Antinociceptive Effect of Intrathecal Nefopam and Interaction with Morphine in Formalin-Induced Pain of Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School and Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. jichoi@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1779018
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.1.14
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Nefopam, a non-opiate analgesic, has been regarded as a substance that reduces the requirement for morphine, but conflicting results have also been reported. The inhibition of monoamine reuptake is a mechanism of action for the analgesia of nefopam. The spinal cord is an important site for the action of monoamines however, the antinociceptive effect of intrathecal nefopam was not clear. This study was performed to examine the antinociceptive effect of intrathecal (i.t.) nefopam and the pattern of pharmacologic interaction with i.t. morphine in the formalin test.
METHODS
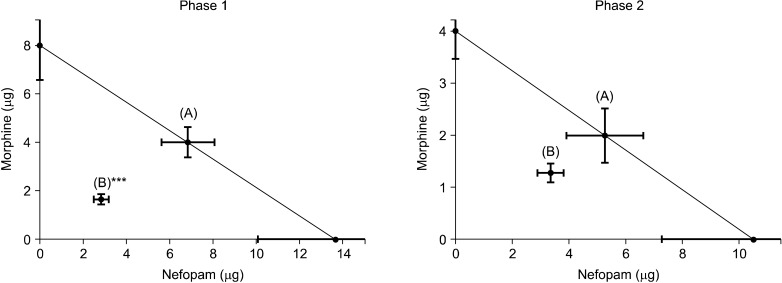
