Yonsei Med J.
2018 Oct;59(8):960-967. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.8.960.
Beneficial Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. wing2392@naver.com
- KMID: 2419730
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.8.960
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is an endogenous gaseous molecule with important physiological roles. It is synthesized from cysteine by cystathionine γ-lyase (CGL) and cystathionine β-synthase (CBS). The present study examined the benefits of exogenous H2S on renal ischemia reperfusion (IR) injury, as well as the effects of CGL or CBS inhibition. Furthermore, we elucidated the mechanism underlying the action of H2S in the kidneys.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
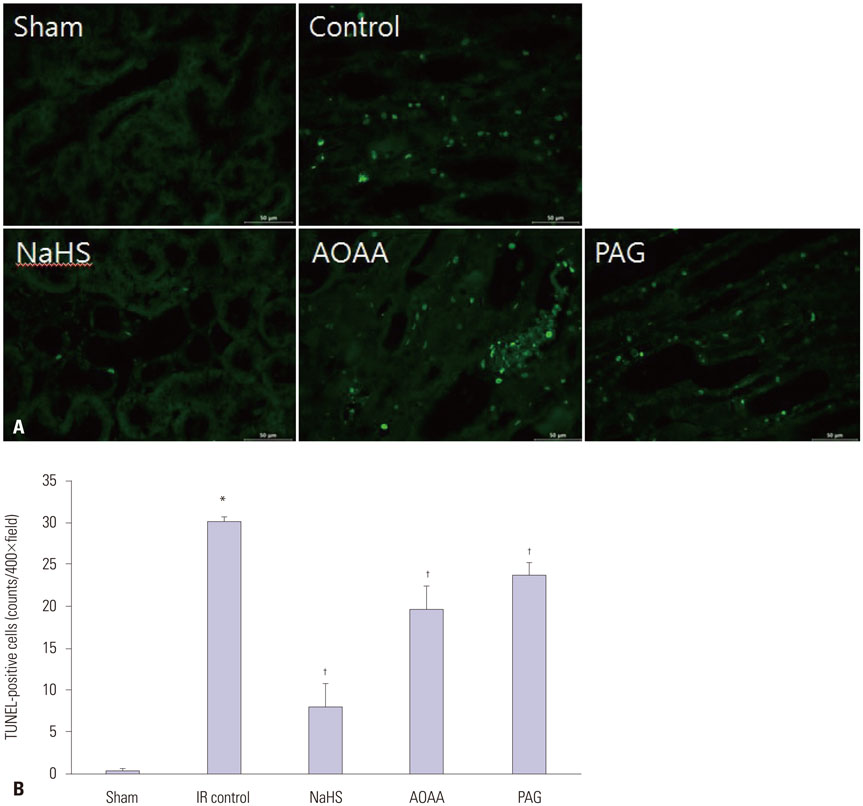
Thirty male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly assigned to five groups: a sham, renal IR control, sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) treatment, H2S donor, and CGL or CBS inhibitor administration group. Levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum creatinine (Cr), renal tissue malondialdehyde (MDA), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were estimated. Histological changes, apoptosis, and expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family members (extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38) were also evaluated.
