Perinatology.
2016 Sep;27(3):149-157. 10.14734/PN.2016.27.3.149.
Neuroprotective Effects of SYM 2081, Targeting Kainate Receptors in the Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. wootykim@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2355572
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/PN.2016.27.3.149
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Glutamate induced excitotoxicity has been implicated as a major factor of central neuronal death in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic (HI) injury. Kainate receptors (KARs) are one of glutamatergic receptors involving glutamate toxicity. However, the expression patterns of KARs in the neonatal HI brain injury have not been clearly established. Therefore, this study was designed to investigate the expression pattern of KARs and to determine the potential of SYM 2081 ((2S, 4R)-4-methylglutamic acid) as a neuronal rescue agent after HI brain injury.
METHODS
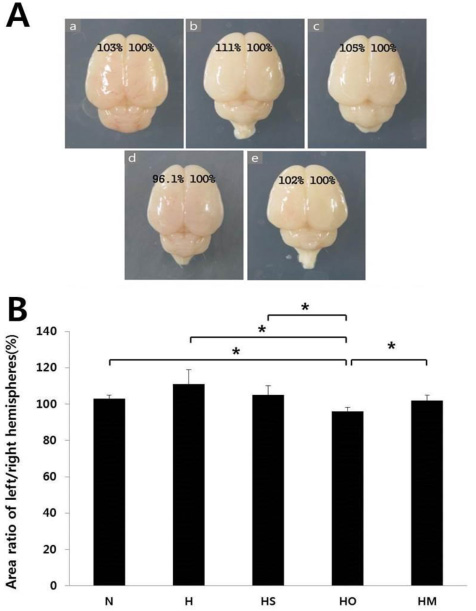
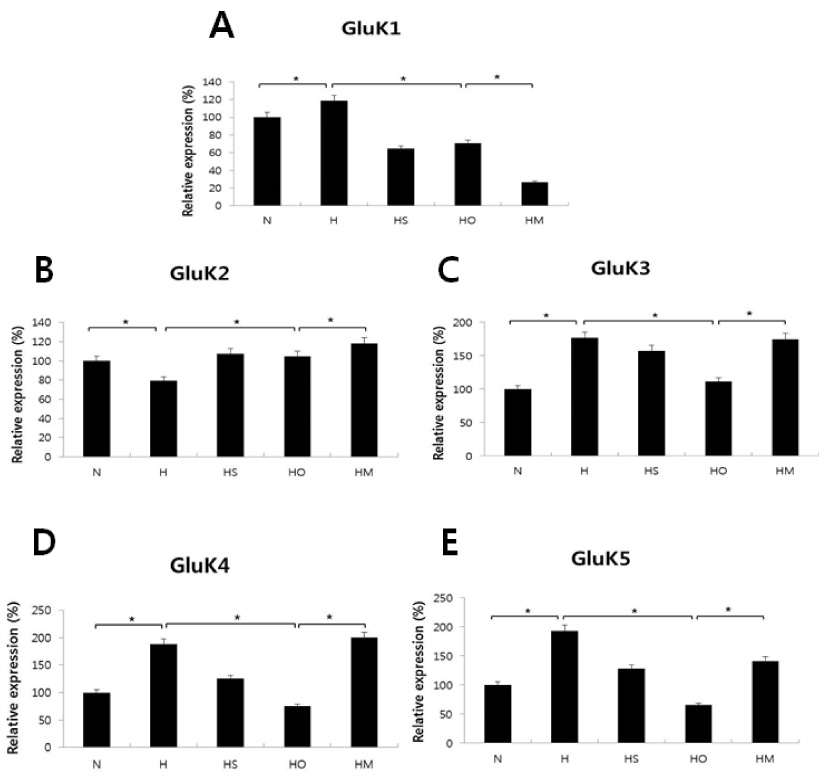
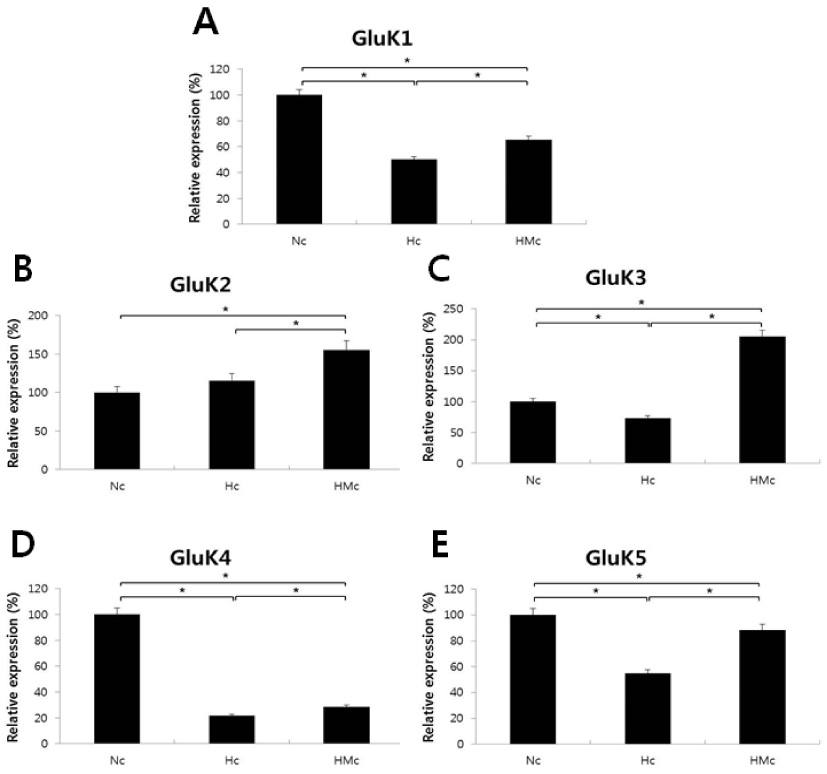
In an in vivo model, left carotid artery ligation (LCA) was done in Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat pups. The animals were divided into five groups; normoxia (N), hypoxia (8% O2, 92% N2) (H), hypoxia with sham-operation (HS), hypoxia with operation (HO), and HO treated with SYM 2081 before a hypoxic insult (HM). In an in vitro model, the cultured embryonic cortical neuronal cells were divided into three groups: normoxia (95% air, 5% COâ‚‚) (Nc), hypoxia (94% N2, 5% COâ‚‚) (Hc), and Hc treated with SYM2081 (HMc) before a hypoxic insult. The expressions of GluK1-5 were assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
RESULTS
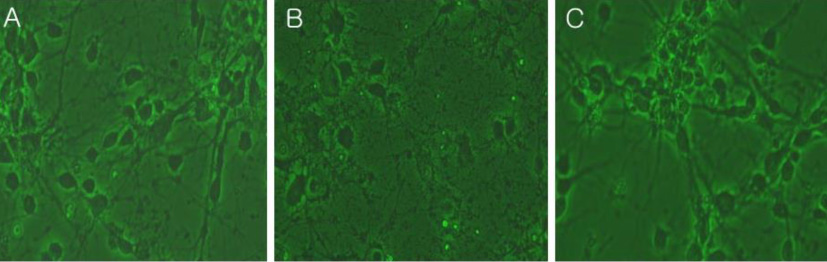
The area of left hemisphere was decreased as compared to contralateral hemisphere in HO group, restored by SYM 2081 treatment. Cell loss observed in the Hc group was decreased in the HMC group. The expressions of all KARs except for GluK2 were decreased in the HO and HC groups, whereas they were increased in HM and HMc groups.