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were implanted with an i.t. catheter, and were randomly treated with a vehicle, nefopam, or morphine. Formalin was injected into the hind-paw 10 min. after an i.t. injection of the above experiment drugs. After obtaining antinociceptive ED50 of nefopam and morphine, the mixture of nefopam and morphine was tested for the antinociceptive effect in the formalin test at a dose of 1/8, 1/4, 1/2 of ED50, or ED50 of each drug followed by an isobolographic analysis.
RESULTS
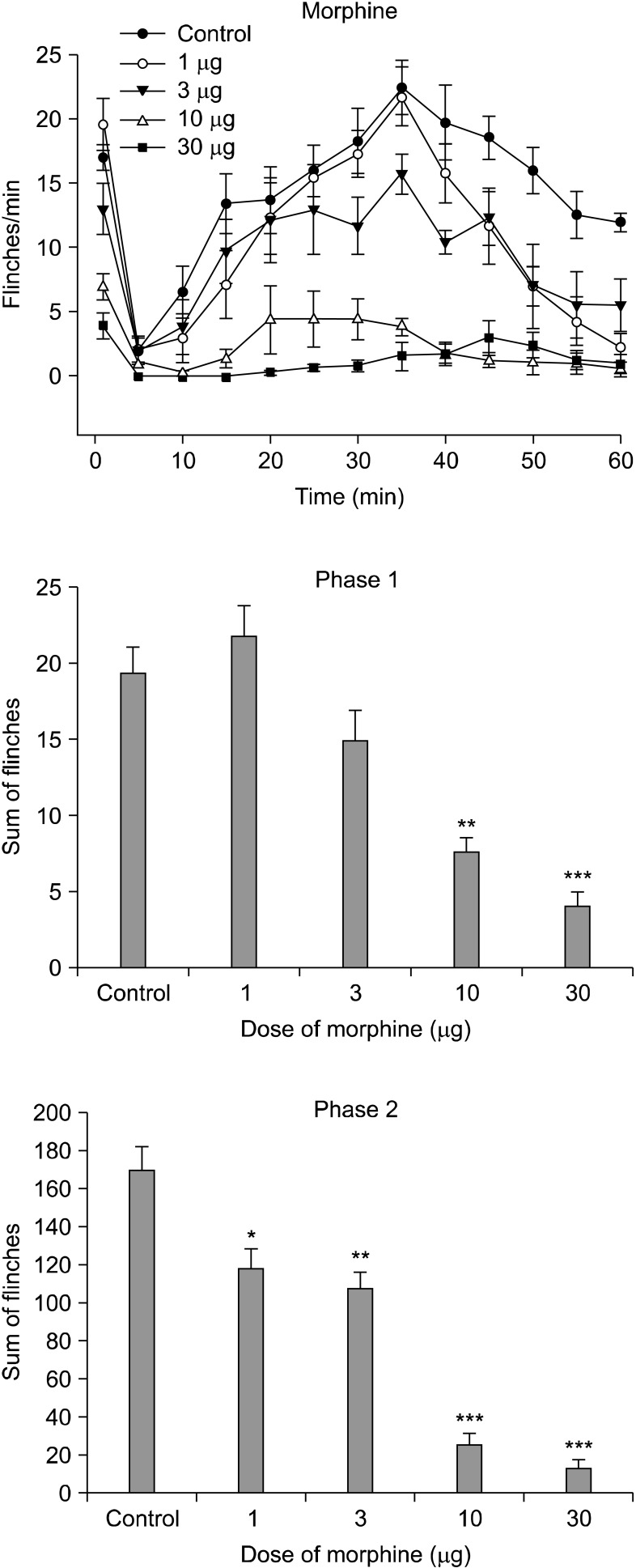
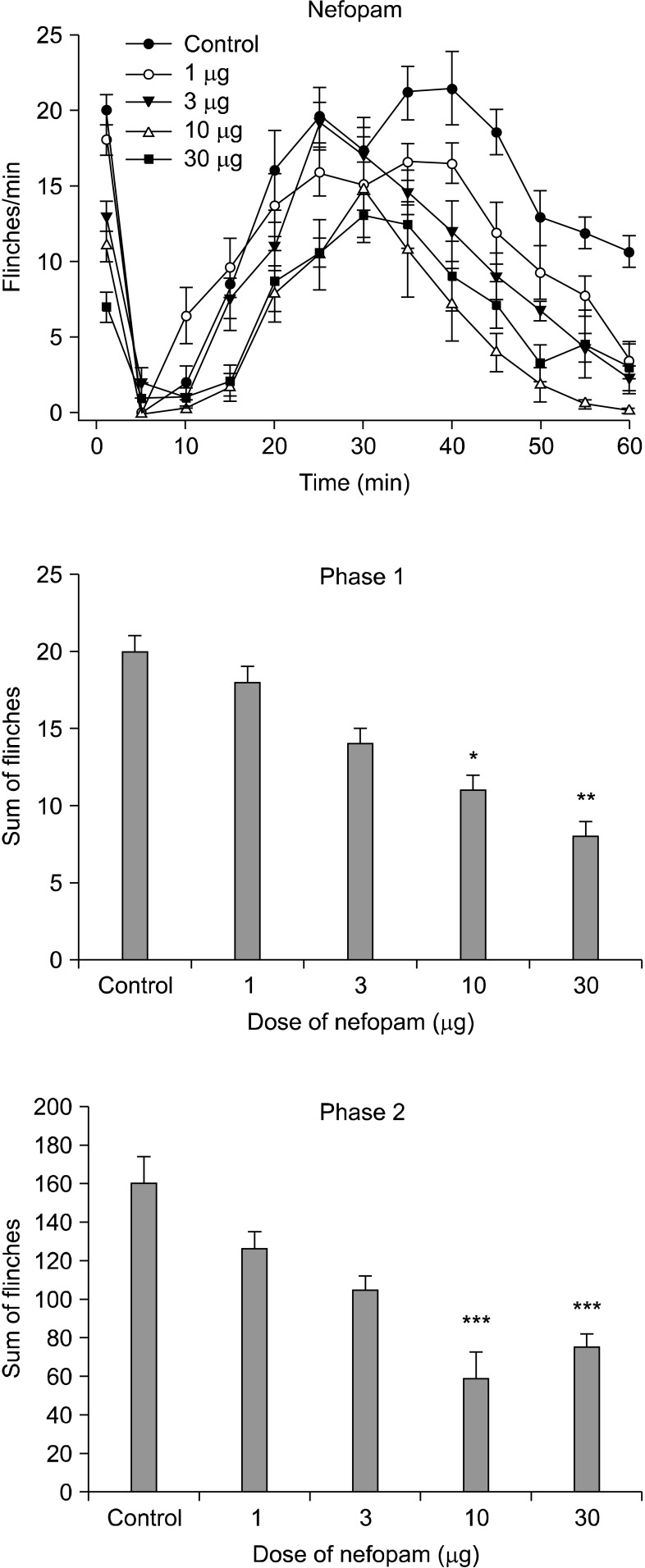
Intrathecal nefopam significantly reduced the flinching responses in both phases of the formalin test in a dose-dependent manner. Its effect, however, peaked at a dose of 30 microg in phase 1 (39.8% of control) and 10 microg during phase 2 (37.6% of control). The isobolograhic analysis indicated an additive interaction of nefopam and morphine during phase 2, and a synergy effect in antinociception during phase 1.
