Tuberc Respir Dis.
2011 Sep;71(3):210-215.
Imatinib-Mesylate Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis in Two CML Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Sanggye-Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yjyuh@paik.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Sanggye-Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
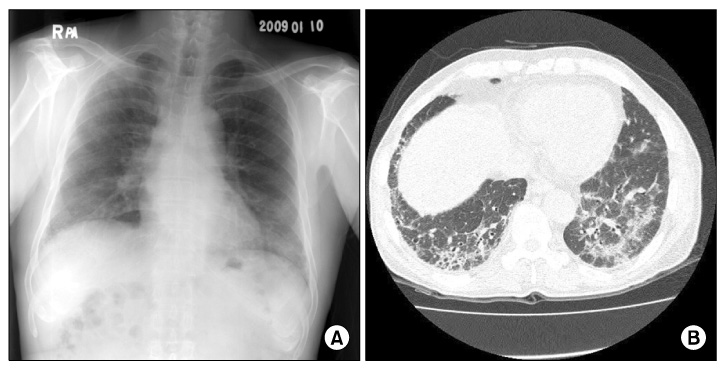
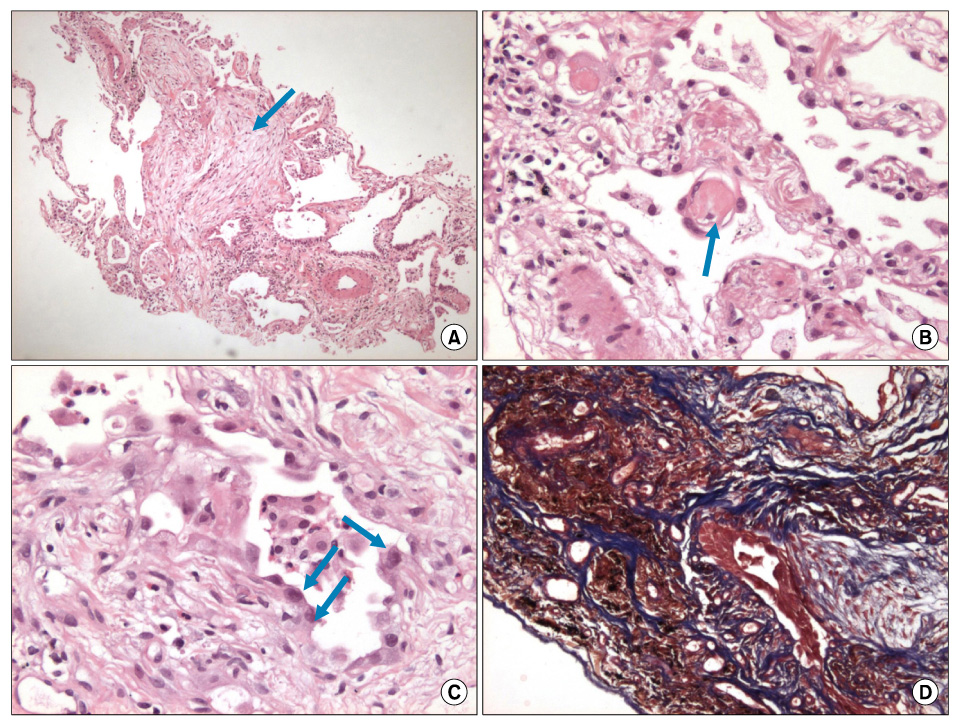
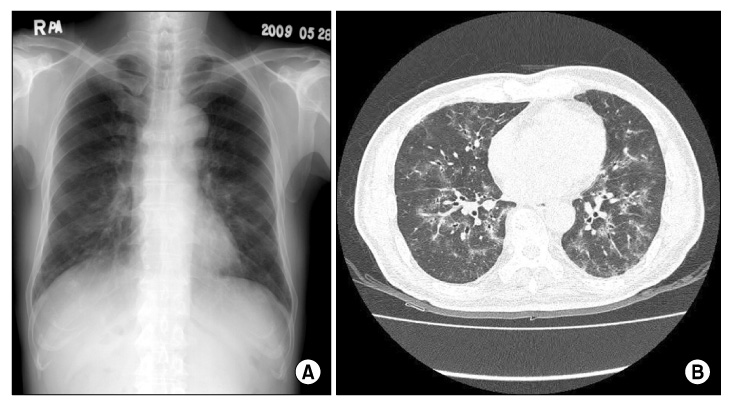
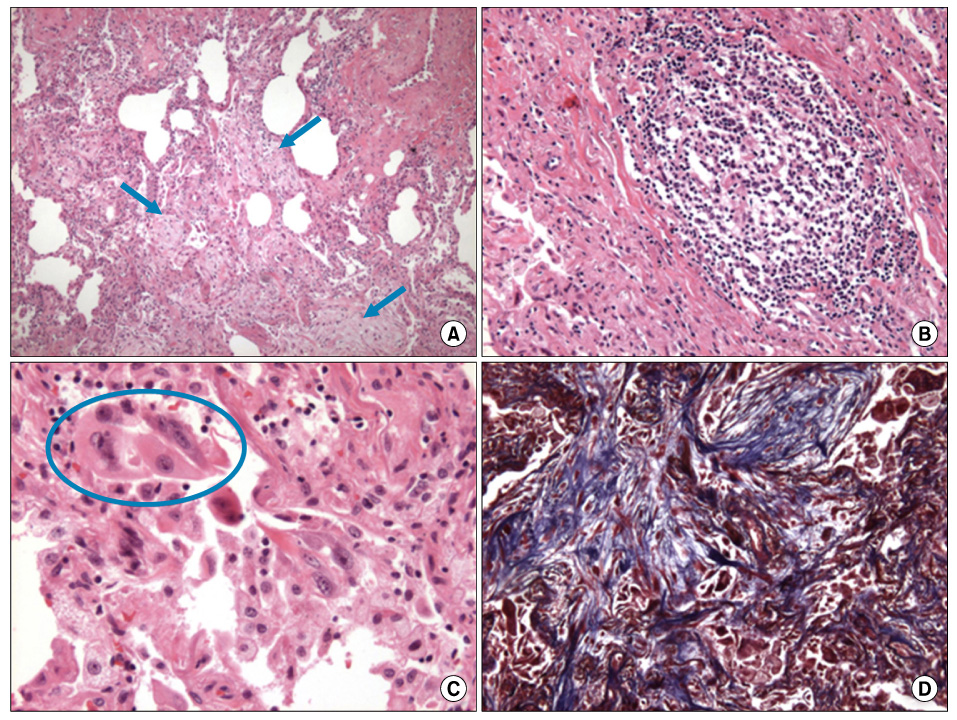
- Imatinib mesylate, a selective inhibitor of BCR-ABL kinase activity, has demonstrated significant clinical efficacy in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). It has become the standard of treatment for these diseases. Although the toxicity profile of imatinib is superior to that of interferon or other cytotoxic agents, some adverse events including edema, gastrointestinal toxicities and hematologic toxicities are commonly observed in the patients treated by imatinib. We present two cases of imatinib induced interstitial pneumonitis during the treatment of a chronic phase of CML.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV. The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2000. 96:3343–3356.2. Melo JV, Barnes DJ. Chronic myeloid leukaemia as a model of disease evolution in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007. 7:441–453.3. Pavlovsky C, Kantarjian H, Cortes JE. First-line therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia: Past, present, and future. Am J Hematol. 2009. 84:287–293.4. Guilhot F, Druker B, Larson RA, Gathmann I, So C, Waltzman R, et al. High rates of durable response are achieved with imatinib after treatment with interferon alpha plus cytarabine: results from the International Randomized Study of Interferon and STI571 (IRIS) trial. Haematologica. 