Cancer Res Treat.
2018 Jul;50(3):835-842. 10.4143/crt.2017.303.
Phase 1 Studies of Poziotinib, an Irreversible Pan-HER Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bangyj@snu.ac.kr
- 2Seoul National University Cancer Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 5Hanmi Pharm. Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2417872
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2017.303
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Poziotinib, a pan-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has shown potent activity againstwild type of epidermal growth factorreceptor(EGFR) family kinases including EGFR, HER2, and HER4 and EGFR-mutant cells in vitro. Two phase I studies were conducted to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD), pharmacokinetics, safety, and antitumor activity against advanced solid tumors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Standard 3+3 dose escalation scheme using two different dosing schedules were studied: once daily, 14-day on, and 7-day off (intermittent schedule); and once daily continuous dosing with food effect. Additional patients were enrolled in an expansion cohort.
RESULTS
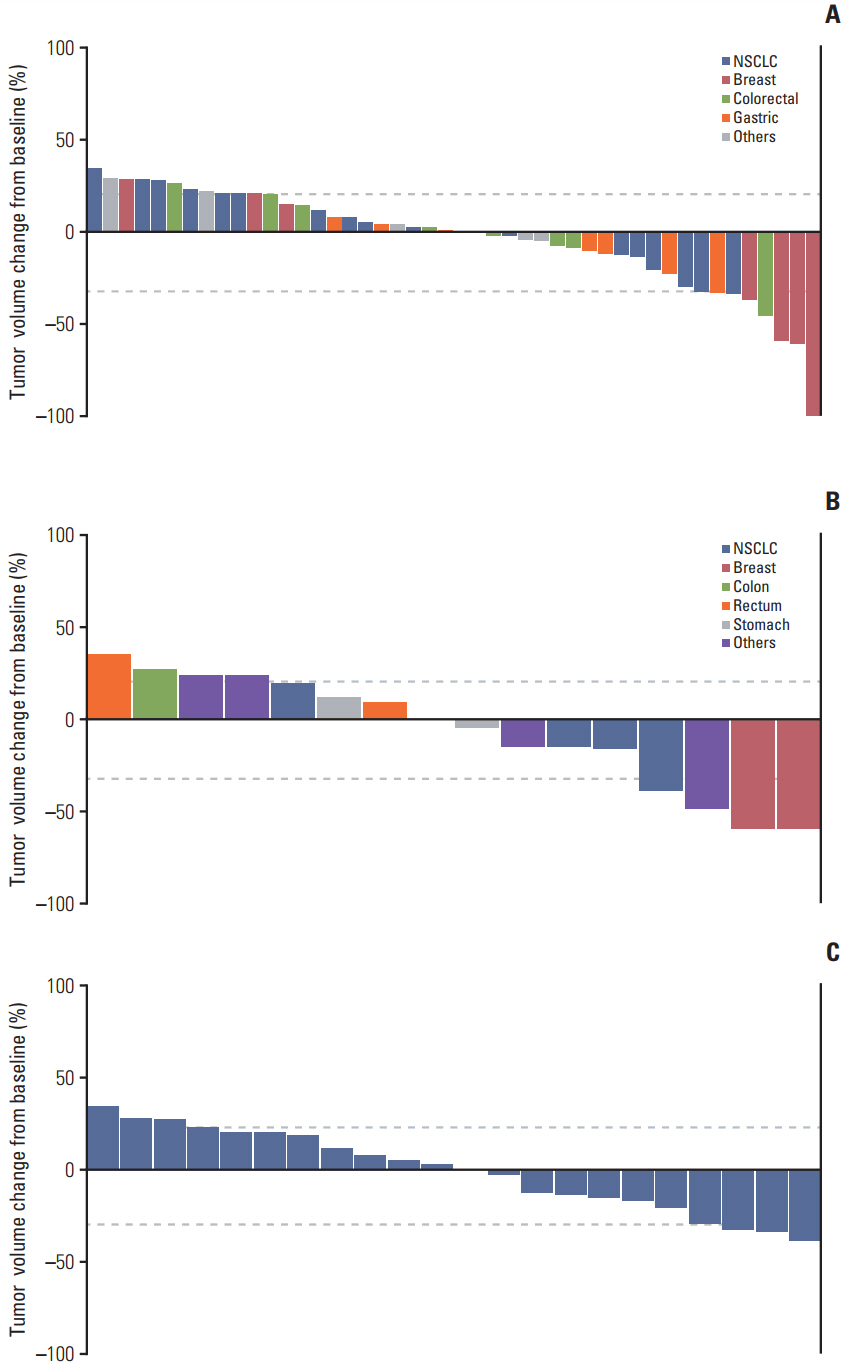
A total of 75 patients were enrolled in the two studies. The most common drug-related treatment-emergent adverse eventswere diarrhea,rash, stomatitis, pruritus, and anorexia. Dose-limiting toxicities were grade 3 diarrhea in the intermittent schedule and grade 3 anorexia and diarrhea in the continuous dosing schedule. The MTDs were determined as 24 mg/day in the intermittent dosing schedule and 18 mg/day in the continuous dosing schedule. Eight (16%) and 24 (47%) of 51 evaluable patients in the intermittent schedule achieved partial response (PR) and stable disease (SD), respectively. Four (21%) and six (32%) of 19 evaluable patients in continuous dosing schedule achieved PR and SD, respectively. Patients with PR (n=7) or SD ≥ 12 weeks (n=7) had HER2 amplification (n=7; breast cancer, 5; and stomach cancer, 2) and EGFR amplification (n=1, squamous cell lung cancer).
CONCLUSION
Poziotinib was safe and well tolerated in patients with advanced solid tumors. It showed an encouraging activity against EGFR-mutant and HER2-amplified cancers.
MeSH Terms
-
Anorexia
Appointments and Schedules
Breast Neoplasms
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung
Cohort Studies
Diarrhea
Epithelial Cells
Humans
In Vitro Techniques
Lung
Maximum Tolerated Dose
Pharmacokinetics
Phosphotransferases
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases*
Pruritus
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Stomach Neoplasms
Stomatitis
Tyrosine*
Phosphotransferases
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Tyrosine
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005; 5:341–54.
Article2. Chong CR, Janne PA. The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Med. 2013; 19:1389–400.
Article3. Dienstmann R, De Dosso S, Felip E, Tabernero J. Drug development to overcome resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung and colorectal cancer. Mol Oncol. 2012; 6:15–26.
Article4. Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, O'Byrne K, Hirsh V, Mok T, et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:3327–34.
Article5. Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, Feng J, Lu S, Huang Y, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:213–22.
Article6. Janne PA, Ou SH, Kim DW, Oxnard GR, Martins R, Kris MG, et al. Dacomitinib as first-line treatment in patients with clinically or molecularly selected advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:1433–41.7. Cha MY, Lee KO, Kim M, Song JY, Lee KH, Park J, et al. Antitumor activity of HM781-36B, a highly effective pan-HER inhibitor in erlotinib-resistant NSCLC and other EGFR-dependent cancer models. Int J Cancer. 2012; 130:2445–54.
Article8. Nam HJ, Kim HP, Yoon YK, Hur HS, Song SH, Kim MS, et al. Antitumor activity of HM781-36B, an irreversible Pan-HER inhibitor, alone or in combination with cytotoxic chemotherapeutic agents in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2011; 302:155–65.
Article9. Kim HJ, Kim HP, Yoon YK, Kim MS, Lee GS, Han SW, et al. Antitumor activity of HM781-36B, a pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in HER2-amplified breast cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2012; 23:288–97.
Article10. Noh YH, Lim HS, Jung JA, Song TH, Bae KS. Population pharmacokinetics of HM781-36 (poziotinib), pan-human EGF receptor (HER) inhibitor, and its two metabolites in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015; 75:97–109.
Article11. Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000; 92:205–16.12. Kim HJ, Lee KY, Kim YC, Kim KS, Lee SY, Jang TW, et al. Detection and comparison of peptide nucleic acid-mediated real-time polymerase chain reaction clamping and direct gene sequencing for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2012; 75:321–5.
Article13. Eskens FA, Mom CH, Planting AS, Gietema JA, Amelsberg A, Huisman H, et al. A phase I dose escalation study of BIBW 2992, an irreversible dual inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor 1 (EGFR) and 2 (HER2) tyrosine kinase in a 2-week on, 2-week off schedule in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 2008; 98:80–5.
Article14. Janne PA, Boss DS, Camidge DR, Britten CD, Engelman JA, Garon EB, et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of the pan-HER inhibitor, PF299804, in patients with advanced malignant solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:1131–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management of Severe Fatigue Induced by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Radioiodine Refractory Thyroid Cancer
- Primary Extragastrointestinal Stromal Tumor of Retroperitoneum: Poor Response to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor
- Management of Bleeding Induced by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Radioiodine Refractory Thyroid Cancer
- Phase 1/2a Study of Rivoceranib, a Selective VEGFR-2 Angiogenesis Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors
- Sunitinib-induced hypothyroidism