Korean J Ophthalmol.
2017 Oct;31(5):452-459. 10.3341/kjo.2017.0020.
Comparative Study of the Effects of Trabecular Meshwork Outflow Drugs on the Permeability and Nitric Oxide Production in Trabecular Meshwork Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. jwkim@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2390289
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0020
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the effects of the barrier function in human trabecular meshwork (TM) cells monolayer and the production of nitric oxide (NO) between trabecular outflow drugs, Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) inhibitors, adenosine, and statin.
METHODS
Primary cultured TM cells were exposed to 10 or 25 µM Y-27632, 0.1 or 1 µM N6-cyclohexyladenosine (CHA), or 15 or 30 µM simvastatin for 24 hours. NO production and expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA were measured by Griess assay and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, respectively. Barrier functions of the TM cell monolayer were measured by carboxyfluorescein and trans-endothelial electrical resistance. The expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 mRNA was assessed with reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
RESULTS
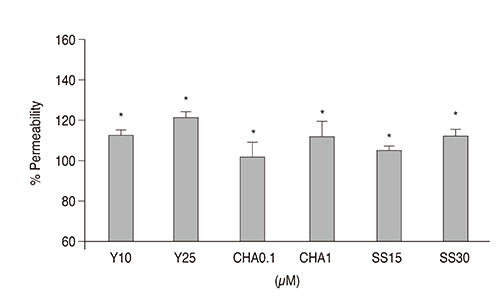
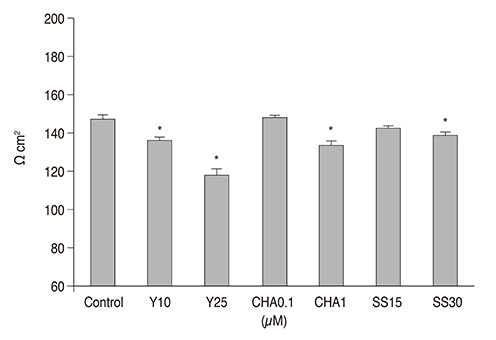
In TM cells, treatment with each drug increased endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA expression. Treatment with 25 µM Y-27632 and 1.0 µM CHA increased NO production significantly (p = 0.035 and p = 0.043, respectively). Treatment with each drug increased the permeability (all p = 0.001) and decreased the trans-endothelial electron resistance of the TM cell monolayer. Treatment with 0.1 µM and 1.0 µM CHA significantly increased matrix metalloproteinase-2 mRNA expression, but simvastatin inhibited its expression.
CONCLUSIONS
Since treatment with ROCK inhibitor more greatly increased NO production and permeability than did adenosine or statin, ROCK inhibitor seems to be more effective for lowering intraocular pressure.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenosine
Electric Impedance
Humans
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Intraocular Pressure
Matrix Metalloproteinase 2
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type III
Nitric Oxide*
Permeability*
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Reverse Transcription
rho-Associated Kinases
RNA, Messenger
Simvastatin
Trabecular Meshwork*
Adenosine
Matrix Metalloproteinase 2
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type III
RNA, Messenger
Simvastatin
rho-Associated Kinases
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 Expression by an Adenosine A1 Agonist in Trabecular Meshwork Cells
Min Ju Baek, Keun Hae Kim, Jae Woo Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(10):946-952. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.10.946.Effect and Mechanism of Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors on Trabecular Outflow
Jae Woo Kim, Jong Been Lee, So Hyung Lee
Korean J Ophthalmol. 2019;33(5):414-421. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2019.0057.
Reference
-
1. Alvarado J, Murphy C, Juster R. Trabecular meshwork cellularity in primary open-angle glaucoma and nonglaucomatous normals. Ophthalmology. 1984; 91:564–579.2. Rohen JW, Lutjen-Drecoll E, Flugel C, et al. Ultrastructure of the trabecular meshwork in untreated cases of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG). Exp Eye Res. 1993; 56:683–692.3. Schmidl D, Schmetterer L, Garhofer G, Popa-Cherecheanu A. Pharmacotherapy of glaucoma. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 31:63–77.4. Kopczynski CC, Epstein DL. Emerging trabecular outflow drugs. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 30:85–87.5. Inoue T, Tanihara H. Rho-associated kinase inhibitors: a novel glaucoma therapy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013; 37:1–12.6. Thieme H, Nuskovski M, Nass JU, et al. Mediation of calcium-independent contraction in trabecular meshwork through protein kinase C and rho-A. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000; 41:4240–4246.7. Rao PV, Deng PF, Kumar J, Epstein DL. Modulation of aqueous humor outflow facility by the Rho kinase-specific inhibitor Y-27632. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001; 42:1029–1037.8. Honjo M, Tanihara H, Inatani M, et al. Effects of rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor Y-27632 on intraocular pressure and outf low facility. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001; 42:137–144.9. Novack GD. Rho kinase inhibitors for the treatment of glaucoma. Drugs Future. 2013; 38:107–113.10. Zhong Y, Yang Z, Huang WC, Luo X. Adenosine, adenosine receptors and glaucoma: an updated overview. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013; 1830:2882–2890.11. Song J, Deng PF, Stinnett SS, et al. Effects of cholesterol-lowering statins on the aqueous humor outflow pathway. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46:2424–2432.12. Stein JD, Newman-Casey PA, Talwar N, et al. The relationship between statin use and open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:2074–2081.13. Wiederholt M, Dorschner N, Groth J. Effect of diuretics, channel modulators and signal interceptors on contractility of the trabecular meshwork. Ophthalmologica. 