Korean J Pain.
2016 Jul;29(3):164-171. 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.3.164.
The Role of Spinal Dopaminergic Transmission in the Analgesic Effect of Nefopam on Rat Inflammatory Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. kimwm@jnu.ac.kr
- 2Center for Creative Biomedical Scientists, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2327637
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2016.29.3.164
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Nefopam has been known as an inhibitor of the reuptake of monoamines, and the noradrenergic and/or serotonergic system has been focused on as a mechanism of its analgesic action. Here we investigated the role of the spinal dopaminergic neurotransmission in the antinociceptive effect of nefopam administered intravenously or intrathecally.
METHODS
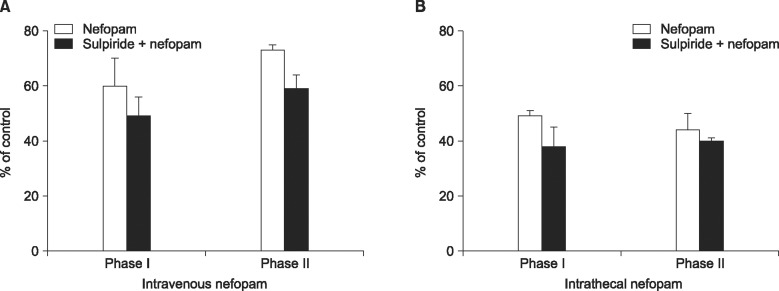
The effects of intravenously and intrathecally administered nefopam were examined using the rat formalin test. Then we performed a microdialysis study to confirm the change of extracellular dopamine concentration in the spinal dorsal horn by nefopam. To determine whether the changes of dopamine level are associated with the nefopam analgesia, its mechanism was investigated pharmacologically via pretreatment with sulpiride, a dopaminergic D2 receptor antagonist.
RESULTS
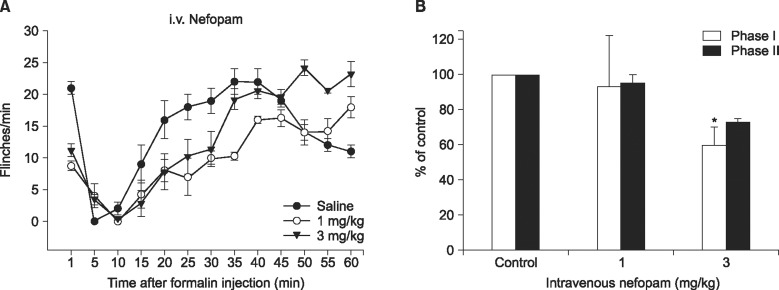
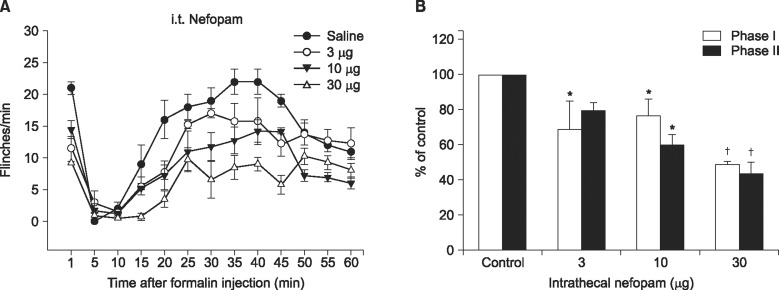
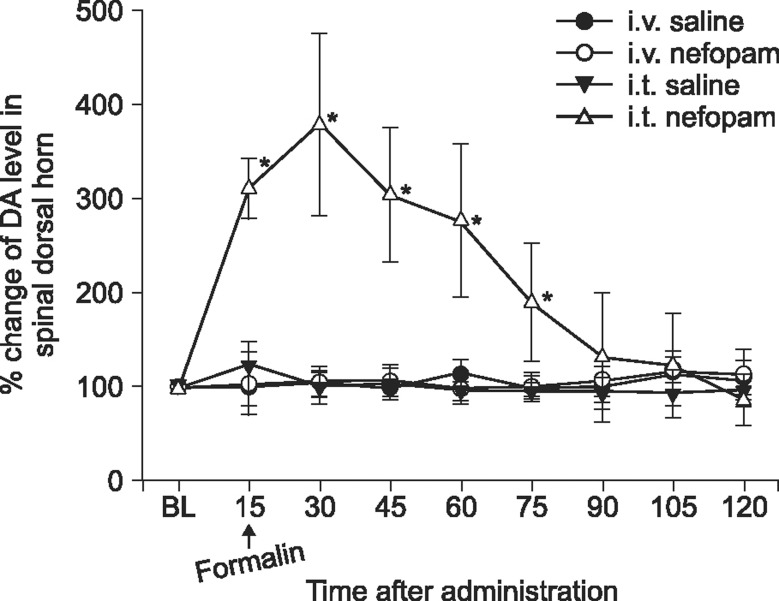
When nefopam was administered intravenously the flinching responses in phase I of the formalin test were decreased, but not those in phase II of the formalin test were decreased. Intrathecally injected nefopam reduced the flinching responses in both phases of the formalin test in a dose dependent manner. Microdialysis study revealed a significant increase of the level of dopamine in the spinal cord by intrathecally administered nefopam (about 3.8 fold the baseline value) but not by that administered intravenously. The analgesic effects of intrathecally injected nefopam were not affected by pretreatment with sulpiride, and neither were those of the intravenous nefopam.
