Electrolyte Blood Press.
2010 Dec;8(2):59-65.
Membrane Trafficking of Collecting Duct Water Channel Protein AQP2 Regulated by Akt/AS160
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. thkwon@knu.ac.kr
Abstract
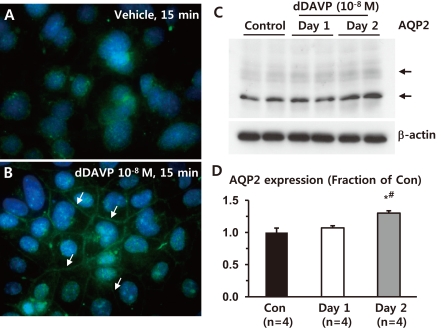
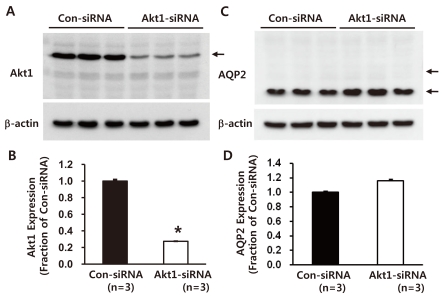
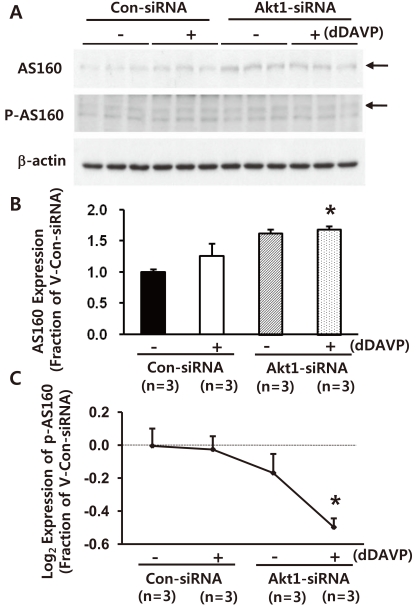
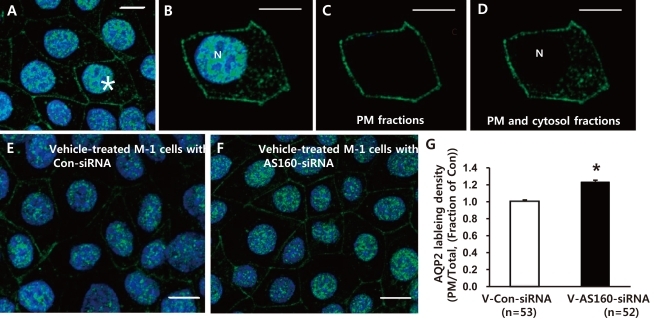
- Akt (protein kinase B (PKB)) is a serine/threonine kinase that acts in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway. The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, triggered by growth factors and hormones including vasopressin, is an important pathway that is widely involved in cellular mechanisms regulating transcription, translation, cell growth and death, cell proliferation, migration, and cell cycles. In particular, Akt and Akt substrate protein of 160 kDa (AS160) are likely to participate in the trafficking of aquaporin-2 (AQP2) in the kidney collecting duct. In this study, we demonstrated that 1) small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated gene silencing of Akt1 significantly decreased Akt1 and phospho-AS160 protein expression; and 2) confocal laser scanning microscopy of AQP2 in mouse cortical collecting duct cells (M-1 cells) revealed AS160 knockdown by siRNA increased AQP2 expression in the plasma membrane compared with controls, despite the absence of dDAVP stimulation. Thus, the results suggest that PI3K/Akt pathways could play a role in AQP2 trafficking via the AS160 protein.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Aquaporin 2
Cell Cycle
Cell Death
Cell Membrane
Deamino Arginine Vasopressin
Gene Silencing
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Kidney Tubules, Collecting
Membranes
Mice
Microscopy, Confocal
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase
Phosphotransferases
Protein Transport
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-akt
rab GTP-Binding Proteins
RNA, Small Interfering
Vasopressins
Water
Aquaporin 2
Deamino Arginine Vasopressin
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase
Phosphotransferases
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-akt
RNA, Small Interfering
Vasopressins
Water
rab GTP-Binding Proteins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002; 296:1655–1657. PMID: 12040186.
Article2. Casamayor A, Morrice NA, Alessi DR. Phosphorylation of Ser-241 is essential for the activity of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1: identification of five sites of phosphorylation in vivo. Biochem J. 1999; 342:287–292. PMID: 10455013.
Article3. Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 2005; 307:1098–1101. PMID: 15718470.
Article4. Kumar CC, Madison V. AKT crystal structure and AKT-specific inhibitors. Oncogene. 2005; 24:7493–7501. PMID: 16288296.
Article5. Zinda MJ, Johnson MA, Paul JD, et al. AKT-1, -2, and -3 are expressed in both normal and tumor tissues of the lung, breast, prostate, and colon. Clin Cancer Res. 2001; 7:2475–2479. PMID: 11489829.6. Santi SA, Lee H. The Akt isoforms are present at distinct subcellular locations. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010; 298:C580–C591. PMID: 20018949.
Article7. Kazi AS, Tao JQ, Feinstein SI, Zhang L, Fisher AB, Bates SR. Role of the PI3-kinase signaling pathway in trafficking of the surfactant protein A receptor P63 (CKAP4) on type II pneumocytes. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010; 299:L794–L807. PMID: 20870746.
Article8. Sharpe LJ, Luu W, Brown AJ. Akt phosphorylates Sec24: new clues into the regulation of ER-to-Golgi trafficking. Traffic. 2011; 12:19–27. PMID: 20950345.
Article9. Robertson SD, Matthies HJ, Owens WA, et al. Insulin reveals Akt signaling as a novel regulator of norepinephrine transporter trafficking and norepinephrine homeostasis. J Neurosci. 2010; 30:11305–11316. PMID: 20739551.
Article10. Boxer RB, Stairs DB, Dugan KD, et al. Isoform-specific requirement for Akt1 in the developmental regulation of cellular metabolism during lactation. Cell Metab. 2006; 4:475–490. PMID: 17141631.
Article11. Czech MP, Corvera S. Signaling mechanisms that regulate glucose transport. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:1865–1868. PMID: 9890935.
Article12. Khan AH, Pessin JE. Insulin regulation of glucose uptake: a complex interplay of intracellular signalling pathways. Diabetologia. 2002; 45:1475–1483. PMID: 12436329.
Article13. Eguez L, Lee A, Chavez JA, et al. Full intracellular retention of GLUT4 requires AS160 Rab GTPase activating protein. Cell Metab. 2005; 2:263–272. PMID: 16213228.
Article14. Miinea CP, Sano H, Kane S, et al. AS160, the Akt substrate regulating GLUT4 translocation, has a functional Rab GTPase-activating protein domain. Biochem J. 2005; 391:87–93. PMID: 15971998.15. Su X, Lodhi IJ, Saltiel AR, Stahl PD. Insulin-stimulated Interaction between insulin receptor substrate 1 and p85alpha and activation of protein kinase B/Akt require Rab5. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:27982–27990. PMID: 16880210.16. Barbieri MA, Kohn AD, Roth RA, Stahl PD. Protein kinase B/akt and rab5 mediate Ras activation of endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:19367–19370. PMID: 9677351.
Article17. Comellas AP, Kelly AM, Trejo HE, et al. Insulin regulates alveolar epithelial function by inducing Na+/K+-ATPase translocation to the plasma membrane in a process mediated by the action of Akt. J Cell Sci. 2010; 123:1343–1351. PMID: 20332111.
Article18. Wieman HL, Wofford JA, Rathmell JC. Cytokine stimulation promotes glucose uptake via phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt regulation of Glut1 activity and trafficking. Mol Biol Cell. 2007; 18:1437–1446. PMID: 17301289.
Article19. Yoshizaki T, Imamura T, Babendure JL, Lu JC, Sonoda N, Olefsky JM. Myosin 5a is an insulin-stimulated Akt2 (protein kinase Bbeta) substrate modulating GLUT4 vesicle translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 2007; 27:5172–5183. PMID: 17515613.20. Sano H, Roach WG, Peck GR, Fukuda M, Lienhard GE. Rab10 in insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation. Biochem J. 2008; 411:89–95. PMID: 18076383.
Article21. Sano H, Eguez L, Teruel MN, et al. Rab10, a target of the AS160 Rab GAP, is required for insulin-stimulated translocation of GLUT4 to the adipocyte plasma membrane. Cell Metab. 2007; 5:293–303. PMID: 17403373.
Article22. Larance M, Ramm G, Stockli J, et al. Characterization of the role of the Rab GTPase-activating protein AS160 in insulin-regulated GLUT4 trafficking. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:37803–37813. PMID: 16154996.
Article23. Romanelli RJ, LeBeau AP, Fulmer CG, Lazzarino DA, Hochberg A, Wood TL. Insulin-like growth factor type-I receptor internalization and recycling mediate the sustained phosphorylation of Akt. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:22513–22524. PMID: 17545147.
Article24. Uhlig M, Passlack W, Eckel J. Functional role of Rab11 in GLUT4 trafficking in cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2005; 235:1–9. PMID: 15866422.
Article25. Kessler A, Tomas E, Immler D, Meyer HE, Zorzano A, Eckel J. Rab11 is associated with GLUT4-containing vesicles and redistributes in response to insulin. Diabetologia. 2000; 43:1518–1527. PMID: 11151761.
Article26. Kwon TH, Nielsen J, Moller HB, Fenton RA, Nielsen S, Frokiaer J. Aquaporins in the kidney. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009; 190:95–132. PMID: 19096774.
Article27. Lee YJ, Song IK, Jang KJ, et al. Increased AQP2 targeting in primary cultured IMCD cells in response to angiotensin II through AT1 receptor. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007; 292:F340–F350. PMID: 16896188.28. Bustamante M, Hasler U, Kotova O, et al. Insulin potentiates AVP-induced AQP2 expression in cultured renal collecting duct principal cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005; 288:F334–F344. PMID: 15494547.
Article29. Pisitkun T, Jacob V, Schleicher SM, Chou CL, Yu MJ, Knepper MA. Akt and ERK1/2 pathways are components of the vasopressin signaling network in rat native IMCD. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008; 295:F1030–F1043. PMID: 18667481.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Minireview on Vasopressin-regulated Aquaporin-2 in Kidney Collecting Duct Cells
- Regulation of aquaporin-2 in the kidney : A molecular mechanism of body-water homeostasis
- Effect of Diet and Water Intake on Aquaporin 2 Function
- New insights into the transcriptional regulation of aquaporin-2 and the treatment of X-linked hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
- The Effect of Oxytocin on Subcellular Localization of Aquaporin-2 in Rat Kidney: an Ultrastructural Immunocytochemical Study