Article19. Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016; 127:2391–2405.
Article20. Cheson BD, Greenberg PL, Bennett JM, et al. Clinical application and proposal for modification of the International Working Group (IWG) response criteria in myelodysplasia. Blood. 2006; 108:419–425.
Article21. Strebhardt K. Multifaceted polo-like kinases: drug targets and antitargets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010; 9:643–660.
Article22. Ikezoe T, Yang J, Nishioka C, et al. A novel treatment strategy targeting polo-like kinase 1 in hematological malignancies. Leukemia. 2009; 23:1564–1576.
Article23. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011; 144:646–674.
Article24. Degenhardt Y, Lampkin T. Targeting Polo-like kinase in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16:384–389.25. Liu L, Zhang M, Zou P. Expression of PLK1 and survivin in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007; 48:2179–2183.
Article26. Hartsink-Segers SA, Exalto C, Allen M, et al. Inhibiting Polo-like kinase 1 causes growth reduction and apoptosis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Haematologica. 2013; 98:1539–1546.
Article27. Jung SH, Kim YJ, Yim SH, et al. Somatic mutations predict outcomes of hypomethylating therapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:55264–55275.
Article28. Garcia-Manero G, Fenaux P, Al-Kali A, et al. Rigosertib versus best supportive care for patients with high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes after failure of hypomethylating drugs (ONTIME): a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016; 17:496–508.
Article29. Palmisiano ND, Kasner MT. Polo-like kinase and its inhibitors: Ready for the match to start? Am J Hematol. 2015; 90:1071–1076.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Myelodysplastic syndromes and overlap syndromes
- Classifications and prognostic scoring systems in myelodysplastic syndrome
- Relation between Cyclooxygenase-2 and Polo-like Kinase-1 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Azathioprine-induced Myelodysplasia Mimicking Myelodysplastic Syndrome
- Copper deficiency mimicking myelodysplastic syndrome