CONCLUSIONS
This study demonstrated that i.t. nefopam produces an antinociceptive effect in formalin induced pain behavior during both phases of the formalin test, while interacting differently with i.t. morphine, synergistically during phase 1, and additively during phase 2.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 7 articles
-
Medications in Treatment of Postherpetic Neuralgia
Sang Wook Shin
Korean J Pain. 2014;27(1):1-2. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.1.Rediscovery of Nefopam for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain
Kyung Hoon Kim, Salahadin Abdi
Korean J Pain. 2014;27(2):103-111. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.2.103.Spinal Noradrenergic Modulation and the Role of the Alpha-2 Receptor in the Antinociceptive Effect of Intrathecal Nefopam in the Formalin Test
Shin Ho Jeong, Bong Ha Heo, Sun Hong Park, Woong Mo Kim, Hyung Gon Lee, Myung Ha Yoon, Jeong Il Choi
Korean J Pain. 2014;27(1):23-29. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.23.The Potential Role of Intrathecal Nefopam in the Management of Neuropathic Pain
Mohamed Amin Ghobadifar, Navid Kalani
Korean J Pain. 2014;27(3):301-302. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.3.301.The Role of Spinal Dopaminergic Transmission in the Analgesic Effect of Nefopam on Rat Inflammatory Pain
Do Yun Kim, Joo Wung Chae, Chang Hun Lim, Bong Ha Heo, Keun Suk Park, Hyung Gon Lee, Jeong Il Choi, Myung Ha Yoon, Woong Mo Kim
Korean J Pain. 2016;29(3):164-171. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.3.164.Use of Nefopam in Perioperative Pain Management; Keeping Nefopam in between
Jeong Il Choi
Korean J Pain. 2016;29(2):71-72. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.2.71.Anti-nociceptive effects of dual neuropeptide antagonist therapy in mouse model of neuropathic and inflammatory pain
Min Su Kim, Bo Yeon Kim, Allen Saghetlians, Xiang Zhang, Takuya Okida, So Yeon Kim
Korean J Pain. 2022;35(2):173-182. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.173.
Reference
-
1. Heel RC, Brogden RN, Pakes GE, Speight TM, Avery GS. Nefopam: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs. 1980; 19:249–267. PMID: 6991238.2. Fuller RW, Snoddy HD. Evaluation of nefopam as a monoamine uptake inhibitor in vivo in mice. Neuropharmacology. 1993; 32:995–999. PMID: 7507578.
Article3. Piercey MF, Schroeder LA. Spinal and Supraspinal sites for morphine and nefopam analgesia in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981; 74:135–140. PMID: 6276187.
Article4. Evans MS, Lysakowski C, Tramèr MR. Nefopam. Br J Anaesth. 2008; 101:610–617. PMID: 18796441.5. Beaver WT, Feise GA. A comparison of the analgesic effect of intramuscular nefopam and morphine in patients with postoperative pain. J Clin Pharmacol. 1977; 17:579–591. PMID: 334807.
Article6. McLintock TT, Kenny GN, Howie JC, McArdle CS, Lawrie S, Aitken H. Assessment of the analgesic efficacy of nefopam hydrochloride after upper abdominal surgery: a study using patient controlled analgesia. Br J Surg. 1988; 75:779–781. PMID: 3167526.
Article7. Tramoni G, Viale JP, Cazals C, Bhageerutty K. Morphinesparing effect of nefopam by continuous intravenous injection after abdominal surgery by laparotomy. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2003; 20:990–992. PMID: 14690106.
Article8. Moffat AC, Kenny GN, Prentice JW. Postoperative nefopam and diclofenac. Evaluation of their morphine-sparing effect after upper abdominal surgery. Anaesthesia. 1990; 45:302–305. PMID: 2337215.
Article9. Du Manoir B, Aubrun F, Langlois M, Le Guern ME, Alquier C, Chauvin M, et al. Randomized prospective study of the analgesic effect of nefopam after orthopaedic surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2003; 91:836–841. PMID: 14633755.
Article10. Beloeil H, Delage N, Nègre I, Mazoit JX, Benhamou D. The median effective dose of nefopam and morphine administered intravenously for postoperative pain after minor surgery: a prospective randomized double-blinded isobolographic study of their analgesic action. Anesth Analg. 2004; 98:395–400. PMID: 14742377.
Article11. Richebé P, Picard W, Rivat C, Jelacic S, Branchard O, Leproust S, et al. Effects of nefopam on early postoperative hyperalgesia after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2012; [in press].
Article12. Aveline C, Gautier JF, Vautier P, Cognet F, Hetet HL, Attali JY, et al. Postoperative analgesia and early rehabilitation after total knee replacement: a comparison of continuous low-dose intravenous ketamine versus nefopam. Eur J Pain. 2009; 13:613–619. PMID: 18793861.
Article13. Bernatzky G, Jurna I. Intrathecal injection of codeine, buprenorphine, tilidine, tramadol and nefopam depresses the tail-flick response in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986; 120:75–80. PMID: 3753938.