CONCLUSION
This study showed that SYM 2081 had neuroprotective effects on HI brain injury in neonatal rats through modulating KAR expression.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
SYM 2081 Exerts Neuroprotective Effect Modulating Anti-Apoptosis in the Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury of Neonatal Rats
Jin Kyung Park, Yoon Young Jang, Ji Eun Jeong, Eun Joo Lee, Eun Jin Choi, Hai Lee Chung, Woo Taek Kim
Perinatology. 2019;30(3):117-125. doi: 10.14734/PN.2019.30.3.117.
Reference
-
1. Lerma J, Marques JM. Kainate receptors in health and disease. Neuron. 2013; 80:292–311.
Article2. Contractor A, Mulle C, Swanson GT. Kainate receptors coming of age: milestones of two decades of research. Trends Neurosci. 2011; 34:154–163.
Article3. Hwang JY, Kim YH, Ahn YH, Wie MB, Koh JY. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor blockade induces neuronal apoptosis in cortical culture. Exp Neurol. 1999; 159:124–130.
Article4. Vannucci RC. Experimental biology of cerebral hypoxia-ischemia: relation to perinatal brain damage. Pediatr Res. 1990; 27:317–326.
Article5. Johnston MV, Trescher WH, Ishida A, Nakajima W. Neurobiology of hypoxic-ischemic injury in the developing brain. Pediatr Res. 2001; 49:735–741.6. Collingridge GL, Olsen RW, Peters J, Spedding M. A nomenclature for ligand-gated ion channels. Neuropharmacology. 2009; 56:2–5.
Article7. Chittajallu R, Braithwaite SP, Clarke VR, Henley JM. Kainate receptors: subunits, synaptic localization and function. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1999; 20:26–35.
Article8. Komuro H, Rakic P. Modulation of neuronal migration by NMDA receptors. Science. 1993; 260:95–97.
Article9. Johnston MV, Trescher WH, Ishida A, Nakajima W. Novel treatments after experimental brain injury. Semin Neonatol. 2000; 5:75–86.