CONCLUSIONS
Both the intravenously and intrathecally administered nefopam effectively relieved inflammatory pain in rats. Nefopam may act as an inhibitor of dopamine reuptake when delivered into the spinal cord. However, the analgesic mechanism of nefopam may not involve the dopaminergic transmission at the spinal level.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim KH, Abdi S. Rediscovery of nefopam for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Korean J Pain. 2014; 27:103–111. PMID: 24748937.
Article2. Esposito E, Romandini S, Merlo-Pich E, Mennini T, Samanin R. Evidence of the involvement of dopamine in the analgesic effect of nefopam. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986; 128:157–164. PMID: 3098570.
Article3. Fuller RW, Snoddy HD. Evaluation of nefopam as a monoamine uptake inhibitor in vivo in mice. Neuropharmacology. 1993; 32:995–999. PMID: 7507578.
Article4. Hunskaar S, Fasmer OB, Broch OJ, Hole K. Involvement of central serotonergic pathways in nefopam-induced antinociception. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987; 138:77–82. PMID: 2442003.
Article5. Rosland JH, Hole K. The effect of nefopam and its enantiomers on the uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline and dopamine in crude rat brain synaptosomal preparations. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1990; 42:437–438. PMID: 1979627.
Article6. Vonvoigtlander PF, Lewis RA, Neff GL, Triezenberg HJ. Involvement of biogenic amines with the mechanisms of novel analgesics. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1983; 7:651–656. PMID: 6141608.
Article7. Gray AM, Nevinson MJ, Sewell RD. The involvement of opioidergic and noradrenergic mechanisms in nefopam antinociception. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999; 365:149–157. PMID: 9988097.
Article8. Girard P, Coppé MC, Verniers D, Pansart Y, Gillardin JM. Role of catecholamines and serotonin receptor subtypes in nefopam-induced antinociception. Pharmacol Res. 2006; 54:195–202. PMID: 16750379.
Article9. Jeong SH, Heo BH, Park SH, Kim WM, Lee HG, Yoon MH, et al. Spinal noradrenergic modulation and the role of the alpha-2 receptor in the antinociceptive effect of intrathecal nefopam in the formalin test. Korean J Pain. 2014; 27:23–29. PMID: 24478897.
Article10. Yaksh TL, Rudy TA. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976; 17:1031–1036. PMID: 14677603.
Article11. Cho SY, Park AR, Yoon MH, Lee HG, Kim WM, Choi JI. Antinociceptive effect of intrathecal nefopam and interaction with morphine in formalin-induced pain of rats. Korean J Pain. 2013; 26:14–20. PMID: 23342202.
Article12. Coderre TJ, Melzack R. The contribution of excitatory amino acids to central sensitization and persistent nociception after formalin-induced tissue injury. J Neurosci. 1992; 12:3665–3670. PMID: 1326610.
Article13. Lee HG, Choi JI, Yoon MH, Obata H, Saito S, Kim WM. The antiallodynic effect of intrathecal tianeptine is exerted by increased serotonin and norepinephrine in the spinal dorsal horn. Neurosci Lett. 2014; 583:103–107. PMID: 25233863.
Article14. Smith DF, Glaser R, Gee A, Gjedde A. [11C]Nefopam as a potential PET tracer of serotonin reuptake sites. In : Myers R, Cunningham V, Bailey D, Jones T, editors. Quantification of brain function using PET. San Diego (CA): Academic Press;1996. p. 38–41.15. Millan MJ. Descending control of pain. Prog Neurobiol. 2002; 66:355–474. PMID: 12034378.
Article16. Potvin S, Grignon S, Marchand S. Human evidence of a supra-spinal modulating role of dopamine on pain perception. Synapse. 2009; 63:390–402. PMID: 19173266.
Article17. Franklin KB. Analgesia and abuse potential: an accidental association or a common substrate? Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1998; 59:993–1002. PMID: 9586860.
Article18. Altier N, Stewart J. The role of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens in analgesia. Life Sci. 1999; 65:2269–2287. PMID: 10597883.
Article19. Cobacho N, de la Calle JL, Paíno CL. Dopaminergic modulation of neuropathic pain: analgesia in rats by a D2-type receptor agonist. Brain Res Bull. 2014; 106:62–71. PMID: 24959942.
Article20. Fairbanks CA. Spinal delivery of analgesics in experimental models of pain and analgesia. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003; 55:1007–1041. PMID: 12935942.
Article21. Xu JJ, Walla BC, Diaz MF, Fuller GN, Gutstein HB. Intermittent lumbar puncture in rats: a novel method for the experimental study of opioid tolerance. Anesth Analg. 2006; 103:714–720. PMID: 16931686.
Article22. Ohkubo Y, Nomura K, Yamaguchi I. Involvement of dopamine in the mechanism of action of FR64822, a novel non-opioid antinociceptive compound. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991; 204:121–125. PMID: 1839620.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spinal Noradrenergic Modulation and the Role of the Alpha-2 Receptor in the Antinociceptive Effect of Intrathecal Nefopam in the Formalin Test
- The Analgesic Effect of Nefopam with Fentanyl at the End of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
- Use of Nefopam in Perioperative Pain Management; Keeping Nefopam in between
- Antinociceptive Effect of Intrathecal Nefopam and Interaction with Morphine in Formalin-Induced Pain of Rats
- Comparison of meperidine and nefopam for prevention of shivering during spinal anesthesia