Article14. Fasmer OB, Berge OG, Jørgensen HA, Hole K. Antinociceptive effects of (+/-)-, (+)- and (-)-nefopam in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1987; 39:508–511. PMID: 2886617.
Article15. Millan MJ. Descending control of pain. Prog Neurobiol. 2002; 66:355–474. PMID: 12034378.
Article16. Yaksh TL, Rudy TA. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976; 17:1031–1036. PMID: 14677603.
Article17. Coderre TJ, Melzack R. The contribution of excitatory amino acids to central sensitization and persistent nociception after formalin-induced tissue injury. J Neurosci. 1992; 12:3665–3670. PMID: 1326610.
Article18. Tallarida RJ. Drug synergism and dose-effect data analysis. 2000. 1st ed. New York: Chapman & Hall/CRC;p. 57–71.19. Kehlet H, Dahl JB. The value of "multimodal" or "balanced analgesia" in postoperative pain treatment. Anesth Analg. 1993; 77:1048–1056. PMID: 8105724.
Article20. Rosland JH, Hole K. The effect of nefopam and its enantiomers on the uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline and dopamine in crude rat brain synaptosomal preparations. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1990; 42:437–438. PMID: 1979627.
Article21. Girard P, Pansart Y, Coppe MC, Gillardin JM. Nefopam reduces thermal hypersensitivity in acute and postoperative pain models in the rat. Pharmacol Res. 2001; 44:541–545. PMID: 11735363.
Article22. Girard P, Pansart Y, Gillardin JM. Nefopam potentiates morphine antinociception in allodynia and hyperalgesia in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2004; 77:695–703. PMID: 15099914.
Article23. Buritova J, Besson JM. Effects of nefopam on the spinal nociceptive processes: a c-Fos protein study in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002; 441:67–74. PMID: 12007921.
Article24. Kapfer B, Alfonsi P, Guignard B, Sessler DI, Chauvin M. Nefopam and ketamine comparably enhance postoperative analgesia. Anesth Analg. 2005; 100:169–174. PMID: 15616073.
Article25. Saghaei E, Moini Zanjani T, Sabetkasaei M, Naseri K. Enhancement of antinociception by co-administrations of nefopam, morphine, and nimesulide in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Korean J Pain. 2012; 25:7–15. PMID: 22259710.
Article26. Girard P, Niedergang B, Pansart Y, Coppé MC, Verleye M. Systematic evaluation of the nefopam-paracetamol combination in rodent models of antinociception. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011; 38:170–178.
Article27. Girard P, Verniers D, Coppé MC, Pansart Y, Gillardin JM. Nefopam and ketoprofen synergy in rodent models of antinociception. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008; 584:263–271. PMID: 18316069.
Article28. Delage N, Maaliki H, Beloeil H, Benhamou D, Mazoit JX. Median effective dose (ED50) of nefopam and ketoprofen in postoperative patients: a study of interaction using sequential analysis and isobolographic analysis. Anesthesiology. 2005; 102:1211–1216. PMID: 15915035.
Article29. Abbott FV, Franklin KB, Westbrook RF. The formalin test: scoring properties of the first and second phases of the pain response in rats. Pain. 1995; 60:91–102. PMID: 7715946.
Article30. Rahman W, Suzuki R, Rygh LJ, Dickenson AH. Descending serotonergic facilitation mediated through rat spinal 5HT3 receptors is unaltered following carrageenan inflammation. Neurosci Lett. 2004; 361:229–231. PMID: 15135935.
Article31. Green GM, Scarth J, Dickenson A. An excitatory role for 5-HT in spinal inflammatory nociceptive transmission; state-dependent actions via dorsal horn 5-HT(3) receptors in the anaesthetized rat. Pain. 2000; 89:81–88. PMID: 11113296.
Article32. Verleye M, Gillardin JM. Contribution of transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 to the analgesic and antihyperalgesic activity of nefopam in rodents. Pharmacology. 2009; 83:116–121. PMID: 19096234.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spinal Noradrenergic Modulation and the Role of the Alpha-2 Receptor in the Antinociceptive Effect of Intrathecal Nefopam in the Formalin Test
- Antinociceptive Effects of Intrathecal Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Compounds and Morphine in Rats
- Antinociceptive Effect of the Intrathecal Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor, Zaprinast, in a Rat Formalin Test
- The Analgesic Interactions Among Intrathecal Morphine, Ketorolac and L-NAME on Formalin-induced Pain in Rats
- Additive Antinociception between Intrathecal Sildenafil and Morphine in the Rat Formalin Test