Clin Exp Vaccine Res.
2018 Jan;7(1):61-69. 10.7774/cevr.2018.7.1.61.
Efficacy of inactivated variant porcine epidemic diarrhea virus vaccines in growing pigs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Viral Disease Research Division, Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, Gimcheon, Korea. yangdk@korea.kr
- KMID: 2402539
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7774/cevr.2018.7.1.61
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The first aim of this study was to develop a novel inactivated porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) vaccine using the recently isolated Korean PEDV QIAP1401 strain and to evaluate its protective efficacy in growing pigs. The second was to determine the optimum adjuvant formulation of the inactivated PEDV vaccine that induces protection against viral challenge.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
To generate high titers of infectious PEDV, the QIAP1401 isolate was passaged in Vero cells. The experimental vaccines were prepared from a binary ethyleneimine-inactivated QIAP1401 strain passaged sequentially 70 times (QIAP1401-p70), formulated with four commercial adjuvants, and administered twice intramuscularly to growing pigs. Challenge studies using a virulent homologous strain of PEDV QIAP1401-p11, which was passaged 11 times after isolation, were performed to assess protection against disease progression and viral shedding during the 15-day observation period. The vaccine-induced antibody responses were measured in serum samples collected at predetermined time points by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and virus neutralization test.
RESULTS
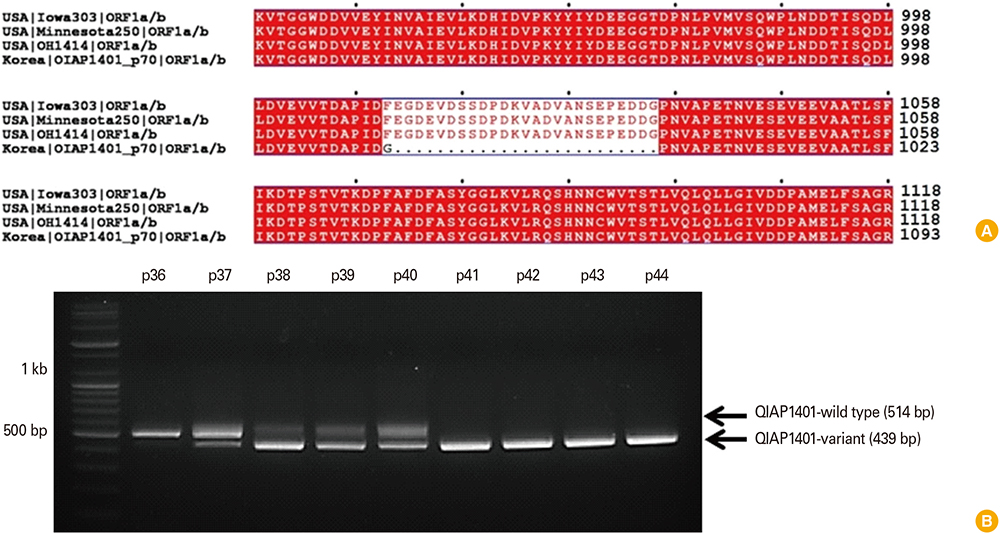
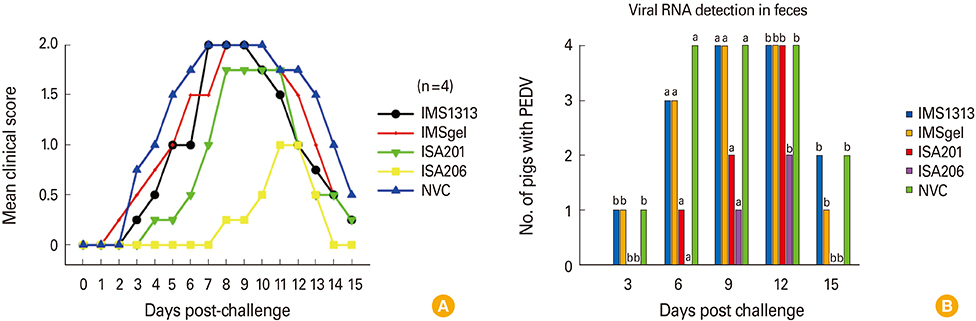
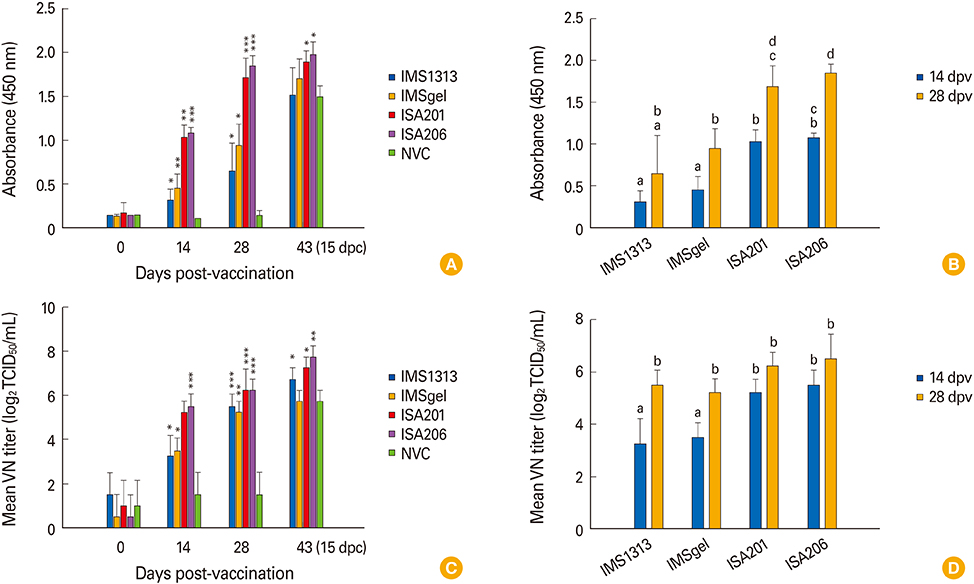
The QIAP1401-p70 strain had 42 amino acid (aa) mutations, including a 25 aa deletion, and was selected as the inactivated PEDV vaccine candidate. Although none of the pigs that received the experimental vaccines were completely protected against subsequent viral challenge, they exhibited a significantly higher immune response than did non-vaccinated control pigs. Among the vaccine groups, the highest antibody responses were observed in the pigs that received an oil-based multiphasic water/oil/water (W/O/W) emulsion adjuvanted vaccine, which delayed the onset of clinical symptoms and viral shedding.
CONCLUSION
A novel inactivated PEDV vaccine formulated with a W/O/W emulsion adjuvant was both immunogenic and protective against viral challenge.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Debouck P, Pensaert M. Experimental infection of pigs with a new porcine enteric coronavirus, CV 777. Am J Vet Res. 1980; 41:219–223.2. Pensaert MB, Yeo SG. Porcine epidemic diarrhea. In : Straw BE, Zimmerman JJ, D'Allaire S, Taylor DJ, editors. Disease of swine. 9th ed. Ames, IW: Blackwell Publishing;2006. p. 367–372.3. Pijpers A, van Nieuwstadt AP, Terpstra C, Verheijden JH. Porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus as a cause of persistent diarrhoea in a herd of breeding and finishing pigs. Vet Rec. 1993; 132:129–131.
Article4. Oldham J. Letter to the editor. Pig Farming. 1972; 10:72–73.
Article5. Pensaert MB, de Bouck P. A new coronavirus-like particle associated with diarrhea in swine. Arch Virol. 1978; 58:243–247.
Article6. Lee C. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: an emerging and re-emerging epizootic swine virus. Virol J. 2015; 12:193.
Article7. Song DS, Oh JS, Kang BK, et al. Oral efficacy of Vero cell attenuated porcine epidemic diarrhea virus DR13 strain. Res Vet Sci. 2007; 82:134–140.
Article8. Saif LJ, Pensaert MP, Sestak K, Yeo SG, Jung K. Coronaviruses. In : Zimmerman JJ, Karriker LA, Ramirez A, Schwartz KJ, Stevenson GW, editors. Diseases of swine. 10th ed. Ames, IW: Wiley-Blackwell;2012. p. 501–524.9. Song D, Park B. Porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus: a comprehensive review of molecular epidemiology, diagnosis, and vaccines. Virus Genes. 2012; 44:167–175.
Article10. Bosch BJ, van der Zee R, de Haan CA, Rottier PJ. The coronavirus spike protein is a class I virus fusion protein: structural and functional characterization of the fusion core complex. J Virol. 2003; 77:8801–8811.
Article11. Chang SH, Bae JL, Kang TJ, et al. Identification of the epitope region capable of inducing neutralizing antibodies against the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Mol Cells. 2002; 14:295–299.12. Gallagher TM, Buchmeier MJ. Coronavirus spike proteins in viral entry and pathogenesis. Virology. 2001; 279:371–374.
Article13. Sato T, Takeyama N, Katsumata A, Tuchiya K, Kodama T, Kusanagi K. Mutations in the spike gene of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus associated with growth adaptation in vitro and attenuation of virulence in vivo. Virus Genes. 2011; 43:72–78.
Article14. Lee S, Lee C. Outbreak-related porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains similar to US strains, South Korea, 2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014; 20:1223–1226.
