Endocrinol Metab.
2014 Dec;29(4):553-560. 10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.553.
Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Attenuates Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha-Induced Lipolysis via Protection of Perilipin in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Medical Research, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drlwy@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2384254
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.553
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) are known to stimulate and repress lipolysis in adipocytes, respectively; however, the mechanisms regulating these processes have not been completely elucidated.
METHODS
The key factors and mechanism of action of TNF-alpha and AMPK in lipolysis were investigated by evaluating perilipin expression and activity of protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK)/eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2alpha) by Western blot and an immunofluorescence assay in 24-hour TNF-alpha-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes with artificial manipulation of AMPK activation.
RESULTS
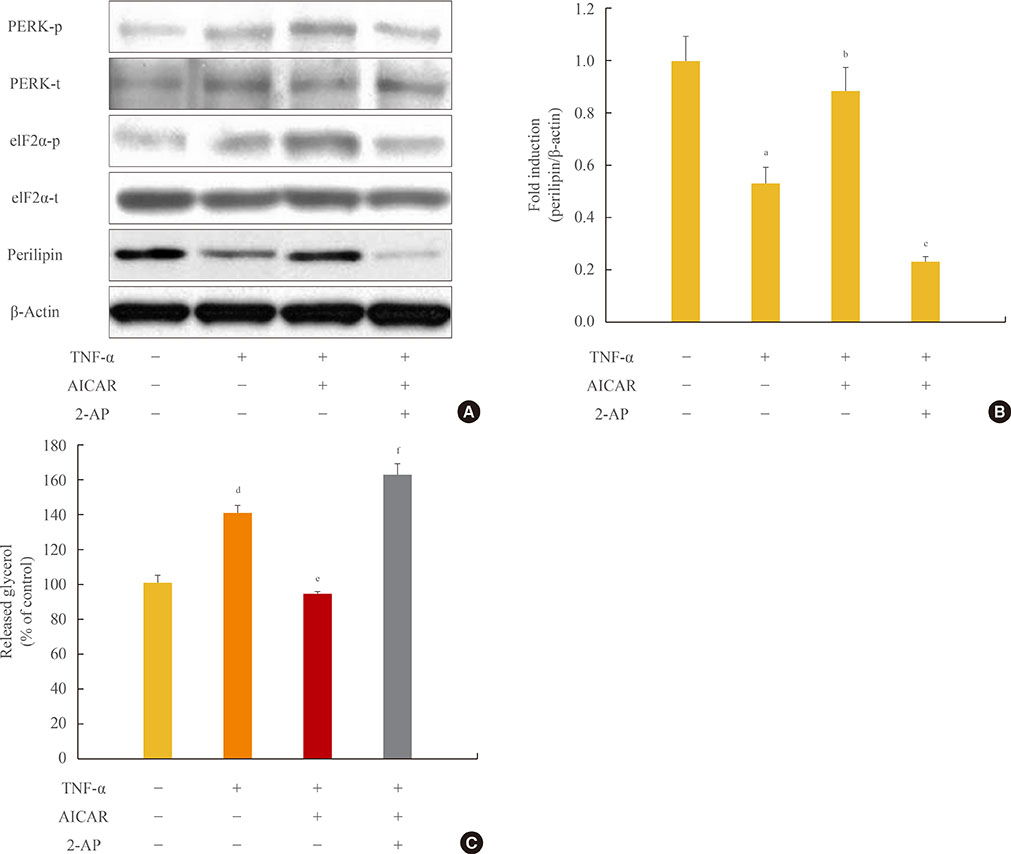
Enhancement of AMPK activity by the addition of activator minoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) suppressed TNF-alpha-induced lipolysis, whereas the addition of compound C, an inhibitor of AMPK phosphorylation, enhanced lipolysis. Perilipin, a lipid droplet-associated protein, was decreased by TNF-alpha and recovered following treatment with AICAR, showing a correlation with the antilipolytic effect of AICAR. Significant activation of PERK/eIF2alpha, a component of the unfolded protein response signaling pathway, was observed in TNF-alpha or vesicle-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The antilipolytic effect and recovery of perilipin expression by AICAR in TNF-alpha-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes were significantly diminished by treatment with 2-aminopurine, a specific inhibitor of eIF2alpha.
CONCLUSION
These data indicated that AICAR-induced AMPK activation attenuates TNF-alpha-induced lipolysis via preservation of perilipin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. In addition, PERK/eIF2alpha activity is a novel mechanism of the anti-lipolytic effect of AICAR.