RESULTS
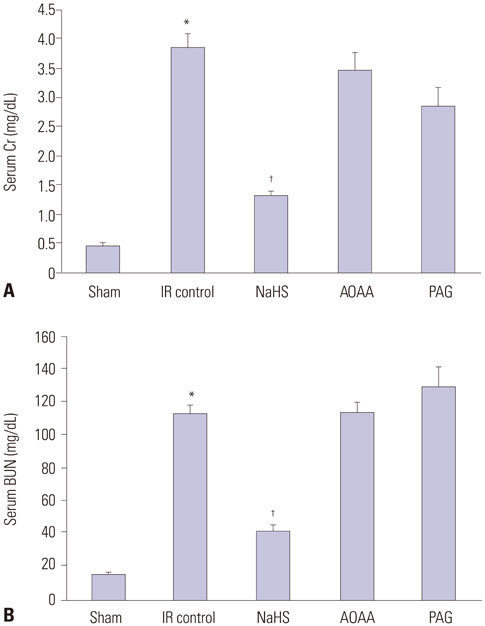
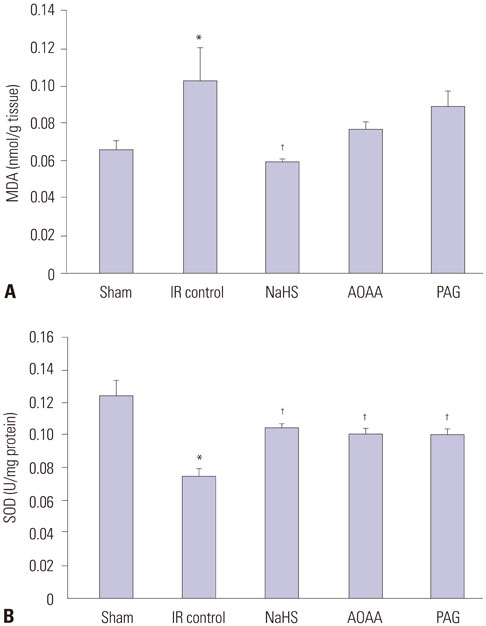
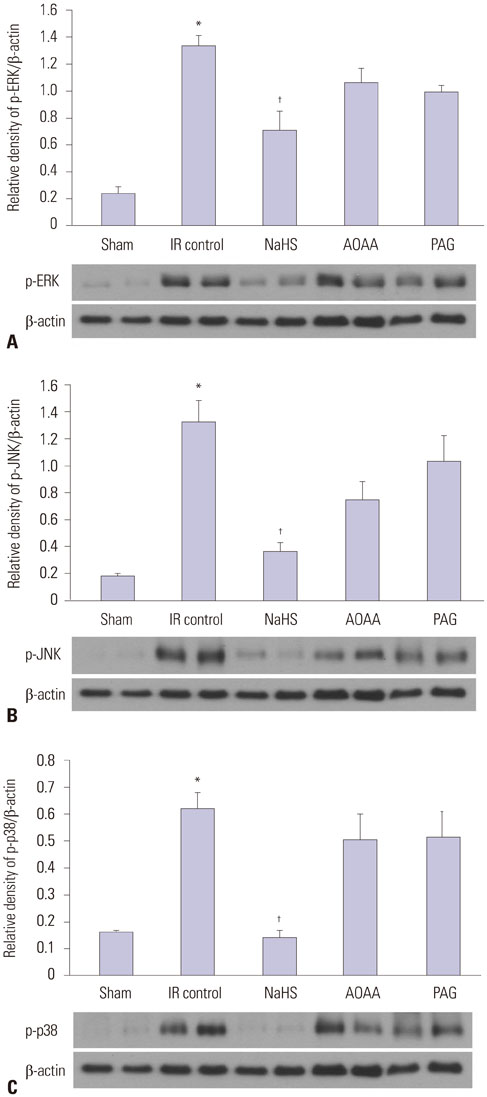
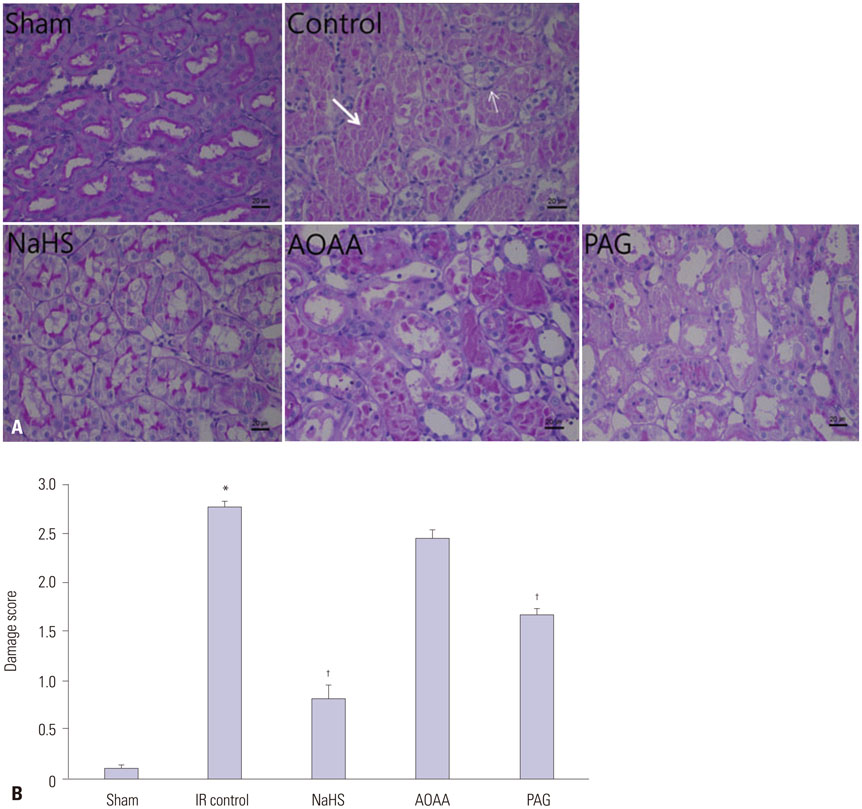
NaHS attenuated serum BUN and Cr levels, as well as histological damage caused by renal IR injury. Administration of NaHS also reduced oxidative stress as evident from decreased MDA, preserved SOD, and reduced apoptotic cells. Additionally, NaHS prevented renal IR-induced MAPK phosphorylation. The CGL or CBS group showed increased MAPK family activity; however, there was no significant difference in the IR control group.
