Korean J Hematol.
2010 Mar;45(1):73-75. 10.5045/kjh.2010.45.1.73.
A case of subdural hematoma in patient with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with high-dose imatinib mesylate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. kshmoon@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Brain Tumor Institute, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2252094
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2010.45.1.73
Abstract
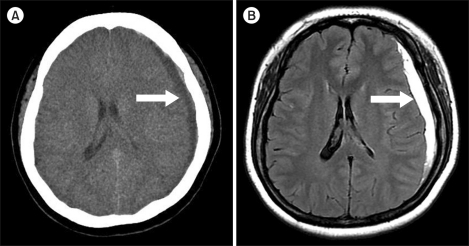
- Imatinib mesylate (IM) is used to treat a wide range of diseases, including Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), on account of its high tolerability and low incidence of minor adverse events. Hemorrhage is thought to be a rare complication of IM. Recently, IM has been associated with reduced alpha2-plasmin inhibitor and platelet dysfunction. We report here the case of a 33-year-old female patient with CML who experienced subdural hematoma after an incremental increase in IM dosage due to a loss of complete molecular response. This case indicates that physicians should be alert to this atypical cause of headache in patients taking high-dose IM.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Usefulness of Middle Meningeal Embolization to Prevent Recurrent Spontaneous Chronic Subdural Hemorrhage
Sooji Sirh, Hye Ran Park, Sukh Que Park
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2018;20(1):40-46. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2018.20.1.40.
Reference
-
2. O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:994–1004. PMID: 12637609.3. Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:1031–1037. PMID: 11287972.
Article4. Talpaz M, Silver RT, Druker BJ, et al. Imatinib induces durable hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia: results of a phase 2 study. Blood. 2002; 99:1928–1937. PMID: 11877262.
Article5. Chen JC, Levy ML. Causes, epidemiology, and risk factors of chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2000; 11:399–406. PMID: 10918008.
Article6. Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Capdeville R, Ford JM, Baccarani M, Goldman JM. Chronic myelogenous leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2001; 87–112. PMID: 11722980.
Article7. Larson RA, Druker BJ, Guilhot F, et al. Imatinib pharmacokinetics and its correlation with response and safety in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: a subanalysis of the IRIS study. Blood. 2008; 111:4022–4028. PMID: 18256322.
Article8. Song KW, Rifkind J, Al-Beirouti B, et al. Subdural hematomas during CML therapy with imatinib mesylate. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004; 45:1633–1636. PMID: 15370217.
Article9. Radaelli F, Vener C, Ripamonti F, et al. Conjunctival hemorrhagic events associated with imatinib mesylate. Int J Hematol. 2007; 86:390–393. PMID: 18192104.
Article10. Matsue K, Aoki T, Odawara J, Kimura S, Yamakura M, Takeuchi M. Haemorrhagic complications associated with reduced alpha2-plasmin inhibitor during imatinib use in a patient with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Leuk Res. 2009; 33:867–869. PMID: 18951628.11. Okajima K, Kohno I, Tsuruta J, Okabe H, Takatsuki K, Binder BR. Direct evidence for systemic fibrinogenolysis in a patient with metastatic prostatic cancer. Thromb Res. 1992; 66:717–727. PMID: 1519230.
Article12. Kluft C, Vellenga E, Brommer EJ, Wijngaards G. A familial hemorrhagic diathesis in a Dutch family: an inherited deficiency of alpha 2-antiplasmin. Blood. 1982; 59:1169–1180. PMID: 6177359.
Article13. Favier R, Aoki N, de Moerloose P. Congenital alpha(2)-plasmin inhibitor deficiencies: a review. Br J Haematol. 2001; 114:4–10. PMID: 11472338.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Complete remission of philadelphia chromosome-positive acute myeloid leukemia with imatinib mesylate
- Loeffler endocarditis in chronic eosinophilic leukemia with FIP1L1/PDGFRA rearrangement: full recovery with low dose imatinib
- A Case of Drug Eruption with Localized ExfoliativeDermatitis Induced by Imatinib Mesylate
- Peripheral neuropathy associated with imatinib therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia
- Imatinib-Mesylate Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis in Two CML Patients