MeSH Terms
-
2-Aminopurine
Adipocytes*
AMP-Activated Protein Kinases*
Blotting, Western
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Fluorescent Antibody Technique
Lipolysis*
Necrosis*
Phosphorylation
Phosphotransferases
Prokaryotic Initiation Factor-2
Protein Kinases
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Unfolded Protein Response
2-Aminopurine
AMP-Activated Protein Kinases
Phosphotransferases
Prokaryotic Initiation Factor-2
Protein Kinases
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Qi C, Pekala PH. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance in adipocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 2000; 223:128–135.2. Hausman DB, DiGirolamo M, Bartness TJ, Hausman GJ, Martin RJ. The biology of white adipocyte proliferation. Obes Rev. 2001; 2:239–254.3. Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993; 259:87–91.4. Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM. Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1995; 95:2409–2415.5. Kern PA, Saghizadeh M, Ong JM, Bosch RJ, Deem R, Simsolo RB. The expression of tumor necrosis factor in human adipose tissue: regulation by obesity, weight loss, and relationship to lipoprotein lipase. J Clin Invest. 1995; 95:2111–2119.6. Kawakami M, Murase T, Ogawa H, Ishibashi S, Mori N, Takaku F, Shibata S. Human recombinant TNF suppresses lipoprotein lipase activity and stimulates lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biochem. 1987; 101:331–338.7. Feingold KR, Doerrler W, Dinarello CA, Fiers W, Grunfeld C. Stimulation of lipolysis in cultured fat cells by tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, and the interferons is blocked by inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. Endocrinology. 1992; 130:10–16.8. Hauner H, Petruschke T, Russ M, Rohrig K, Eckel J. Effects of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) on glucose transport and lipid metabolism of newly-differentiated human fat cells in cell culture. Diabetologia. 1995; 38:764–771.9. Orban Z, Remaley AT, Sampson M, Trajanoski Z, Chrousos GP. The differential effect of food intake and beta-adrenergic stimulation on adipose-derived hormones and cytokines in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999; 84:2126–2133.10. Ruderman N, Prentki M. AMP kinase and malonyl-CoA: targets for therapy of the metabolic syndrome. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004; 3:340–351.11. Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J, Wu M, Ventre J, Doebber T, Fujii N, Musi N, Hirshman MF, Goodyear LJ, Moller DE. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest. 2001; 108:1167–1174.12. Fryer LG, Parbu-Patel A, Carling D. The Anti-diabetic drugs rosiglitazone and metformin stimulate AMP-activated protein kinase through distinct signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:25226–25232.13. Yin W, Mu J, Birnbaum MJ. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in cyclic AMP-dependent lipolysis In 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:43074–43080.14. Daval M, Diot-Dupuy F, Bazin R, Hainault I, Viollet B, Vaulont S, Hajduch E, Ferre P, Foufelle F. Anti-lipolytic action of AMP-activated protein kinase in rodent adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:25250–25257.15. Xu L, Spinas GA, Niessen M. ER stress in adipocytes inhibits insulin signaling, represses lipolysis, and alters the secretion of adipokines without inhibiting glucose transport. Horm Metab Res. 2010; 42:643–651.16. Zhou QG, Zhou M, Lou AJ, Xie D, Hou FF. Advanced oxidation protein products induce inflammatory response and insulin resistance in cultured adipocytes via induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010; 26:775–786.17. Habinowski SA, Witters LA. The effects of AICAR on adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001; 286:852–856.18. Koh HJ, Hirshman MF, He H, Li Y, Manabe Y, Balschi JA, Goodyear LJ. Adrenaline is a critical mediator of acute exercise-induced AMP-activated protein kinase activation in adipocytes. Biochem J. 2007; 403:473–481.19. Lefterova MI, Mullican SE, Tomaru T, Qatanani M, Schupp M, Lazar MA. Endoplasmic reticulum stress regulates adipocyte resistin expression. Diabetes. 2009; 58:1879–1886.20. van der Kallen CJ, van Greevenbroek MM, Stehouwer CD, Schalkwijk CG. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in the development of diabetes: is there a role for adipose tissue and liver? Apoptosis. 2009; 14:1424–1434.21. Altarejos JY, Taniguchi M, Clanachan AS, Lopaschuk GD. Myocardial ischemia differentially regulates LKB1 and an alternate 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase kinase. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:183–190.22. Esumi H, Izuishi K, Kato K, Hashimoto K, Kurashima Y, Kishimoto A, Ogura T, Ozawa T. Hypoxia and nitric oxide treatment confer tolerance to glucose starvation in a 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:32791–32798.23. Marsin AS, Bouzin C, Bertrand L, Hue L. The stimulation of glycolysis by hypoxia in activated monocytes is mediated by AMP-activated protein kinase and inducible 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:30778–30783.24. Horie T, Ono K, Nagao K, Nishi H, Kinoshita M, Kawamura T, Wada H, Shimatsu A, Kita T, Hasegawa K. Oxidative stress induces GLUT4 translocation by activation of PI3-K/Akt and dual AMPK kinase in cardiac myocytes. J Cell Physiol. 2008; 215:733–742.25. Kim SJ, Nian C, McIntosh CH. Activation of lipoprotein lipase by glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in adipocytes. A role for a protein kinase B, LKB1, and AMP-activated protein kinase cascade. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:8557–8567.26. Dagon Y, Avraham Y, Berry EM. AMPK activation regulates apoptosis, adipogenesis, and lipolysis by eIF2alpha in adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006; 340:43–47.27. Langin D, Arner P. Importance of TNFalpha and neutral lipases in human adipose tissue lipolysis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 17:314–320.28. Viollet B, Mounier R, Leclerc J, Yazigi A, Foretz M, Andreelli F. Targeting AMP-activated protein kinase as a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of metabolic disorders. Diabetes Metab. 2007; 33:395–402.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cryptotanshinone Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in Differentiating 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Down-regulating C/EBP-α, PPAR-γ, FAS, Perilipin A, and STAT-3
- Cryptotanshinone Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in Differentiating 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Down-regulating C/EBP-α, PPAR-γ, FAS, Perilipin A, and STAT-3
- Cryptotanshinone Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in Differentiating 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Down-regulating C/EBP-α, PPAR-γ, FAS, Perilipin A, and STAT-3
- Carnosic acid inhibits TLR4-MyD88 signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- The Inhibitory Effect of Testosterone on PPARγ-induced Adipogenesis