CONCLUSION
Exogenous H2S can mitigate IR injury-led renal damage. The proposed beneficial effect of H2S is, in part, because of the anti-oxidative stress associated with modulation of the MAPK signaling pathways.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Apoptosis
Blood Urea Nitrogen
Creatinine
Cystathionine
Cysteine
Humans
Hydrogen Sulfide*
Hydrogen*
Ischemia*
JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Kidney
Male
Malondialdehyde
Oxidative Stress
Phosphorylation
Phosphotransferases
Protein Kinases
Rats*
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Reperfusion
Reperfusion Injury*
Sodium
Superoxide Dismutase
Tissue Donors
Creatinine
Cystathionine
Cysteine
Hydrogen
Hydrogen Sulfide
JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Malondialdehyde
Phosphotransferases
Protein Kinases
Sodium
Superoxide Dismutase
Figure
Reference
-
1. Son Y, Cheong YK, Kim NH, Chung HT, Kang DG, Pae HO. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: how can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J Signal Transduct. 2011; 2011:792639.
Article2. Ferrandi C, Ballerio R, Gaillard P, Giachetti C, Carboni S, Vitte PA, et al. Inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase decreases cardiomyocyte apoptosis and infarct size after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in anaesthetized rats. Br J Pharmacol. 2004; 142:953–960.
Article3. Li J, Miller EJ, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Russell RR 3rd, Young LH. AMP-activated protein kinase activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase by increasing recruitment of p38 MAPK to TAB1 in the ischemic heart. Circ Res. 2005; 97:872–879.
Article4. Yuan L, Wang J, Xiao H, Wu W, Wang Y, Liu X. MAPK signaling pathways regulate mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis induced by isoorientin in human hepatoblastoma cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013; 53:62–68.
Article5. Wang R. Two's company, three's a crowd: can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter? FASEB J. 2002; 16:1792–1798.
Article6. Elrod JW, Calvert JW, Morrison J, Doeller JE, Kraus DW, Tao L, et al. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by preservation of mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104:15560–15565.
Article7. Guo C, Liang F, Shah Masood W, Yan X. Hydrogen sulfide protected gastric epithelial cell from ischemia/reperfusion injury by Keap1 s-sulfhydration, MAPK dependent anti-apoptosis and NF-κB dependent anti-inflammation pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014; 725:70–78.
Article8. Yan H, Du JB, Tang CS. [Possible effects of endogenous hydrogen sulfide on aortic remodeling in hypertensive rats]. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2004; 36:234–237.9. Boehning D, Snyder SH. Novel neural modulators. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003; 26:105–131.10. Stipanuk MH, Beck PW. Characterization of the enzymic capacity for cysteine desulphhydration in liver and kidney of the rat. Biochem J. 1982; 206:267–277.
Article11. Wang R. Hydrogen sulfide: the third gasotransmitter in biology and medicine. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010; 12:1061–1064.
Article12. Xu Z, Prathapasinghe G, Wu N, Hwang SY, Siow YL, Karmin O. Ischemia-reperfusion reduces cystathionine-beta-synthase-mediated hydrogen sulfide generation in the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009; 297:F27–F35.13. Tripatara P, Patel NS, Collino M, Gallicchio M, Kieswich J, Castiglia S, et al. Generation of endogenous hydrogen sulfide by cystathionine gamma-lyase limits renal ischemia/reperfusion injury and dysfunction. Lab Invest. 2008; 88:1038–1048.
Article14. Kang K, Zhao M, Jiang H, Tan G, Pan S, Sun X. Role of hydrogen sulfide in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury in rats. Liver Transpl. 2009; 15:1306–1314.