Article10. Whitelaw A. Systematic review of therapy after hypoxic-ischaemic brain injury in the perinatal period. Semin Neonatol. 2000; 5:33–40.
Article11. Matute C, Sánchez-Gómez MV, Martínez-Millán L, Miledi R. Glutamate receptor-mediated toxicity in optic nerve oligodendrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997; 94:8830–8835.
Article12. Paternain AV, Morales M, Lerma J. Selective antagonism of AMPA receptors unmasks kainate receptor-mediated responses in hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1995; 14:185–189.
Article13. Toms NJ, Reid ME, Phillips W, Kemp MC, Roberts PJ. A novel kainate receptor ligand [3H]-(2S,4R)-4-methylglutamate: pharmacological characterization in rabbit brain membranes. Neuropharmacology. 1997; 36:1483–1488.
Article14. Jane DE, Lodge D, Collingridge GL. Kainate receptors: Pharmacology, function and therapeutic potential. Neuropharmacology. 2009; 56:90–113.
Article15. Gu ZQ, Hesson DP, Pelletier JC, Maccecchini ML, Zhou LM, Skolnick P. Synthesis, resolution, and biological evaluation of the four stereoisomers of 4-methylglutamic acid: selective probes of kainate receptors. J Med Chem. 1995; 38:2518–2520.
Article16. Zhou LM, Gu ZQ, Costa AM, Yamada KA, Mansson PE, Giordano T, et al. (2S,4R)-4-methylglutamic acid (SYM 2081): a selective, high-affinity ligand for kainate receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997; 280:422–427.17. Rice JE 3rd, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol. 1981; 9:131–141.
Article18. Brewer GJ. Isolation and culture of adult rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Methods. 1997; 71:143–155.
Article19. Roohey T, Raju TN, Moustogiannis AN. animal models for the study of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a critical analysis. Early Hum Dev. 1997; 47:115–146.
Article20. Jones KA, Wilding TJ, Huettner JE, Costa AM. Desensitization of kainate receptors by kainate, glutamate and diastereomers of 4-methylglutamate. Neuropharmacology. 1997; 36:853–863.
Article21. Hunter RG, Bellani R, Bloss E, Costa A, McCarthy K, McEwen BS. Regulation of kainate receptor subunit mRNA by stress and corticosteroids in the rat hippocampus. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e4328.
Article22. Bahn S, Volk B, Wisden W. Kainate receptor gene expression in the developing rat brain. J Neurosci. 1994; 14:5525–5547.
Article23. Paternain AV, Cohen A, Stern-Bach Y, Lerma J. A role for extracellular Na+ in the channel gating of native and recombinant kainate receptors. J Neurosci. 2003; 23:8641–8648.24. Clarke VR, Ballyk BA, Hoo KH, Mandelzys A, Pellizzari A, Bath CP, et al. A hippocampal GluR5 kainate receptor regulating inhibitory synaptic transmission. Nature. 1997; 389:599–603.
Article25. Xu X, Sun R, Jin R. The effect of the ketogenic diet on hippocampal GluR5 and Glu(R6 mRNA expression and Q/R site editing in the kainate-induced epilepsy model. Epilepsy Behav. 2008; 13:445–448.
Article26. Sagot E, Pickering DS, Pu X, Umberti M, Stensbol TB, Nielsen B, et al. Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of a series of 2,4-syn-functionalized (S)-glutamate analogues: New insight into the structure-activity relation of ionotropic glutamate receptor subtypes 5, 6, and 7. J Med Chem. 2008; 51:4093–4103.
Article27. Ullal G, Fahnestock M, Racine R. Time-dependent effect of kainate-induced seizures on glutamate receptor GluR5, GluR6, and GluR7 mRNA and protein expression in rat hippocampus. Epilepsia. 2005; 46:616–623.
Article28. Perrais D, Pinheiro PS, Jane DE, Mulle C. Antagonism of recombinant and native GluK3-containing kainate receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2009; 56:131–140.
Article29. Alt A, Weiss B, Ogden AM, Knauss JL, Oler J, Ho K, et al. Pharmacological characterization of glutamatergic agonists and antagonists at recombinant human homomeric and heteromeric kainate receptors in vitro. Neuropharmacology. 2004; 46:793–806.
Article30. Plested AJ, Vijayan R, Biggin PC, Mayer ML. Molecular basis of kainate receptor modulation by sodium. Neuron. 2008; 58:720–735.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- SYM 2081 Exerts Neuroprotective Effect Modulating Anti-Apoptosis in the Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury of Neonatal Rats
- Neuroprotective Effect of Growth Hormone in Neonatal Rat with Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury
- Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor mRNAs according to Administration of Geneticin in Hypoxic Neuron Cell Culture
- The effect of erythropoietin in neonatal rat model of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
- Effects of carnosine and hypothermia combination therapy on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats