J Bacteriol Virol.
2017 Dec;47(4):179-188. 10.4167/jbv.2017.47.4.179.
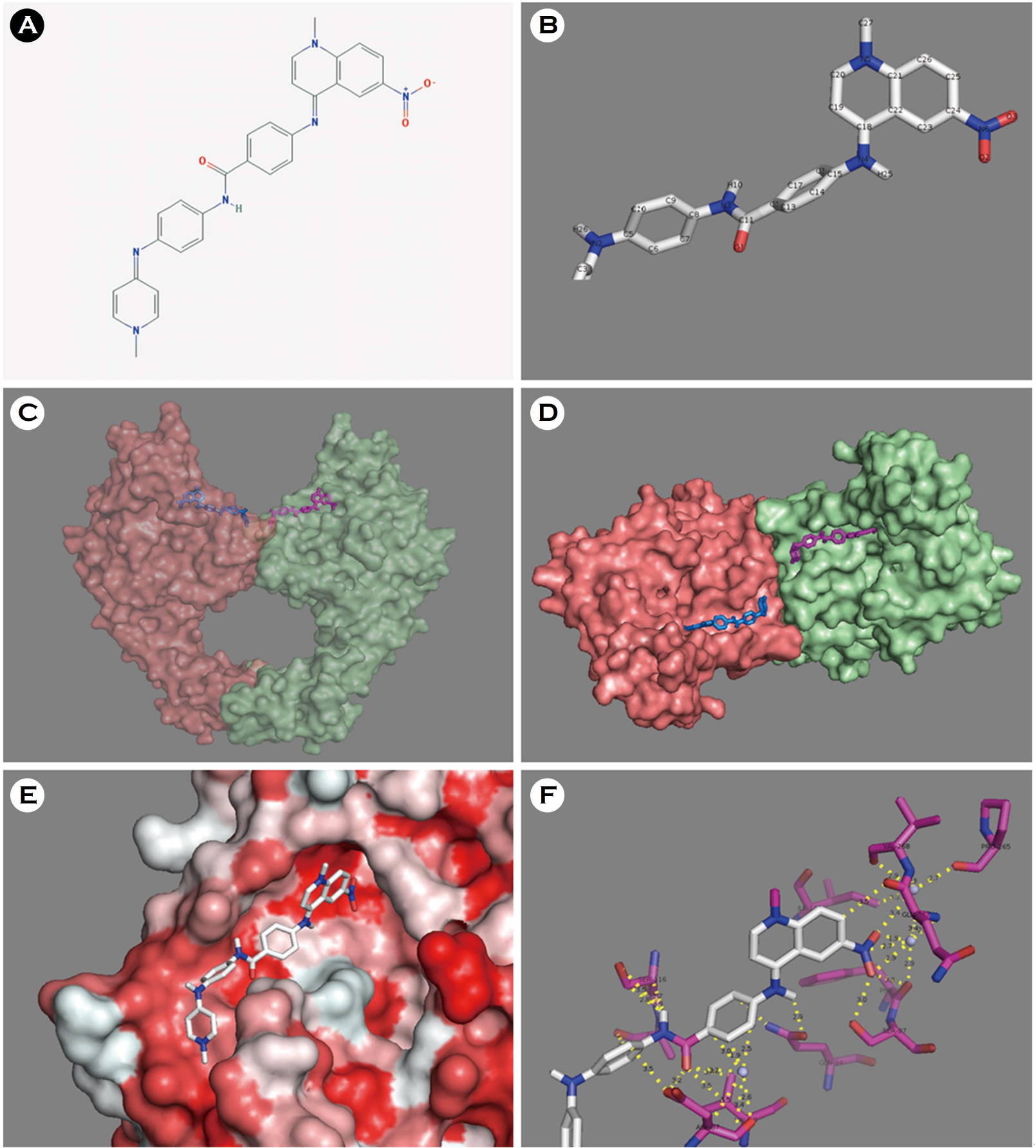
Discovery of a New DNA Gyrase A Inhibitor, 4-[(1-methyl-6-nitroquinolin-1-ium-4-yl)amino]-N-[4-[(1-methylpyridin-1-ium-4-yl)amino]phenyl]benzamide
- Affiliations
-
- 1Public Health & Welfare Bureau, Daegu Metropolitan City, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea. wonki@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2399977
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2017.47.4.179
Abstract
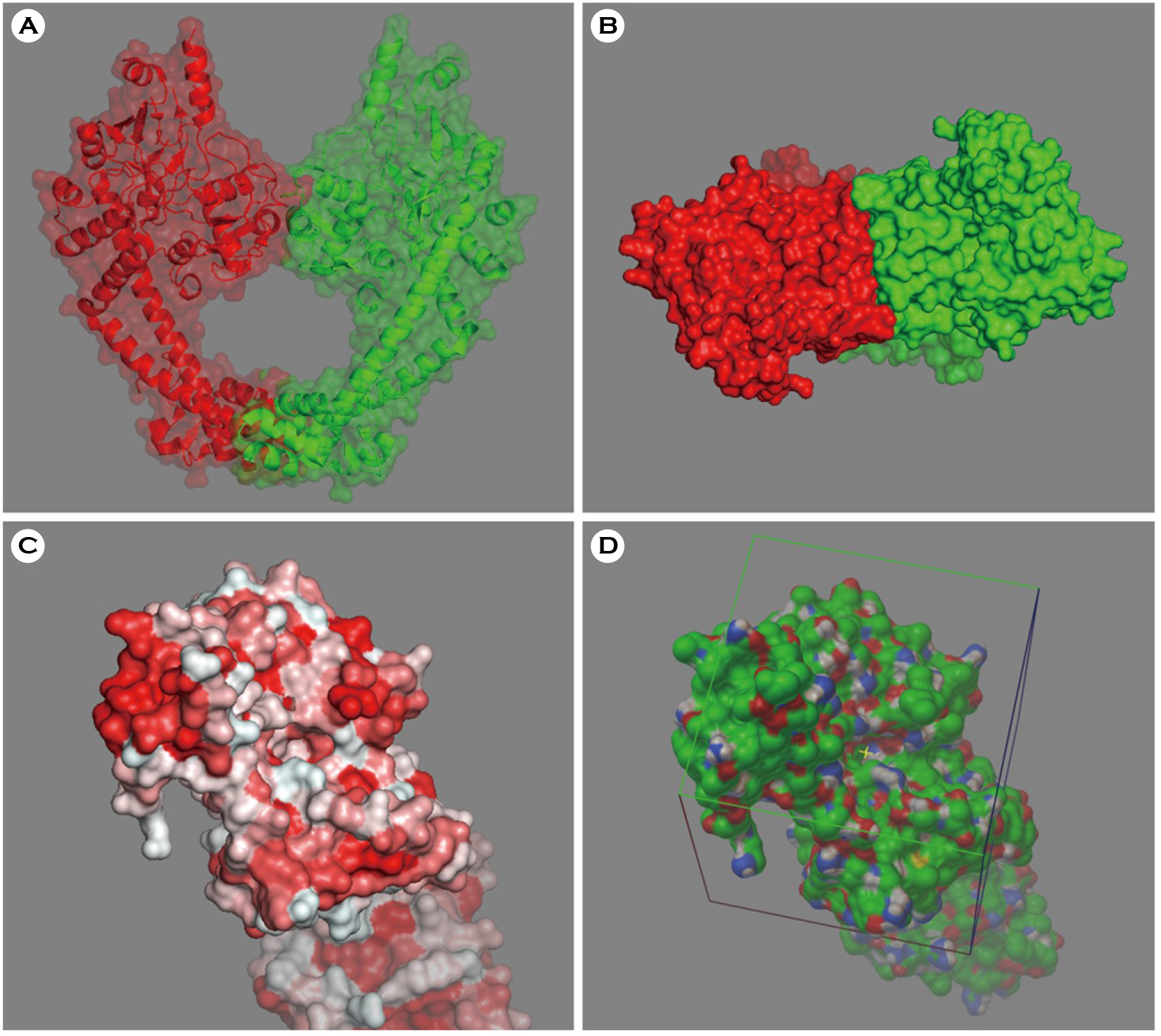
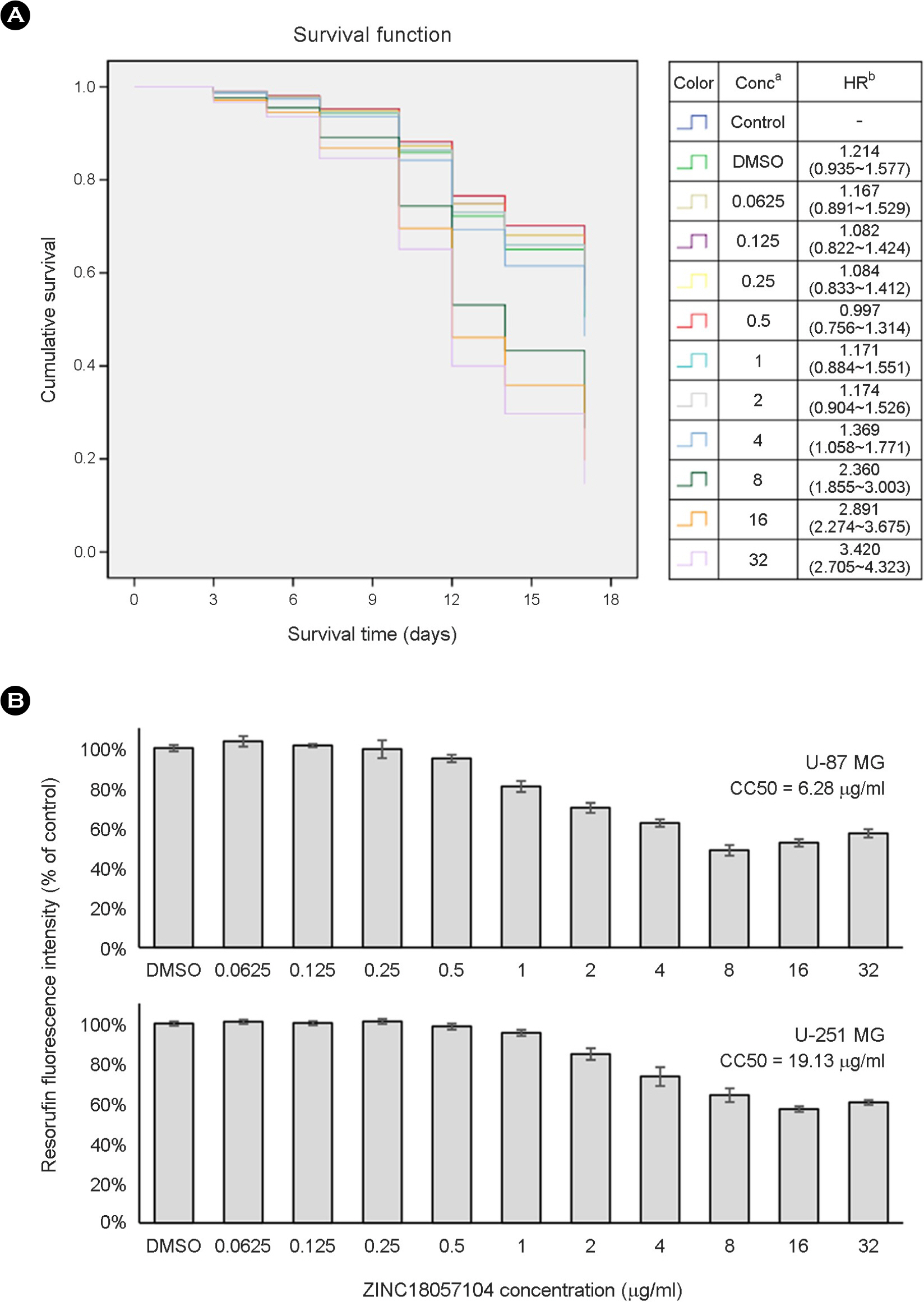
- Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a clinically important causative organism that can lead to urinary tract infections. Quinolone antibiotics are among the first-line treatments for urinary tract infections. However, the frequency of resistance to quinolone in E. coli has been increasing. Therefore, new antimicrobial agents that can be used for treatment in lieu of quinolone antibiotics are needed. In this study, thirty-six compounds with higher scores in a virtual screening based on the three-dimensional structure of E. coli DNA gyrase were selected for in vitro antimicrobial activity testing. An in vitro test confirmed the antimicrobial activity of 4-[(1-methyl-6-nitroquinolin-1-ium-4-yl)amino]-N-[4-[(1-methylpyridin-1-ium-4-yl)amino]phenyl]benzamide (ZINC18057104) against E. coli among the 36 compounds. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of ZINC18057104 against E. coli ATCC® 25922â„¢ was 2 μg/ml, and the MICâ‚…â‚€ and MIC₉₀ for the 72 quinolone-resistant E. coli clinical isolates were 4 and 64 μg/ml, respectively. ZINC18057104, which has a quinoline structure which is similar to the quinolone antibiotics, is predicted to exhibit antimicrobial activity in quinolone-resistant E. coli because it has different molecular interactions with the DNA gyrase than that of existing quinolone antibiotics.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Kaper JB, Nataro JP, Mobley HL. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004; 2:123–40.