2009. 94:1669–1675.5. Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, Peng B, Buchdunger E, Ford JM, et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:1031–1037.6. Ma CX, Hobday TJ, Jett JR. Imatinib mesylate-induced interstitial pneumonitis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003. 78:1578–1579.7. Ohnishi K, Sakai F, Kudoh S, Ohno R. Twenty-seven cases of drug-induced interstitial lung disease associated with imatinib mesylate. Leukemia. 2006. 20:1162–1164.8. Rosado MF, Donna E, Ahn YS. Challenging problems in advanced malignancy: case 3. Imatinib mesylate-induced interstitial pneumonitis. J Clin Oncol. 2003. 21:3171–3173.9. Seki N, Ito A, Watanabe K, Shibakuki R, Seto T, Uematsu K, et al. Irreversible imatinib-induced pneu monitis following long-term imatinib administration. Intern Med. 2007. 46:1941–1942.10. Lee JW, Kim HJ, Kim KJ, Shin KC, Hong YH, Chung JH, et al. A case of imatinib-mesylate associated hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005. 59:423–426.11. Ando M, Okamoto I, Yamamoto N, Takeda K, Tamura K, Seto T, et al. Predictive factors for interstitial lung disease, antitumor response, and survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:2549–2556.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Rechallenge with Imatinib in a Patient with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Who Previously Experienced Imatinib Mesylate Induced Pneumonitis
- A Case of Imatinib-mesylate associated Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Imatinib-induced Pneumonitis in a Patient with High-risk Rectal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
- A Case of Drug Eruption with Localized ExfoliativeDermatitis Induced by Imatinib Mesylate
- Pityriasis rosea-like Drug Eruption Induced by Imatinib Mesylate (Gleevec(TM))