Article15. Park BK, Song D. Recent outbreaks and emergence of mutants of porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses (PEDV) in Korea. Jpn J Vet Res. 2016; 64:Suppl 1. S25–S32.16. Lee DK, Park CK, Kim SH, Lee C. Heterogeneity in spike protein genes of porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses isolated in Korea. Virus Res. 2010; 149:175–182.
Article17. Yang DK, Kim HH, Lee SH, Yoon SS, Park JW, Cho IS. Isolation and characterization of a new porcine epidemic diarrhea virus variant that occurred in Korea in 2014. J Vet Sci. 2017; 07. 10. [Epub].
Article18. Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994; 22:4673–4680.
Article19. Robert X, Gouet P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014; 42:W320–W324.
Article20. Song D, Moon H, Kang B. Porcine epidemic diarrhea: a review of current epidemiology and available vaccines. Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2015; 4:166–176.
Article21. Liu S, Xiao L, Nelson C, Hagedorn CH. A cell culture adapted HCV JFH1 variant that increases viral titers and permits the production of high titer infectious chimeric reporter viruses. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e44965.
Article22. Daemer RJ, Feinstone SM, Gust ID, Purcell RH. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in African green monkey kidney cell culture: primary isolation and serial passage. Infect Immun. 1981; 32:388–393.
Article23. Collin EA, Anbalagan S, Okda F, Batman R, Nelson E, Hause BM. An inactivated vaccine made from a U.S. field isolate of porcine epidemic disease virus is immunogenic in pigs as demonstrated by a dose-titration. BMC Vet Res. 2015; 11:62.
Article24. Thiel V, Herold J, Schelle B, Siddell SG. Viral replicase gene products suffice for coronavirus discontinuous transcription. J Virol. 2001; 75:6676–6681.
Article25. Xing N, Guan X, An B, et al. Ultrasensitive detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus from fecal samples using functionalized nanoparticles. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0167325.
Article26. Goede D, Murtaugh MP, Nerem J, Yeske P, Rossow K, Morrison R. Previous infection of sows with a “mild” strain of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus confers protection against infection with a “severe” strain. Vet Microbiol. 2015; 176:161–164.
Article27. Park ME, Lee SY, Kim RH, et al. Enhanced immune responses of foot-and-mouth disease vaccine using new oil/gel adjuvant mixtures in pigs and goats. Vaccine. 2014; 32:5221–5227.
Article28. Comi G, Freedman MS, Kappos L, et al. Pooled safety and tolerability data from four placebo-controlled teriflunomide studies and extensions. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2016; 5:97–104.
Article29. Ibrahim Eel-S, Gamal WM, Hassan AI, Mahdy Sel D, Hegazy AZ, Abdel-Atty MM. Comparative study on the immunopotentiator effect of ISA 201, ISA 61, ISA 50, ISA 206 used in trivalent foot and mouth disease vaccine. Vet World. 2015; 8:1189–1198.
Article30. Bouguyon E, Goncalves E, Shevtsov A, et al. A new adjuvant combined with inactivated influenza enhances specific CD8 T cell response in mice and decreases symptoms in swine upon challenge. Viral Immunol. 2015; 28:524–531.
Article31. Aziz-Boaron O, Gleser D, Yadin H, et al. The protective effectiveness of an inactivated bovine ephemeral fever virus vaccine. Vet Microbiol. 2014; 173:1–8.
Article32. Aucouturier J, Dupuis L, Ganne V. Adjuvants designed for veterinary and human vaccines. Vaccine. 2001; 19:2666–2672.
Article33. Jang SI, Lillehoj HS, Lee SH, et al. Mucosal immunity against Eimeria acervulina infection in broiler chickens following oral immunization with profilin in Montanide adjuvants. Exp Parasitol. 2011; 129:36–41.
Article34. Walders B, Raschke A, Neugebauer M, et al. Blending of a conventional Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccine with a positive marker: tracking of immunised pigs by peptide-specific antibodies raised to the marker component. Res Vet Sci. 2005; 78:135–141.
Article35. Deville S, Arous JB, Bertrand F, Borisov V, Dupuis L. Efficacy of intranasal and spray delivery of adjuvanted live vaccine against infectious bronchitis virus in experimentally infected poultry. Procedia Vaccinol. 2012; 6:85–92.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent vaccine technology in industrial animals
- Augmented immune responses in pigs immunized with an inactivated porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus containing the deglycosylated glycoprotein 5 under field conditions
- Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus vaccine does not fit in classical vaccinology
- Isolation and characterization of a new porcine epidemic diarrhea virus variant that occurred in Korea in 2014
- Porcine epidemic diarrhea: a review of current epidemiology and available vaccines