Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Dec;75(6):256-259.
Successful Rechallenge with Imatinib in a Patient with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Who Previously Experienced Imatinib Mesylate Induced Pneumonitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. rkdwldud@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
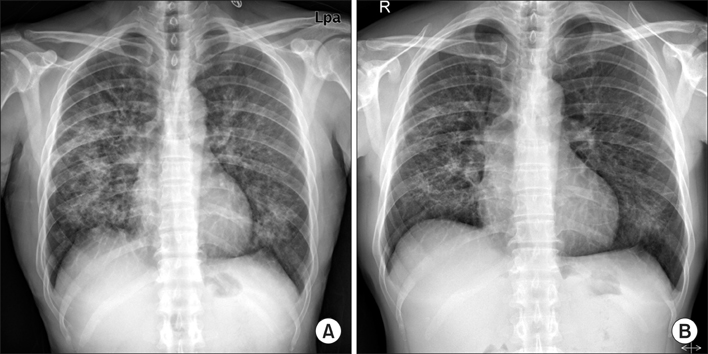
- Imatinib mesylate is a targeted therapy that acts by inhibiting tyrosine kinase of the bcr-abl fusion oncoprotein, which is specific to chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), and the c-transmembrane receptor, which is specific to gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Interstitial pneumonitis is a rare adverse event of imatinib therapy. It is clinically difficult to distinguish from infectious pneumonia, which can frequently occur due to the underlying disease. The standard treatment for imatinib-induced pneumonitis is to discontinue the medication and optionally administer corticosteroids. However, there are a few cases of successful retrial with imatinib. We describe a case of successful rechallenge of imatinib in a patient with imatinib-induced interstitial pneumonitis and CML without a recurrence of the underlying disease after 3 months of follow-up.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV. The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2000; 96:3343–3356.2. Ohnishi K, Sakai F, Kudoh S, Ohno R. Twenty-seven cases of drug-induced interstitial lung disease associated with imatinib mesylate. Leukemia. 2006; 20:1162–1164.3. Kim TH, Kim BG, Cho SW, Cho SK, Kim HJ, Yuh YJ, et al. Imatinib-mesylate induced interstitial pneumonitis in two CML patients. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2011; 71:210–215.4. Lee JW, Kim HJ, Kim KJ, Shin KC, Hong YH, Chung JH, et al. A case of imatinib-mesylate associated hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005; 59:423–426.5. Barber NA, Ganti AK. Pulmonary toxicities from targeted therapies: a review. Target Oncol. 2011; 6:235–243.6. Yokoyama T, Miyazawa K, Kurakawa E, Nagate A, Shimamoto T, Iwaya K, et al. Interstitial pneumonia induced by imatinib mesylate: pathologic study demonstrates alveolar destruction and fibrosis with eosinophilic infiltration. Leukemia. 2004; 18:645–646.7. Snyder LS, Hertz MI, Peterson MS, Harmon KR, Marinelli WA, Henke CA, et al. Acute lung injury: pathogenesis of intraalveolar fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1991; 88:663–673.8. Walsh J, Absher M, Kelley J. Variable expression of plateletderived growth factor family proteins in acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993; 9:637–644.9. Rossi SE, Erasmus JJ, McAdams HP, Sporn TA, Goodman PC. Pulmonary drug toxicity: radiologic and pathologic manifestations. Radiographics. 2000; 20:1245–1259.10. Seki N, Ito A, Watanabe K, Shibakuki R, Seto T, Uematsu K, et al. Irreversible imatinib-induced pneumonitis following longterm imatinib administration. Intern Med. 2007; 46:1941–1942.11. Delomas T, Darne C, Besson C. Lack of recurrence of imatinib-induced interstitial lung disease with nilotinib. Leuk Lymphoma. 2012; 53:332–333.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Imatinib-Mesylate Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis in Two CML Patients
- A Case of Drug Eruption with Localized ExfoliativeDermatitis Induced by Imatinib Mesylate
- Peripheral neuropathy associated with imatinib therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia
- Complete remission of philadelphia chromosome-positive acute myeloid leukemia with imatinib mesylate
- A Case of Lichenoid Drug Eruption Associated with Imatinib Mesylate