Article2). Sanchez GV, Master RN, Karlowsky JA, Bordon JM. In vitro antimicrobial resistance of urinary E. coli isolates among U.S. outpatients from 2000 to 2010. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012; 56:2181–3.3). Petty NK, Ben Zakour NL, Stanton-Cook M, Skippington E, Totsika M, Forde BM, et al. Global dissemination of a multidrug resistant Escherichia coli clone. Proc Nati Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111:5694–9.
Article4). Drlica K, Zhao X. DNA gyrase, topoisomerase IV, and the 4-quinolones. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1997; 61:377–92.
Article5). Flores-Mireles AL, Walker JN, Caparon M, Hultgren SJ. Urinary tract infections: epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015; 13:269–84.
Article6). Jean SS, Coombs G, Ling T, Balaji V, Rodrigues C, Mikamo H, et al. Epidemiology and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of pathogens causing urinary tract infections in the Asia-Pacific region: Results from the Study for Monitoring Antimicrobial Resistance Trends (SMART), 2010–2013. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016; 47:328–34.
Article7). Kitchen DB, Decornez H, Furr JR, Bajorath J. Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: methods and applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004; 3:935–49.
Article8). Sliwoski G, Kothiwale S, Meiler J, Lowe EW Jr. Computational methods in drug discovery. Pharmacol Rev. 2013; 66:334–95.
Article9). Rose PW, Bi C, Bluhm WF, Christie CH, Dimitropoulos D, Dutta S, et al. The RCSB Protein Data Bank: new resources for research and education. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013; 41:D475–82.
Article10). Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, et al. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem. 2009; 30:2785–91.
Article11). Irwin JJ, Shoichet BK. ZINC–a free database of commercially available compounds for virtual screening. J Chem Inf Model. 2005; 45:177–82.12). Trott O, Olson AJ. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem. 2010; 31:455–61.
Article13). Patel JB, Cockerill FR, Alder J, Bradford PA, Eliopoulos GM, Hardy D, et al. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twenty-fourth informational supplement. CLSI standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. 2014; 34:1–226.14). Solis GM, Petrascheck M. Measuring Caenorhabditis elegans life span in 96 well microtiter plates. J Vis Exp. 2011; 49:2496.15). Chou TC, Talalay P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984; 22:27–55.
Article16). Aldred KJ, Kerns RJ, Osheroff N. Mechanism of quinolone action and resistance. Biochemistry. 2014; 53:1565–74.
Article17). Gönüllü N, Aktaş Z, Şalcioğlu M, Bal C, Anğ Ö. Comparative in vitro activities of five quinolone antibiotics, including gemifloxacin, against clinical isolates. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001; 7:499–503.18). Morgan-Linnell SK, Becnel Boyd L, Steffen D, Zechiedrich L. Mechanisms accounting for fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53:235–41.19). Wohlkonig A, Chan PF, Fosberry AP, Homes P, Huang J, Kranz M, et al. Structural basis of quinolone inhibition of type IIA topoisomerases and target-mediated resistance. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010; 17:1152–3.
Article20). Pan XS, Gould KA, Fisher LM. Probing the differential interactions of quinazolinedione PD 0305970 and quinolones with gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53:3822–31.
Article21). Malik M, Marks KR, Mustaev A, Zhao X, Chavda K, Kerns RJ, et al. Fluoroquinolone and quinazolinedione activities against wild-type and gyrase mutant strains of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011; 55:2335–43.
Article22). Aldred KJ, Schwanz HA, Li G, McPherson SA, Turnbough CL Jr, Kerns RJ, et al. Overcoming target-mediated quinolone resistance in topoisomerase IV by introducing metal-ion-independent drug-enzyme interactions. ACS Chem Biol. 2013; 8:2660–8.
Article23). Lipinski CA. Lead-and drug-like compounds: the rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2004; 1:337–41.24). Veber DF, Johnson SR, Cheng HY, Smith BR, Ward KW, Kopple KD. Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. J Med Chem. 2002; 45:2615–23.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Amino Acid Transporters as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Thyroid Cancer
- The ontogeny of excitatory amino acid receptors in the rat brain quantitative autoradiographic study: I. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors
- Phylogenetic Relationship in Different Commercial Strains of Pleurotus nebrodensis Based on ITS Sequence and RAPD
- Topographic positions of coposcopic findings and pathologic epithel : ium on early carcinoma of the uterine cervix
- Expression and functional characterization of amino acid transport system L in Saos2 human osteogenic sarcoma cells