Article15. Wang P, Isaak CK, Siow YL, Karmin O. Downregulation of cystathionine β-synthase and cystathionine γ-lyase expression stimulates inflammation in kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Physiol Rep. 2014; 2:e12251.16. Mihara M, Uchiyama M. Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem. 1978; 86:271–278.
Article17. Marklund S, Marklund G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem. 1974; 47:469–474.
Article18. Kim J, Park JW, Park KM. Increased superoxide formation induced by irradiation preconditioning triggers kidney resistance to ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009; 296:F1202–F1211.
Article19. Bos EM, Leuvenink HG, Snijder PM, Kloosterhuis NJ, Hillebrands JL, Leemans JC, et al. Hydrogen sulfide-induced hypometabolism prevents renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009; 20:1901–1905.
Article20. Sen N, Paul BD, Gadalla MM, Mustafa AK, Sen T, Xu R, et al. Hydrogen sulfide-linked sulfhydration of NF-κB mediates its antiapoptotic actions. Mol Cell. 2012; 45:13–24.
Article21. Papapetropoulos A, Pyriochou A, Altaany Z, Yang G, Marazioti A, Zhou Z, et al. Hydrogen sulfide is an endogenous stimulator of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:21972–21977.
Article22. Kimura Y, Dargusch R, Schubert D, Kimura H. Hydrogen sulfide protects HT22 neuronal cells from oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006; 8:661–670.
Article23. Kimura Y, Kimura H. Hydrogen sulfide protects neurons from oxidative stress. FASEB J. 2004; 18:1165–1167.
Article24. Szabó C. Hydrogen sulphide and its therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007; 6:917–935.
Article25. Whiteman M, Armstrong JS, Chu SH, Jia-Ling S, Wong BS, Cheung NS, et al. The novel neuromodulator hydrogen sulfide: an endogenous peroxynitrite ‘scavenger’? J Neurochem. 2004; 90:765–768.
Article26. Circu ML, Aw TY. Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010; 48:749–762.
Article27. Tripatara P, Patel NS, Brancaleone V, Renshaw D, Rocha J, Sepodes B, et al. Characterisation of cystathionine gamma-lyase/hydrogen sulphide pathway in ischaemia/reperfusion injury of the mouse kidney: an in vivo study. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009; 606:205–209.
Article28. Han SJ, Kim JI, Park JW, Park KM. Hydrogen sulfide accelerates the recovery of kidney tubules after renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015; 30:1497–1506.
Article29. Roy A, Khan AH, Islam MT, Prieto MC, Majid DS. Interdependency of cystathione γ-lyase and cystathione β-synthase in hydrogen sulfide-induced blood pressure regulation in rats. Am J Hypertens. 2012; 25:74–81.
Article30. Cortese-Krott MM, Kuhnle GG, Dyson A, Fernandez BO, Grman M, DuMond JF, et al. Key bioactive reaction products of the NO/H2S interaction are S/N-hybrid species, polysulfides, and nitroxyl. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015; 112:E4651–E4660.
Article31. Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu BE, Karandikar M, Berman K, et al. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev. 2001; 22:153–183.
Article32. Roux PP, Blenis J. ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004; 68:320–344.
Article33. Ballif BA, Blenis J. Molecular mechanisms mediating mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK cell survival signals. Cell Growth Differ. 2001; 12:397–408.34. Lin A. Activation of the JNK signaling pathway: breaking the brake on apoptosis. Bioessays. 2003; 25:17–24.
Article35. Lu M, Hu LF, Hu G, Bian JS. Hydrogen sulfide protects astrocytes against H(2)O(2)-induced neural injury via enhancing glutamate uptake. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008; 45:1705–1713.
Article36. Lan A, Liao X, Mo L, Yang C, Yang Z, Wang X, et al. Hydrogen sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced injury by inhibiting ROS-activated ERK1/2 and p38MAPK signaling pathways in PC12 cells. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e25921.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effects of hydrogen sulfide under sevoflurane administration against ischemia and reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart
- Isolation of hydrogen sulfide producing escherichia coli
- Hydrogen sulfide restores cardioprotective effects of remote ischemic preconditioning in aged rats via HIF-1α/Nrf2 signaling pathway
- The Effect of Allopurinol on the Ischemia-reperfusion Renal Injury in Young Rats
- Serial MRI of Hypoxic Brain Damage after Hydrogen Sulfide Exposure