1997; 211:153–160.14. Wiederholt M, Stumpff F. The trabecular meshwork and aqueous humor reabsorption. In : Civan MM, editor. Current topics in membranes. The eye's aqueous humor: from secretion to glaucoma. Vol. 45. San Diego: Academic Press;1998. p. 163–202.15. Wiederholt M, Sturm A, Lepple-Wienhues A. Relaxation of trabecular meshwork and ciliary muscle by release of nitric oxide. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994; 35:2515–2520.16. Behar-Cohen FF, Goureau O, D'Hermies F, Courtois Y. Decreased intraocular pressure induced by nitric oxide donors is correlated to nitrite production in the rabbit eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996; 37:1711–1715.17. Dismuke WM, Mbadugha CC, Ellis DZ. NO-induced regulation of human trabecular meshwork cell volume and aqueous humor outf low facility involve the BKCa ion channel. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008; 294:C1378–C1386.18. Rikitake Y, Liao JK. Rho GTPases, statins, and nitric oxide. Circ Res. 2005; 97:1232–1235.19. Noma K, Oyama N, Liao JK. Physiological role of ROCKs in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006; 290:C661–C668.20. Bradley JM, Vranka J, Colvis CM, et al. Effect of matrix metalloproteinases activity on outflow in perfused human organ culture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998; 39:2649–2658.21. Sanka K, Maddala R, Epstein DL, Rao PV. Influence of actin cytoskeletal integrity on matrix metalloproteinase-2 activation in cultured human trabecular meshwork cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48:2105–2114.22. Shearer TW, Crosson CE. Adenosine A1 receptor modulation of MMP-2 secretion by trabecular meshwork cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002; 43:3016–3020.23. Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983; 65:55–63.24. Kameda T, Inoue T, Inatani M, et al. The effect of Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor on monkey Schlemm's canal endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012; 53:3092–3103.25. Alvarado JA, Betanzos A, Franse-Carman L, et al. Endothelia of Schlemm's canal and trabecular meshwork: distinct molecular, functional, and anatomic features. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004; 286:C621–C634.26. Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, et al. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982; 126:131–138.27. Alvarado JA, Wood I, Polansky JR. Human trabecular cells. II. Growth pattern and ultrastructural characteristics. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1982; 23:464–478.28. Zhang M, Maddala R, Rao PV. Novel molecular insights into RhoA GTPase-induced resistance to aqueous humor outflow through the trabecular meshwork. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008; 295:C1057–C1070.29. Husain S, Shearer TW, Crosson CE. Mechanisms linking adenosine A1 receptors and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation in human trabecular meshwork cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007; 320:258–265.30. Fleischhauer JC, Mitchell CH, Stamer WD, et al. Common actions of adenosine receptor agonists in modulating human trabecular meshwork cell transport. J Membr Biol. 2003; 193:121–136.31. Kim HY, Kim JW. Effect of nitric oxide on the permeability of trabecular meshwork cell monolayer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:771–775.32. Satoh K, Fukumoto Y, Shimokawa H. Rho-kinase: important new therapeutic target in cardiovascular diseases. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011; 301:H287–H296.33. Honjo M, Tanihara H, Kameda T, et al. Potential role of Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor Y-27632 in glaucoma filtration surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48:5549–5557.34. Tanihara H, Inoue T, Yamamoto T, et al. Intra-ocular pressure-lowering effects of a Rho kinase inhibitor, ripasudil (K-115), over 24 hours in primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension: a randomized, open-label, crossover study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015; 93:e254–e260.35. Kaneko Y, Ohta M, Inoue T, et al. Effects of K-115 (Ripasudil), a novel ROCK inhibitor, on trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal endothelial cells. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:19640.36. Ichikawa M, Yoshida J, Saito K, et al. Differential effects of two ROCK inhibitors, Fasudil and Y-27632, on optic nerve regeneration in adult cats. Brain Res. 2008; 1201:23–33.37. Hata Y, Miura M, Nakao S, et al. Antiangiogenic properties of fasudil, a potent Rho-kinase inhibitor. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2008; 52:16–23.38. Novack GD. Eyes on new product development. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2016; 32:401–402.39. Prasanna G, Li B, Mogi M, Rice DS. Pharmacology of novel intraocular pressure-lowering targets that enhance conventional outflow facility: pitfalls, promises and what lies ahead? Eur J Pharmacol. 2016; 787:47–56.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Mitomycin C on the Proliferation and Nitric Oxide Production in the Cultured Trabecular Meshwork Cells
- Effect of Tetrahydrozoline on the Permeability of Trabecular Meshwork Cell Monolayer
- Effect of beta-adrenergics on the Survival and Production of Nitric Oxide in the Cultured Trabecular Meshwork Cells
- Effect of Latanoprostene Bunod on the Permeability of Trabecular Meshwork Cells
- Effect of Nitric Oxide on the Permeability of Trabecular Meshwork Cell Monolayer